Self-assembling hydrogels for mechanical support and drug delivery have been widely studied in the context of traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, most self-assembling hydrogels rely on polymer carriers or the introduction of exogenous inactive substances, often raising biosafety concerns and making clinical translation difficult.
On October 9, 2024, a research paper titled “Small Molecule Hydrogels Loading Small Molecule Drugs from Chinese Medicine for the Enhanced Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury” was published online by Wang Yang’s team at Central South University in ACS Nano. This study reported a small molecule hydrogel (GBR-gel) loaded with small molecule drugs (glycyrrhizic acid, berberine, and rhein) without additional drug loading or inactive components under physiological conditions.
GBR-gel has several advantages, including ease of preparation, cost-effectiveness, and high biocompatibility, allowing for rapid drug delivery at the site of brain injury, exerting powerful pharmacological effects. Single-cell RNA sequencing and experimental validation indicate that GBR-gel can effectively rescue the inhibited glutamatergic synaptic pathway after TBI, thereby alleviating inflammation and nerve damage, representing an alternative strategy for timely intervention in TBI.
 Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disruption of brain function caused by external forces and represents a significant global health challenge. It is estimated that TBI leads to 50 million deaths and 400 billion USD in economic burden globally each year. Today, global turmoil and conflict have also resulted in more TBI patients among military personnel, with an increasing prevalence of long-term mental dysfunction. Increasing evidence suggests that the complex pathological changes of TBI from the acute to chronic phase (inflammation, edema, etc.) gradually lead to long-term neurological dysfunction and increased mortality. Therefore, early intervention is crucial for improving TBI deterioration and patient prognosis. However, existing TBI therapies are limited by prolonged circulation time of oral and intravenous administration and the blood-brain barrier (BBB), severely affecting patient recovery. Thus, there is an urgent need for advanced local drug delivery technologies and materials to overcome the above limitations and further enhance timely intervention in the acute phase of the traumatized brain region.
Local drug delivery can effectively meet the demand for drug administration into the injury cavity during the acute phase of TBI. Injectable hydrogels with a three-dimensional supporting structure show great potential for in situ administration, suitable for local delivery post-TBI. Although various hydrogel-based drug delivery systems such as hyaluronic acid, gelatin methacryloyl/glycerol monostearate, agarose, and peptides have been used for TBI treatment, their clinical translation still faces significant challenges. Currently, most self-assembling hydrogels rely on polymer carriers or the incorporation of exogenous inactive substances as media (such as polymer compounds and metal ions), but the complex pathological progression post-trauma requires minimizing the incorporation of non-bioactive components in hydrogels to reduce potential toxicity issues caused by drug loads and non-bioactive delivery carriers.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disruption of brain function caused by external forces and represents a significant global health challenge. It is estimated that TBI leads to 50 million deaths and 400 billion USD in economic burden globally each year. Today, global turmoil and conflict have also resulted in more TBI patients among military personnel, with an increasing prevalence of long-term mental dysfunction. Increasing evidence suggests that the complex pathological changes of TBI from the acute to chronic phase (inflammation, edema, etc.) gradually lead to long-term neurological dysfunction and increased mortality. Therefore, early intervention is crucial for improving TBI deterioration and patient prognosis. However, existing TBI therapies are limited by prolonged circulation time of oral and intravenous administration and the blood-brain barrier (BBB), severely affecting patient recovery. Thus, there is an urgent need for advanced local drug delivery technologies and materials to overcome the above limitations and further enhance timely intervention in the acute phase of the traumatized brain region.
Local drug delivery can effectively meet the demand for drug administration into the injury cavity during the acute phase of TBI. Injectable hydrogels with a three-dimensional supporting structure show great potential for in situ administration, suitable for local delivery post-TBI. Although various hydrogel-based drug delivery systems such as hyaluronic acid, gelatin methacryloyl/glycerol monostearate, agarose, and peptides have been used for TBI treatment, their clinical translation still faces significant challenges. Currently, most self-assembling hydrogels rely on polymer carriers or the incorporation of exogenous inactive substances as media (such as polymer compounds and metal ions), but the complex pathological progression post-trauma requires minimizing the incorporation of non-bioactive components in hydrogels to reduce potential toxicity issues caused by drug loads and non-bioactive delivery carriers.
