1Research Background
2Results Overview
In this research, the researchers successfully designed and manufactured a novel all-organic layered dielectric film based on aramid nanofiber membrane (ANFm) and polyimide (PI) layers, achieved through a simple “dip and pull” technique. This PI-ANFm-PI (P-A-P) dielectric film exhibits a higher breakdown strength and lower leakage current density than the single-layer ANFm due to its flat surface and the formation of electron traps. The maximum discharge energy density (Ud) of the P-A-P dielectric film at 25°C is 3.68 J/cm³, with a charge-discharge efficiency (η) exceeding 80%. At 150°C, Ud is 1.76 J/cm³, and η is above 70%, significantly outperforming single-layer ANFm and pure PI dielectric films. These outstanding energy storage characteristics make the all-organic layered structure P-A-P film a promising candidate material for high-temperature energy storage.
3Illustrated Guide
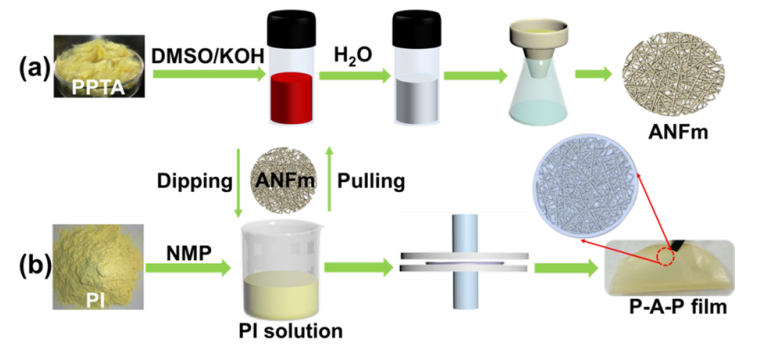
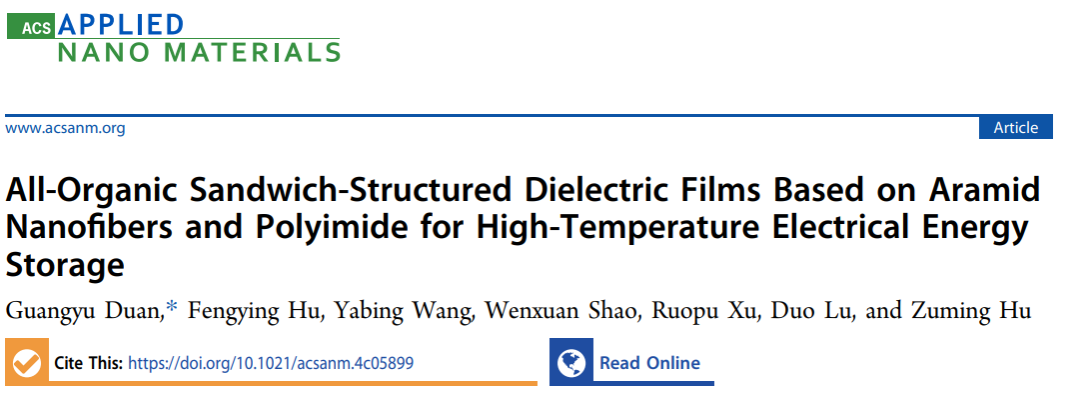
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the fabrication of single-layer ANFm and layered structure P-A-P film.
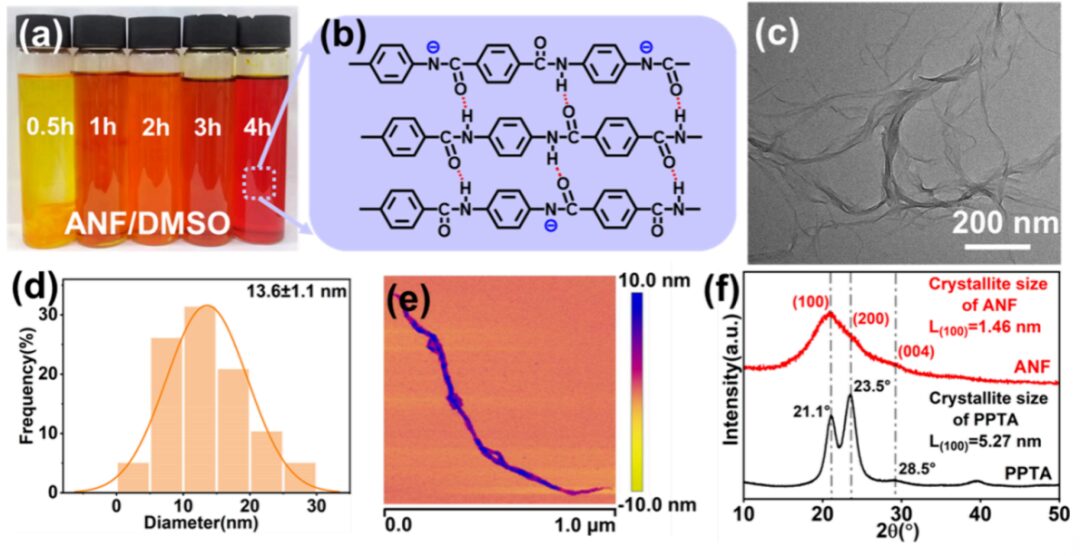
Figure 2: Digital photos of ANF/DMSO dispersion during deprotonation, ANF molecular chain in DMSO, transmission electron microscopy image of ANF in DI water, ANF diameter distribution diagram, atomic force microscopy image of ANF, XRD patterns of PPTA and ANF.
Figure 3: Cross-sectional morphology, surface morphology, AFM 3D images and surface roughness statistics of single-layer ANFm and layered structure P-A-P film.
