ADAS (Advanced Driving Assistance System) refers to advanced driving assistance systems.
ADAS utilizes various sensors installed in vehicles to collect environmental data inside and outside the vehicle in real-time, performing technical processing such as identification, detection, and tracking of static and dynamic objects. This allows drivers to quickly perceive potential dangers, thereby raising awareness and enhancing safety through proactive safety technologies.
The sensors used in ADAS mainly include cameras, radar, lasers, and ultrasonic sensors, which can detect light, heat, pressure, or other variables used to monitor the vehicle’s status. These sensors are typically located on the front and rear bumpers, side mirrors, inside the steering column, or on the windshield.
Early ADAS technologies primarily focused on passive alerts, where the vehicle would issue warnings to alert the driver of abnormal vehicle or road conditions upon detecting potential dangers. In contrast, active intervention is also common in the latest ADAS technologies.
Advanced driver assistance systems typically include:
-
Navigation and real-time traffic systems (TMC);
-
Intelligent Speed Adaptation (ISA) or Intelligent Speed Advice;
-
Vehicular communication systems;
-
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC);
-
Lane Departure Warning System (LDWS);
-
Lane Change Assistance;
-
Collision Avoidance System or Pre-Crash System;
-
Night Vision;
-
Adaptive Light Control;
-
Pedestrian Protection System;
-
Automatic Parking;
-
Traffic Sign Recognition;
-
Blind Spot Detection;
-
Driver Drowsiness Detection;
-
Hill Descent Control;
-
Electric Vehicle Warning Sounds;
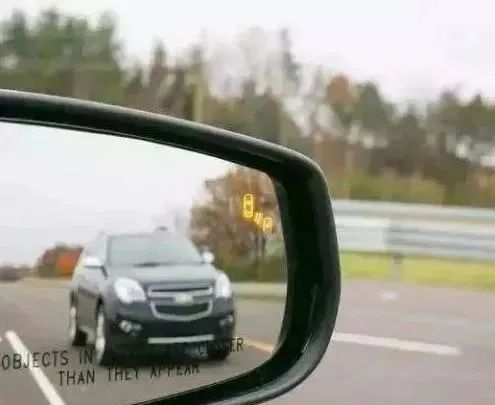
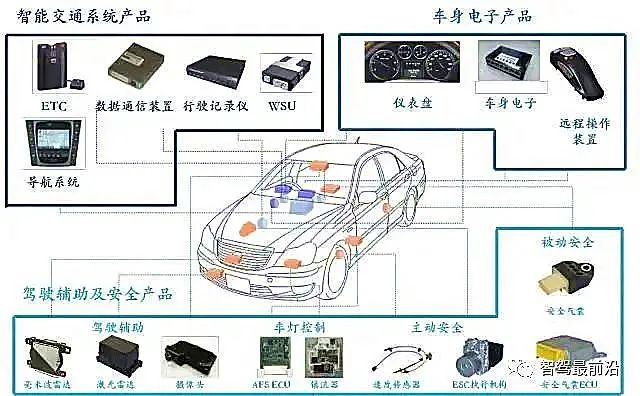
Blind Spot Detection System
The blind spot of a driver refers to areas that cannot be seen by the left, right, and rearview mirrors. Many drivers have a deep impression of blind spots, which are also one of the common causes of accidents. The blind spot detection system uses radar and sensors to detect vehicles approaching from the blind spot area and provides warnings to the driver, helping to minimize the chances of accidents.