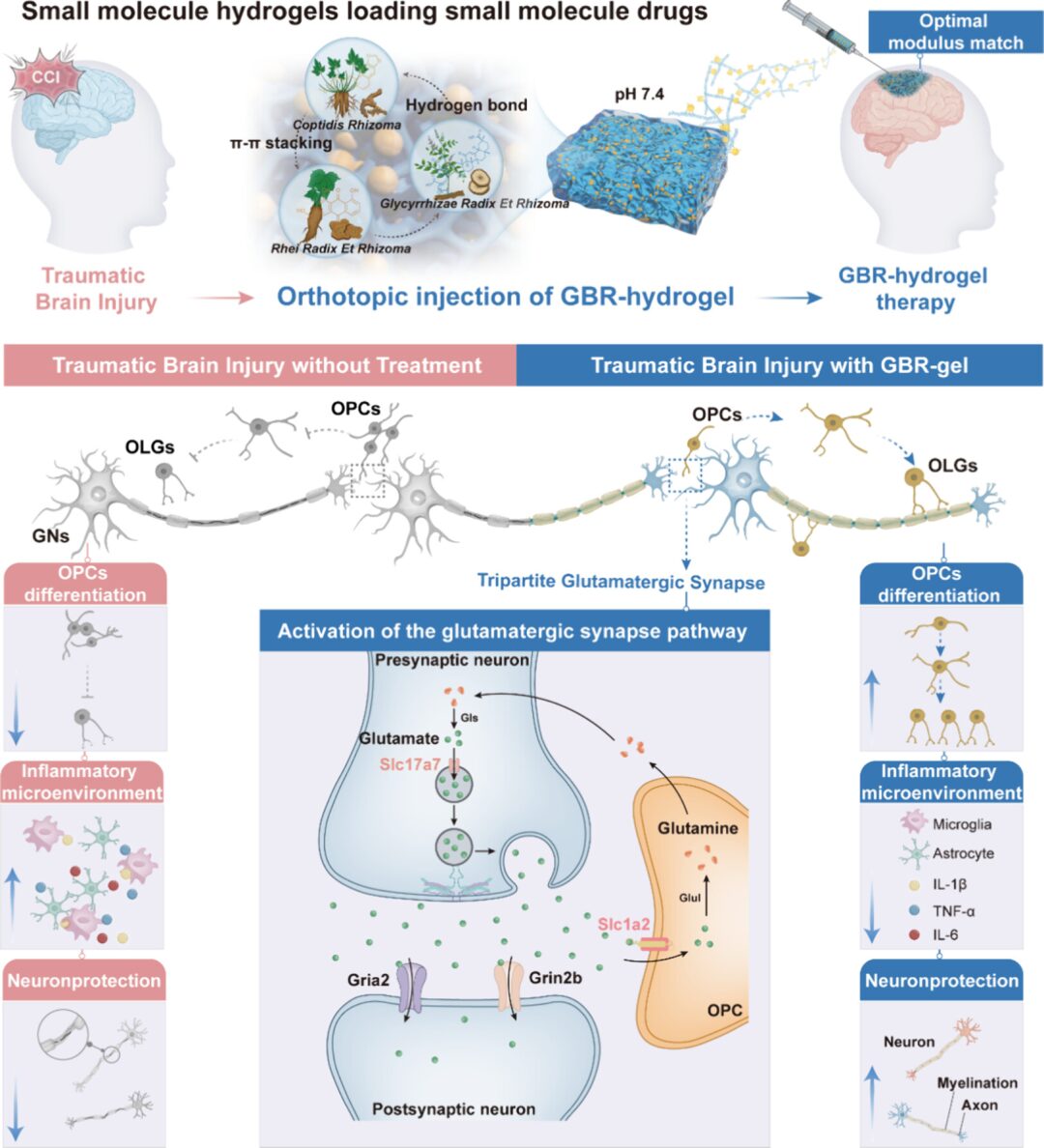 Figure 1: Schematic diagram of self-assembling small molecule hydrogels for local drug delivery enhancing TBI treatment effects (Excerpted from ACS Nano)
Small molecule drugs can directly self-assemble into supramolecular hydrogels, allowing pharmacologically active ingredients to replace exogenous inactive components and carriers, achieving up to 100% drug loading and high biocompatibility. Previous studies have reported a self-assembling hydrogel using a single herbal component, emodin. Due to the limited therapeutic effects of a single drug on TBI, exploring natural hydrogels assembled from multiple small molecule drugs is an important direction. However, due to the complex coordination of component structures and delicate balance, hydrogels based on full-component and multi-component systems are rare and difficult to prepare. Full-component and multi-component hydrogels often require non-bioactive metal ions and non-physiological pH values, and achieving a modulus that matches the elasticity of the brain is quite challenging, limiting their clinical translational application.
