This article will describe the development process of Mi Home BLE devices from three aspects: the Xiaomi Developer Platform, embedded software, and extension programs. The focus here is mainly on introducing the core development steps, while the content that can be completed independently by referring to the documentation will not be elaborated upon.1. Developer Platform Development1.1 Create ProductAccounts with development permissions can create products on the platform. It is important to pay attention to the selection of product type and networking method.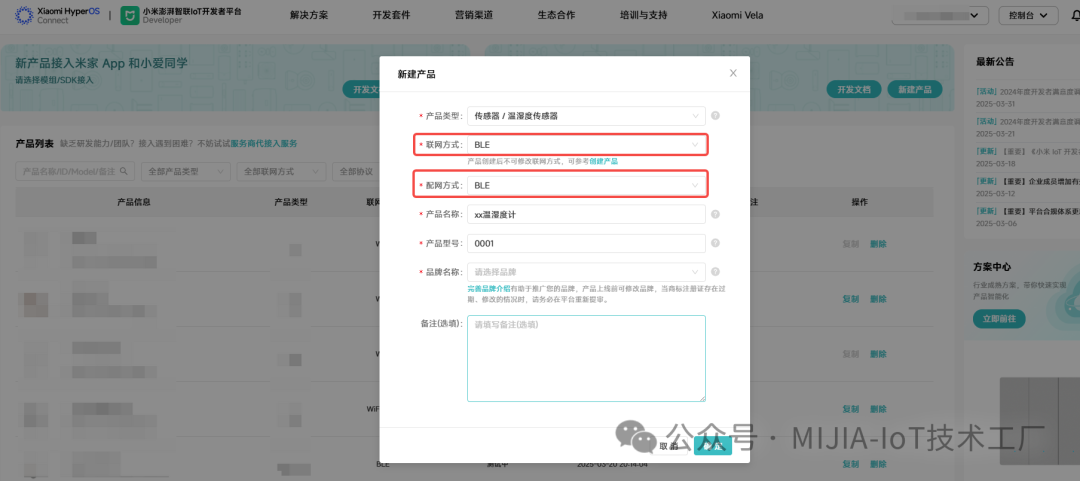 It should be noted that currently, when creating a product, the Xiaomi IoT Developer Platform requires the selection of a brand authorized by the corresponding enterprise. If the enterprise has not yet registered a brand, it needs to complete the brand registration as soon as possible and upload the relevant brand information to the platform for review.1.2 Function DefinitionAfter creating a product, the standard function definitions related to that category will be generated by default. We can add or delete configurations as needed based on the product requirements.
It should be noted that currently, when creating a product, the Xiaomi IoT Developer Platform requires the selection of a brand authorized by the corresponding enterprise. If the enterprise has not yet registered a brand, it needs to complete the brand registration as soon as possible and upload the relevant brand information to the platform for review.1.2 Function DefinitionAfter creating a product, the standard function definitions related to that category will be generated by default. We can add or delete configurations as needed based on the product requirements.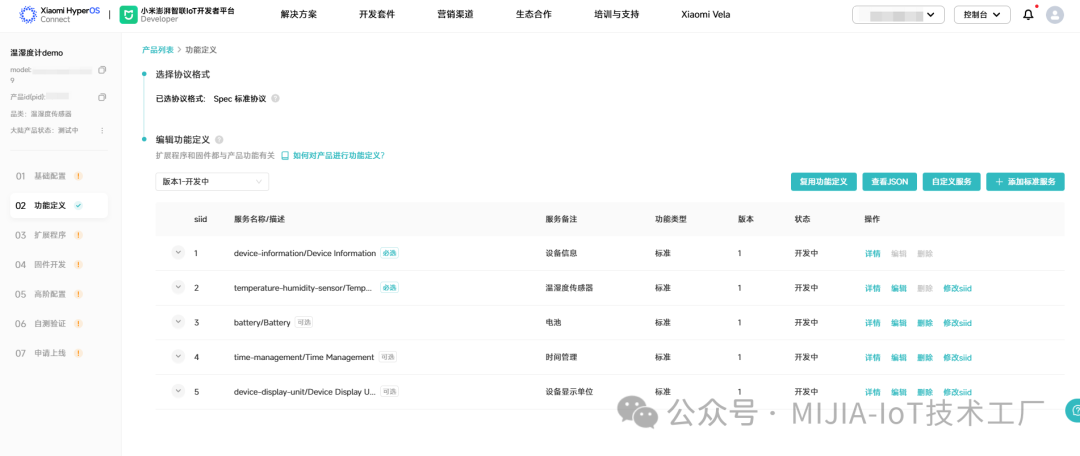 When configuring function definitions, if the id of the attribute/event is > 1000, it indicates that this attribute/event can be reported through the gateway. If direct connection permissions are configured, it can also report directly. It is important to note that a product’s configuration for reportable attributes + events must be ≤ 7.