Parking Assistance System
The parking system of ADAS benefits many novice drivers who struggle with parking. The parking assistance system is divided into two types: active and passive. The former automatically controls the steering wheel to assist the driver in parking, while the driver still needs to control the throttle, brakes, and gear shifts. The latter uses imaging (cameras) and audio (ultrasonic) as sensing units to provide more information about the surroundings of the vehicle, reducing the chances of collisions.
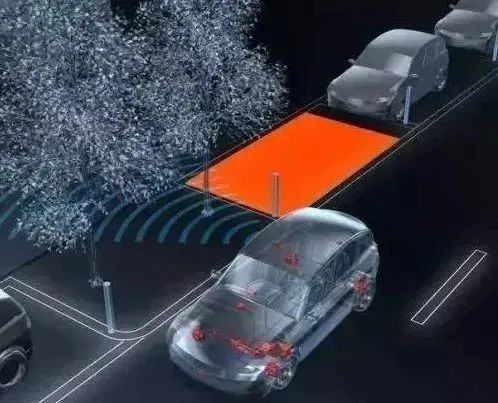
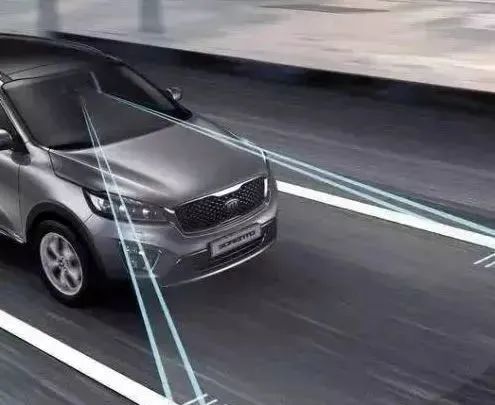
Lane Departure Warning System (LDW)
This system consists of cameras, sensors, and controllers. It works by using a camera mounted on the side of the vehicle or the rearview mirror to sample the lane markings of the current driving lane. Through image processing, it determines the current position of the vehicle in the lane. If the vehicle deviates from the lane, the controller will issue a warning signal. The process from detection to warning takes only about 0.5 seconds, providing real-time reminders to alert the driver and avoid accidents.

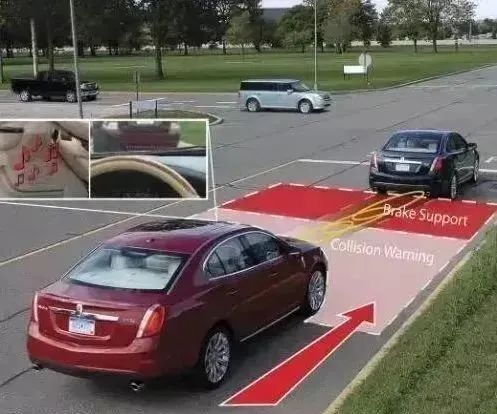
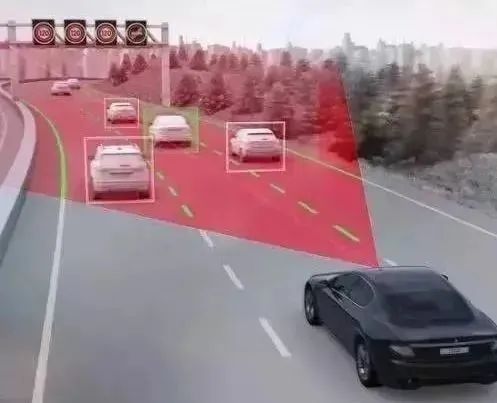
Forward Collision Warning System (FCW)
This system uses radar installed at the front of the vehicle to detect the distance and speed between the vehicle and the vehicle ahead. Initially, it will issue a warning sound to alert the driver to maintain a safe distance. If the distance continues to decrease, the vehicle will automatically apply the brakes lightly and tighten the seatbelt 2-3 times to warn the driver. If the system determines that a collision is unavoidable, it will activate the Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) and simultaneously tighten the seatbelt to secure the driver, reducing injuries in the event of an accident.

Adaptive Headlight System
This system can automatically adjust the lighting range and angle of the headlights according to different road conditions, environments, vehicle speeds, and weather conditions, allowing the headlights to illuminate further without affecting the visibility of other road users. This provides safer and more comfortable lighting for drivers and oncoming vehicles. From the past AFS (Adaptive Front-lighting System) to the current multi-LED intelligent headlights combined with sensors, all fall under this system.
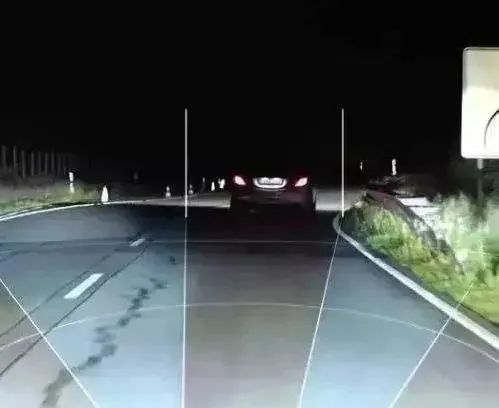

Night Vision System
This system helps drivers automatically identify animals or large objects in low visibility conditions at night or during inclement weather, while warning the driver of road conditions ahead to avoid accidents. It distinguishes between people, animals, vehicles, and environmental differences by sensing heat differences using infrared technology, converting the processed data into images that clearly present previously unclear objects to the driver, thereby reducing driving risks.