This study prepared a self-assembling hydrogel, referred to as GBR-gel, made from berberine (B) and rhein (R) as nanoparticle solutions, followed by the incorporation of glycyrrhizic acid (G). Non-covalent interactions facilitated the crosslinking of these three drugs, resulting in a natural carrier-free hydrogel under physiological pH conditions. Specifically, GBR-gel exhibits better anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective abilities, as well as excellent biocompatibility. The authors explored its potential mechanisms of action using single-cell RNA sequencing and found that GBR gel enhanced the glutamatergic synaptic pathway, thereby maintaining normal neuronal activity and supporting the differentiation and maturation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), ultimately inhibiting the inflammatory response in the brain. This study demonstrates the excellent neuroprotective effects of GBR-gel, providing an effective method for local drug delivery during the acute phase of TBI.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c09097
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of self-assembling small molecule hydrogels for local drug delivery enhancing TBI treatment effects (Excerpted from ACS Nano)
Small molecule drugs can directly self-assemble into supramolecular hydrogels, allowing pharmacologically active ingredients to replace exogenous inactive components and carriers, achieving up to 100% drug loading and high biocompatibility. Previous studies have reported a self-assembling hydrogel using a single herbal component, emodin. Due to the limited therapeutic effects of a single drug on TBI, exploring natural hydrogels assembled from multiple small molecule drugs is an important direction. However, due to the complex coordination of component structures and delicate balance, hydrogels based on full-component and multi-component systems are rare and difficult to prepare. Full-component and multi-component hydrogels often require non-bioactive metal ions and non-physiological pH values, and achieving a modulus that matches the elasticity of the brain is quite challenging, limiting their clinical translational application.
This study prepared a self-assembling hydrogel, referred to as GBR-gel, made from berberine (B) and rhein (R) as nanoparticle solutions, followed by the incorporation of glycyrrhizic acid (G). Non-covalent interactions facilitated the crosslinking of these three drugs, resulting in a natural carrier-free hydrogel under physiological pH conditions. Specifically, GBR-gel exhibits better anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective abilities, as well as excellent biocompatibility. The authors explored its potential mechanisms of action using single-cell RNA sequencing and found that GBR gel enhanced the glutamatergic synaptic pathway, thereby maintaining normal neuronal activity and supporting the differentiation and maturation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), ultimately inhibiting the inflammatory response in the brain. This study demonstrates the excellent neuroprotective effects of GBR-gel, providing an effective method for local drug delivery during the acute phase of TBI.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c09097

—END—
The content is original from 【iNature】,
Reprinting requires stating the source as 【iNature】
Add WeChat Group
iNature gathers 40,000 life science researchers and doctors. We have formed 80 comprehensive groups (16 PI groups and 64 doctoral groups), while also establishing specialized groups (plants, immunology, cells, microbiology, gene editing, neurology, chemistry, physics, cardiovascular, oncology, etc.).Friendly reminder: When joining the group, please note (format as school + major + name; if you are a PI/professor, pleaseindicate as PI/professor, otherwise it will be assumed you are a doctoral student, thank you). You can first add the editor’s WeChat ID (love_iNature), or long press the QR code to add the editor, and then join the relevant group; please only serious inquiries.


For submission, collaboration, and reprint authorization matters
Please contact WeChat ID:13701829856 or email:[email protected]
If you find this article interesting, please click here!