When configuring function definitions, if the id of the attribute/event is > 1000, it indicates that this attribute/event can be reported through the gateway. If direct connection permissions are configured, it can also report directly. It is important to note that a product’s configuration for reportable attributes + events must be ≤ 7.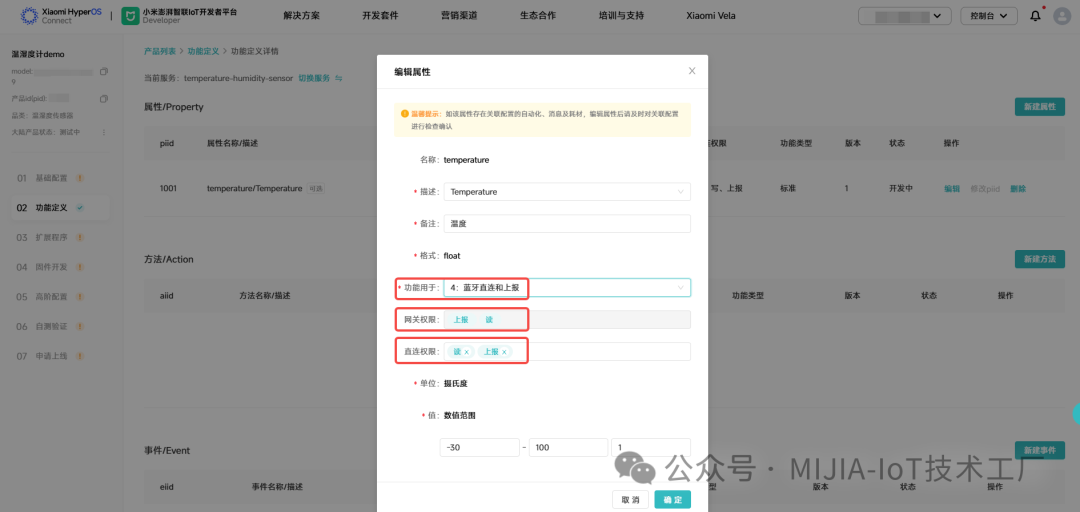 1.3 Extension Program DevelopmentThere are two modes for extension program development: standard development and custom development.
1.3 Extension Program DevelopmentThere are two modes for extension program development: standard development and custom development.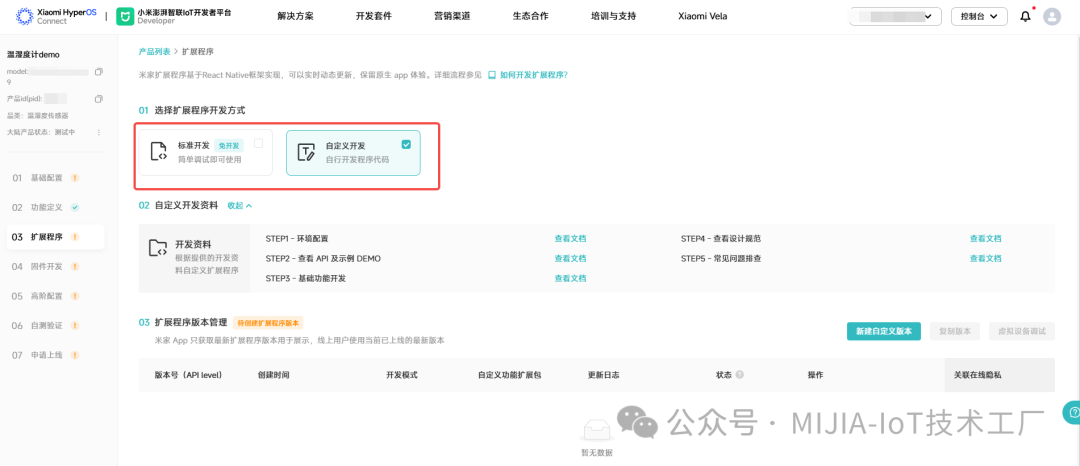 Standard development refers to the programs developed by Xiaomi for product categories. After selection, they can be loaded through the Mi Home App, and the extension program will automatically load related functions based on the standard function definitions (Note: The standard extension program for BLE devices is somewhat limited, as the direct connection protocol is not publicly available, making it unusable). Custom development refers to freely developing related UI and functions based on the Xiaomi extension program SDK, which offers higher flexibility but requires a certain level of technical capability from enterprise developers.1.4 Firmware DevelopmentThe firmware development page requires the correct completion of module model and OTA method configuration, firmware SDK application, and firmware upload for upgrades.