Adaptive Cruise Control System (ACC)
This system uses distance sensors installed at the front of the vehicle to continuously scan the road ahead to determine the speed and relative distance of the vehicle in front. While driving, it automatically detects the speed of the vehicle and adjusts its own speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead, thereby reducing the chances of collisions. This is known as the advanced version of the automatic cruise control system, which is now seen in many vehicle models.
Driver Physiological State Monitoring
Currently, most systems use cameras to detect the driver’s face, assessing their level of focus and signs of drowsiness. Some systems even analyze the frequency of the driver’s eye openings to determine safety levels, providing appropriate warnings or assistance. If the driver’s facial expression changes less or if they close their eyes, the vehicle will alert the driver through sounds and lights to reduce the risk of accidents.

The Trilogy of Each System
Each system mentioned above mainly consists of three processes: information collection, analysis, and command execution.
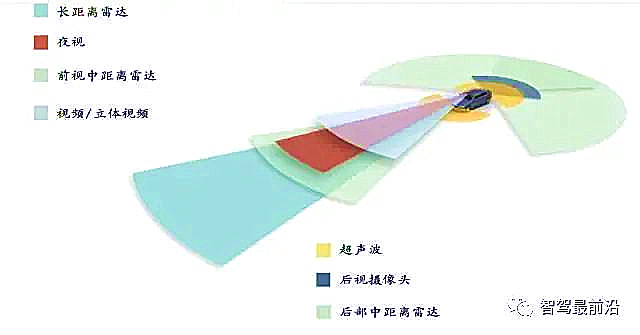
A. First is information collection: Different systems require different types of automotive sensors, including millimeter-wave radar, ultrasonic radar, infrared radar, laser radar, CCD CMOS image sensors, and wheel speed sensors, to collect the operational status of the entire vehicle and its parameter changes, converting the constantly changing mechanical movements into electronic parameters (voltage, resistance, and current). For example, the lane departure warning system uses CMOS image sensors, the night vision system uses infrared sensors, adaptive cruise control typically uses radar, and the parking assistance system uses ultrasonic sensors.
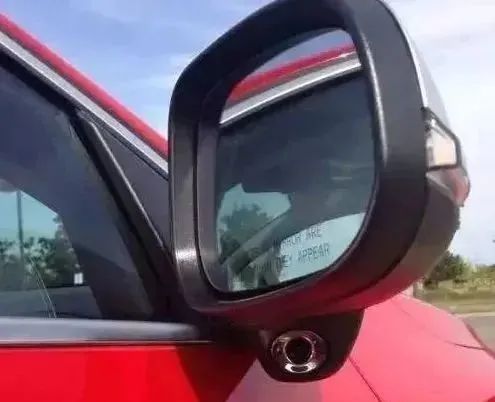

ADAS systems must first utilize different types of automotive sensors, including millimeter-wave radar, ultrasonic radar, infrared radar, laser radar, CCD CMOS image sensors, and wheel speed sensors, to grasp the external vehicle conditions before proceeding with subsequent warnings or reactions.

B. Next is information analysis and command issuance: The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) analyzes the information collected by the sensors and then issues action commands to the controlled actuators.
C. Finally, action execution: This includes systems such as throttle, brakes, lights, and sounds, which are all part of the actuators. They execute various response actions based on the signals output by the ECU, ensuring the vehicle operates safely on the road.