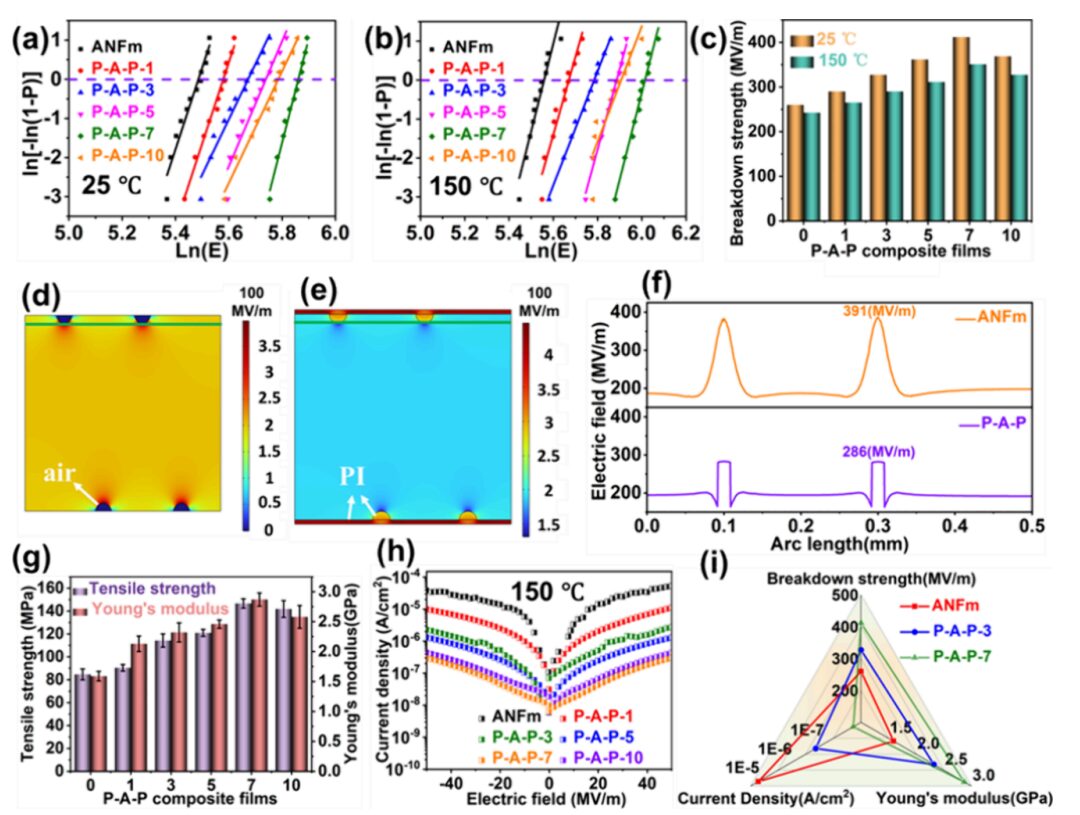
Figure 4: Weibull statistics of breakdown strength of ANFm and P-A-P films at 25°C and 150°C, electric field distribution simulation diagram, and data on mechanical properties, current density, and Young’s modulus.
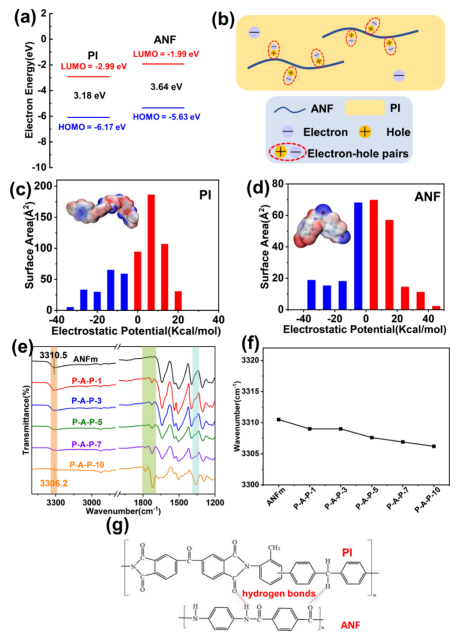
Figure 5: Molecular orbital energy levels of PI and ANF, schematic diagram of electron-hole pair formation, electrostatic force distribution and FTIR spectra, and hydrogen bond formation between ANF and PI molecular chains.
4Conclusion
This research effectively addresses the common challenges of local electric field distortion and mechanical performance degradation in organic-inorganic multilayer dielectric films by constructing a novel all-organic layered structure P-A-P dielectric film based on nanoscale ANF and PI. The surface of the P-A-P film becomes smooth after forming the outer layer of PI. Due to the enhanced Young’s modulus, eliminated grooves and pits, formed electron-hole pairs, and hydrogen bonds, the layered structure P-A-P film exhibits significantly improved breakdown strength and suppressed conduction loss. These advantages significantly enhance energy storage performance across a wide temperature range. For example, the maximum Ud of P-A-P-7 at 25°C is 3.68 J/cm³, with η exceeding 80%, and at 150°C, Ud is 1.76 J/cm³, with η exceeding 70%, clearly outperforming single-layer ANFm and pure PI films. This research provides an excellent strategy for developing advanced polymer dielectric films suitable for high-temperature energy storage by constructing a novel all-organic layered structure film based on nanoscale ANF and PI.
References:


Note:
🔹This article is for academic exchange among researchers.
🔹If there are any copyright issues with this article, please contact us for timely resolution.
🔹Readers are welcome to share and promote this article.
🔹”Materials Chemistry Progress” will continuously improve its level to share more quality interpretations of material research results with readers. Please follow us.
Researchers are welcome to submit their latest research results.