Standard development refers to the programs developed by Xiaomi for product categories. After selection, they can be loaded through the Mi Home App, and the extension program will automatically load related functions based on the standard function definitions (Note: The standard extension program for BLE devices is somewhat limited, as the direct connection protocol is not publicly available, making it unusable). Custom development refers to freely developing related UI and functions based on the Xiaomi extension program SDK, which offers higher flexibility but requires a certain level of technical capability from enterprise developers.1.4 Firmware DevelopmentThe firmware development page requires the correct completion of module model and OTA method configuration, firmware SDK application, and firmware upload for upgrades.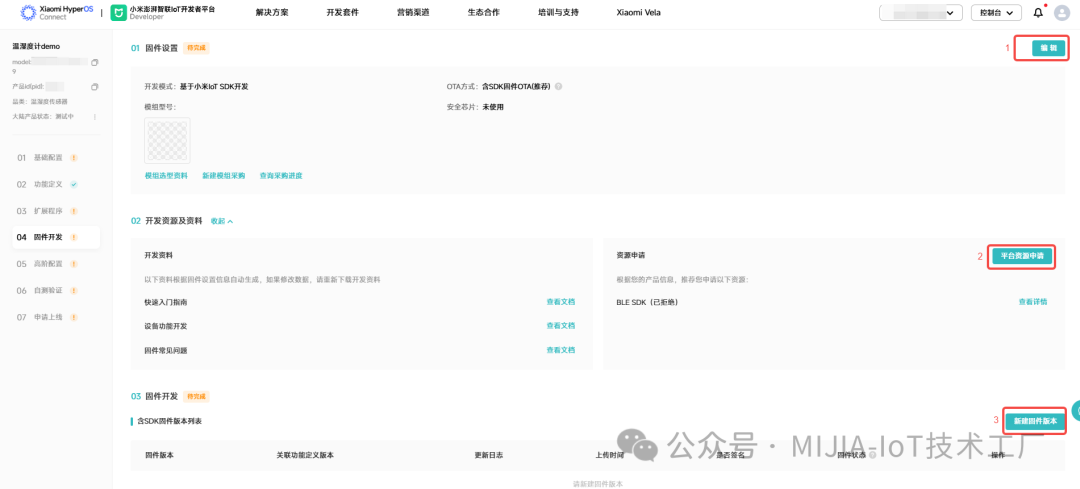 1.5 Advanced ConfigurationDuring development, all options in advanced configuration need to be completed in order.Advanced configuration focuses on message push and automation:
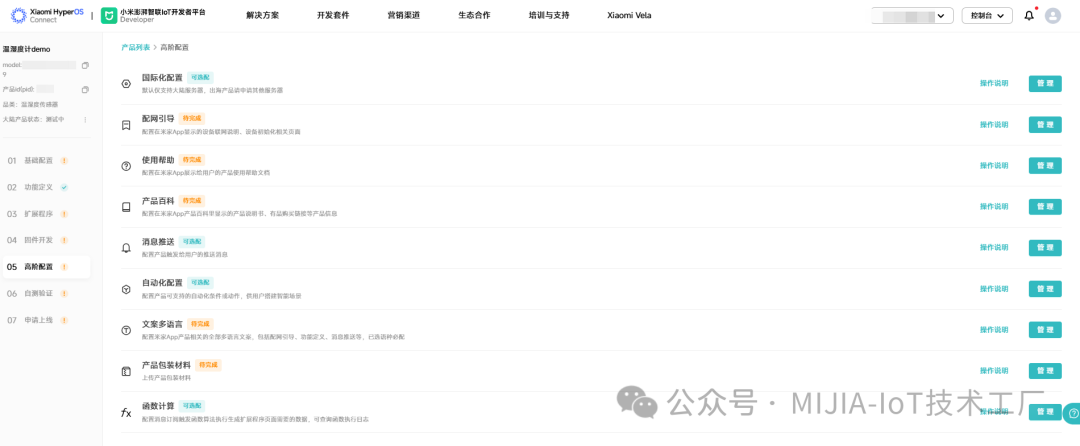
1.5 Advanced ConfigurationDuring development, all options in advanced configuration need to be completed in order.Advanced configuration focuses on message push and automation:
- Message Push: Used for alerts and fault information reporting, such as low battery warnings.