Currently, the main function of ADAS systems is not to fully control the vehicle but to provide the driver with information about the vehicle’s operational status and changes in the external environment, analyzing this information and providing early warnings of potential dangers, allowing the driver to take proactive measures to avoid traffic accidents. The goal of becoming the foundation for autonomous driving technology is also a direction that ADAS systems are actively pursuing. However, this requires continuous accumulation of usage experience and overcoming blind spots, as well as incorporating more active detection systems and even IoT functionalities to further achieve this goal, as the technical requirements for autonomous driving are higher and more complex.
The main systems of ADAS include:
-
APA (Automatic Parking System);
-
ACC (Automatic Cruise Control);
-
AEB (Automatic Emergency Braking);
-
LDW (Lane Departure Warning System);
-
LKA (Lane Keeping Assistance);
-
FCW (Forward Collision Warning);
-
PCW (Pedestrian Collision Warning);
-
TSR (Traffic Sign Recognition);
- HBA (High Beam Assist);
-
etc.
The high intelligence of the ADAS system’s responses is attributed not only to the comprehensive development of sensors but also to the increased processing speed and the continuous establishment of analysis databases. Otherwise, the vast amount of collected information cannot be effectively analyzed and responded to, failing to achieve the goal of avoiding dangers.
Appendix: Introduction to Seven Key ADAS Suppliers
Continental
Company Overview
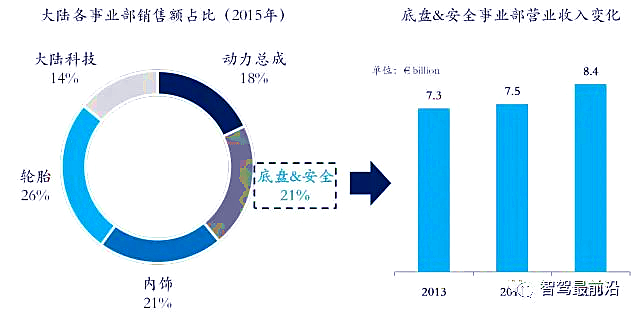
Continental’s ADAS business is part of the Chassis and Safety Division. In 2015, this division accounted for 21% of Continental’s total sales, with revenues of 8.4 billion euros, a growth rate of 12%, mainly benefiting from the rapid growth of the global ADAS market.
In China, Continental’s Chassis and Safety Division currently has 7 production bases and 5 R&D bases, with plans to establish a new ADAS sensor production base in Shanghai, expected to be operational in 2018, primarily producing radar products.
Main ADAS Products
Continental’s ADAS products cover sensors, control strategies, and actuators, providing a complete set of ADAS system services as an ADAS system supplier.

In terms of sensors, Continental has the capability to supply cameras, millimeter-wave radar, and laser radar. The camera system can achieve functions such as IHC, LDW, LKA, TSR, FCW, and SVC; the millimeter-wave radar system can achieve functions such as ACC, AEB, FCW, and BSM; the laser radar system mainly achieves BEA functions.
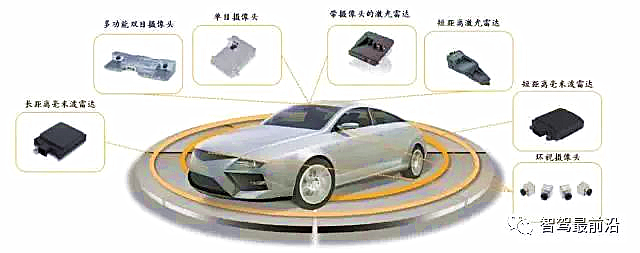
Continental has strong capabilities in camera and millimeter-wave radar products. The detection distance of the camera during the day and at night is 40 meters and 80 meters, respectively; the long-range millimeter-wave radar can detect up to 200 meters; Continental’s infrared laser radar is mainly a low-cost solution for AEB functions, suitable for small vehicles.

Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
Continental has the highest market share in the global ADAS market, with OEMs such as Toyota, Ford, and General Motors as its customers. Several domestic brands, such as GAC and Dongfeng, also use Continental’s ADAS products.
Bosch
Company Overview
Bosch’s Chassis Control Systems are part of the Automotive and Intelligent Transportation Division, focusing on active safety, passive safety, driver assistance (i.e., ADAS), and actuators. In 2015, Bosch’s Automotive and Intelligent Transportation Division achieved revenues of 41.7 billion euros, accounting for 59% of Bosch’s overall revenue, with a 12% growth compared to 2014.
Bosch’s Chassis Control Systems China was established in 2002, headquartered in Suzhou, which is also the location for market sales, engineering technology, and production; it has two testing sites in Mongolia and Jiangsu; and a second factory in Chengdu, Sichuan.
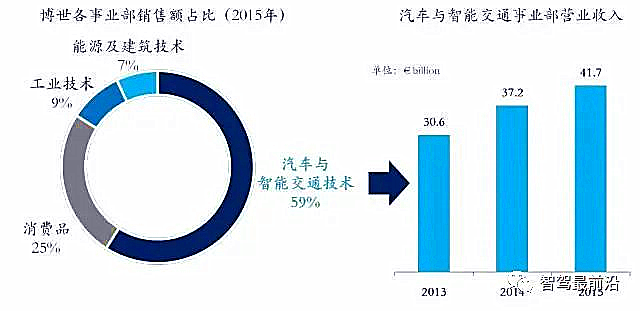
Main ADAS Products
Bosch is an ADAS system supplier with capabilities in sensors, processors, and actuators, providing a complete set of ADAS system services.
In terms of sensors, Bosch offers long-range millimeter-wave radar, mid-range millimeter-wave radar, cameras, and night vision products. It can achieve almost all ADAS functions such as ACC, FCW, AEB, LDW, LKS, TSR, PDS, and NVA. Bosch is well-known for its leading technology in long-range millimeter-wave radar, with a detection distance of up to 250 meters, and its products are already in their third generation. Additionally, Bosch has launched mid-range millimeter-wave radar products based on 77GHz, which are also among the leading technologies in the market.

Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
Bosch has the second-highest market share in the global ADAS market, with long-range millimeter-wave radar being its main area of expertise. OEMs such as Audi, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Volkswagen, and Honda are Bosch’s customers. Several domestic brands, such as Geely and Changan, also use Bosch’s ADAS products.
Autoliv
Company Overview
Autoliv’s ADAS business is part of the Active Safety Division. In 2015, the Active Safety Division achieved revenues of 610 million USD, accounting for 7% of total revenue, with a 25% growth compared to 2014.
Autoliv has 13 wholly-owned or joint venture companies in China, with its China headquarters and R&D headquarters located in Jiading, Shanghai.
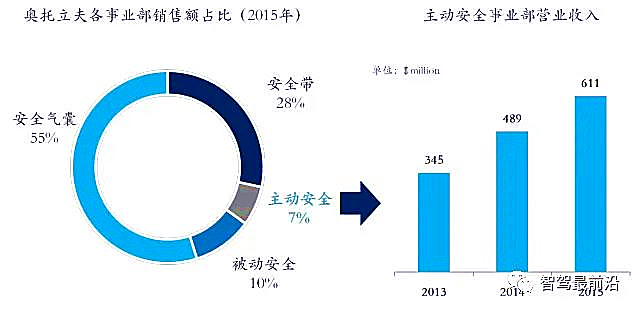
Main ADAS Products
Autoliv’s ADAS-related products involve sensors, processors, and some actuators, making it a globally recognized supplier of steering wheels, seat belts, and airbags. As an ADAS system supplier, Autoliv can provide a complete set of ADAS system service solutions.
Autoliv can also provide both visual and radar ADAS sensors, achieving functions such as AEB, ACC, IHC, LDW, TSR, PDS, and NVA. Autoliv is particularly strong in the night vision system, where it holds a significant market share; in radar, Autoliv has built its R&D design capabilities through the acquisition of MACOM.
Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
Autoliv’s main OEM customers include BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Volvo, Audi, and Honda, with BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volvo using Autoliv’s night vision systems. Autoliv is also a supplier of ADAS systems for several domestic brands, such as Geely and Great Wall.
Delphi
Company Overview
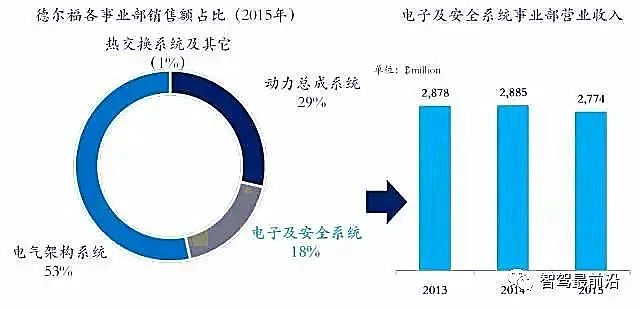
Delphi’s ADAS business is part of the Electronics and Safety Systems Division. In 2015, the Electronics and Safety Systems Division achieved revenues of 2.77 billion USD, accounting for 18% of total revenue.
Delphi has over 20 production bases in China and two technology R&D centers located in Beijing and Shanghai.
Main ADAS Products
Delphi is also an ADAS system supplier with capabilities in sensors, control strategies, and actuators, providing a complete set of ADAS system services.
In terms of ADAS sensors, Delphi’s products cover cameras, millimeter-wave radar, and ultrasonic radar, achieving functions such as AEB, FCW, ACC, LDW, PDS, and NVA. Additionally, in 2015, Delphi invested in Quanergy to develop low-cost mass-produced laser radar products.
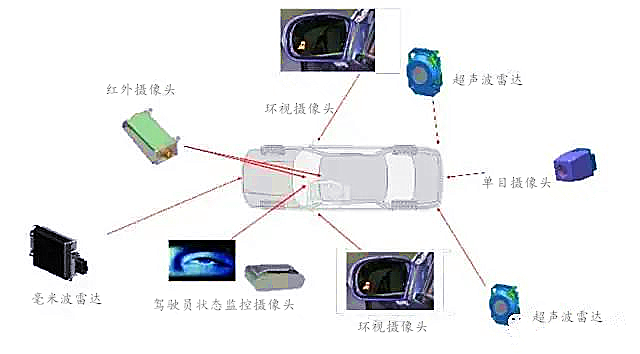
Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
Delphi’s main OEM customers include Ford, Volvo, and Mazda. Domestic brands such as Changan and Geely are also customers of Delphi’s ADAS systems.
ZF & TRW
Company Overview
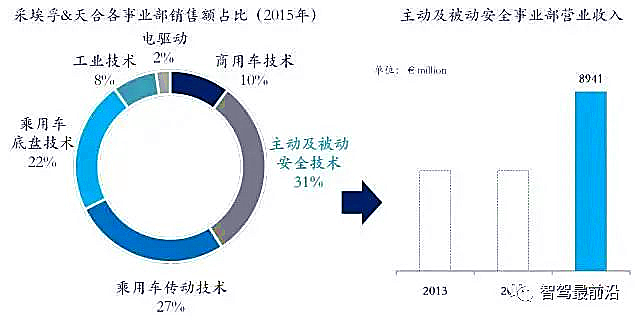
After acquiring TRW Automotive Group in 2015, ZF established the Active and Passive Safety Division, under which the ADAS-related business falls. In 2015, this division achieved revenues of 8.94 billion euros, accounting for 31% of ZF’s overall business.
ZF has established two regional headquarters, 32 production enterprises, and three after-sales service and trading companies in China, with its headquarters located in Shanghai. Additionally, ZF TRW plans to launch the latest camera sensor S-Cam3 in China in 2017, produced at the TRW body electronics plant in Shanghai Anting.
Main ADAS Products
ZF TRW has capabilities in sensors, processors, and actuators, also serving as an ADAS system supplier, providing a complete set of ADAS system services.
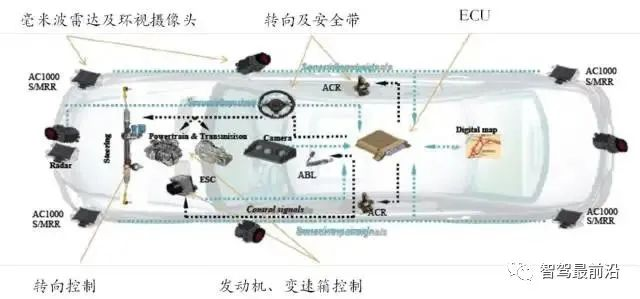


The main ADAS sensors supplied by ZF TRW include cameras and millimeter-wave radar, achieving functions such as ACC, FCW, AEB, LDW, and BSM. Its third-generation monocular camera uses Mobileye’s EyeQ3, which began mass production in 2015, with PSA as ZF TRW’s main partner.
Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
ZF TRW’s main OEM customers include Peugeot Citroën, Volvo, Mercedes-Benz, and Nissan. Domestic brands have relatively fewer ADAS customers.
Denso
Company Overview
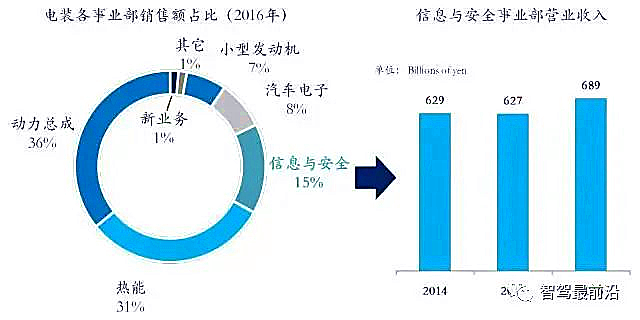
Denso’s ADAS business is part of the Information and Safety Division. In the fiscal year 2016, this division achieved revenues of 689 billion yen, accounting for 15% of Denso’s overall business, with a growth rate of 10% compared to the fiscal year 2015. To date, Denso has established 27 wholly-owned or joint venture companies in China.
Main ADAS Products
Denso is an ADAS system supplier with products ranging from sensors and processors to actuators, providing a complete set of ADAS system services.
Denso’s ADAS sensors include millimeter-wave radar, laser radar, and cameras, capable of achieving almost all ADAS functions. Its 77GHz millimeter-wave radar products have a detection range of ±18°, up to 205 meters; Denso’s camera products are characterized by their small size and low-temperature resistance.
Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
Denso’s main OEM customers are concentrated among Japanese companies, with Toyota, Honda, Mazda, and Suzuki being its primary customers. Domestic brands have relatively fewer ADAS customers.
Valeo
Company Overview
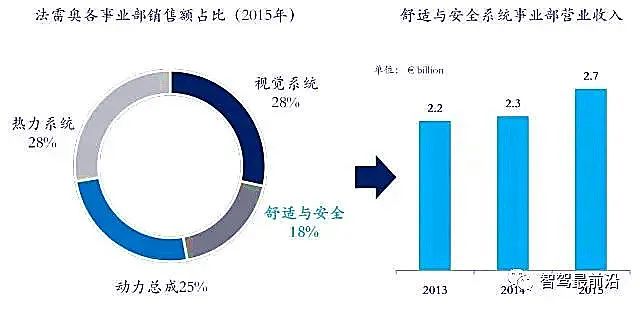
Valeo’s ADAS business is part of the Comfort and Safety Systems Division. In 2015, this division achieved revenues of 270 million euros, accounting for 18% of Valeo’s overall business, with a growth rate of 16% compared to the fiscal year 2015.
Main ADAS Products
Valeo can provide a complete set of ADAS system services, including sensors, algorithms, and actuators. Its sensors cover various products such as infrared cameras, millimeter-wave radar, and cameras, achieving multiple ADAS functions such as AP, SVC, ACC, and AEB.
Main Customers in Intelligent Vehicles
Valeo’s main OEM customers include Nissan, Ford, and General Motors. Its ultrasonic radar and surround-view cameras have a high market share. Domestic brands have relatively fewer ADAS customers.

-
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “Guidelines for the Construction of Cybersecurity and Data Security Standards System for the Internet of Vehicles”
-
The Battle for Autonomous Driving Chips
-
Path Planning in Autonomous Driving
-
Autonomous Driving Industry Weekly Report (03.07)
-
Summary of Industry Policies and Standards Released in February
-
Why Control-by-Wire Technology is a Prerequisite for Achieving Autonomous Driving?
-
Layout and Testing Solutions for High-Performance Computing Platforms for Intelligent Vehicles Facing SOA Services
-
4D Millimeter-Wave Radar is Accelerating, with New and Old “Players” Competing on the Same Stage
-
Discussing the Technological Changes in Automotive Electronics in Five Aspects
-
Driverless Technology in Mining Areas is Entering the Fast Lane, with Large-Scale Commercial Use Imminent