- Automation: After configuration, it can interact with other devices. BLE devices are commonly used as trigger devices, such as when the temperature exceeds xx degrees Celsius.
 2. Embedded Software Development2.1 Network Configuration Binding2.1.1 Macro DefinitionsThe macros related to network configuration are placed in the custom_mi_config.h file:
2. Embedded Software Development2.1 Network Configuration Binding2.1.1 Macro DefinitionsThe macros related to network configuration are placed in the custom_mi_config.h file:
// Product PID, a unique ID for a product on the platform, can be viewed in the "Basic Information" section at the bottom left of the device page on the development platform#define PRODUCT_ID 156
// Model number, product name, corresponds one-to-one with PID#define MODEL_NAME "xiaomi.dev.ble"
// Whether the product has a reset network configuration button, 0-no, 1-yes. When set to 1, after the device is configured, it will send a device configured broadcast, and the Mi Home app cannot discover the device; it can only be discovered again after the device is reset. When set to 0, the device will continuously send an unconfigured broadcast regardless of whether it has been configured, allowing it to be scanned and bound by other accounts. Generally, it is required to set to 1#define HAVE_RESET_BUTTON 1
// Whether the product has a network configuration confirmation button, 0-no, 1-yes. When set to 1, it indicates that the device has a confirmation button, and it will send a non-confirmation broadcast normally. When the button is pressed, the firmware needs to change the broadcast content to a confirmation broadcast. When set to 0, the device does not have a confirmation button, and the firmware cannot change the broadcast content, and it will continuously send a confirmation broadcast. Generally, it is required to set to 1#define HAVE_CONFIRM_BUTTON 12.1.2 Callback Events
The device’s network status changes will ultimately be called back in the mi_schd_event_handler function:
void mi_schd_event_handler(schd_evt_t *p_event){ MI_LOG_INFO("USER CUSTOM CALLBACK RECV EVT ID %d\n", p_event->id); switch (p_event->id) { case SCHD_EVT_KEY_DEL_FAIL: case SCHD_EVT_KEY_DEL_SUCC:// Device local reset successful break; case SCHD_EVT_REG_SUCCESS:// Network configuration successful break; case SCHD_EVT_KEY_FOUND:// Device reset/power on, device has been configured break; case SCHD_EVT_KEY_NOT_FOUND:// Device reset/power on, device has not been configured break; default:break; }}2.1.3 API
The interfaces related to network configuration are declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
// Initialize broadcast, 0-non-confirmation broadcast, 1-confirmation broadcast. This interface only takes effect when HAVE_CONFIRM_BUTTON is set to 1; otherwise, regardless of the input parameter, the interface will initialize the broadcast as a confirmation broadcast.static inline void miio_ble_user_adv_init(uint8_t solicite_bind)
// Start broadcast, input parameter is the broadcast interval, 100ms – 1000msstatic inline int miio_ble_user_adv_start(uint16_t adv_interval_ms)
// Stop broadcaststatic inline void miio_ble_user_adv_stop(void)
// Set broadcast timeout, after the timeout, it will broadcast again. If the parameter is 0, it will immediately stop broadcastingstatic inline int miio_ble_set_adv_timeout(uint32_t timeout)
// Get whether the device has been configured. This is only valid when the macro definition HAVE_RESET_BUTTON is set to 1; otherwise, it will always return that the device is not configured.static inline int miio_ble_get_registered_state(void)
// Reset the device and restore it to factory settingsstatic inline int miio_system_restore(void)The Mi Home App discovers devices based on the broadcast content of the device, so when a device is not discovered, it is necessary to confirm whether the device is sending broadcasts normally.
2.2 Communication Control
2.2.1 Gateway Reporting
The gateway reporting interface is declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
// Device property reporting, piid >1000static inline int miio_ble_property_changed(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, property_value_t *newValue, uint8_t isUrgent)
// Device event reporting, eiid >1000static inline int miio_ble_event_occurred(uint16_t siid, uint16_t eiid, arguments_t *newArgs, uint8_t isUrgent)Data can only be reported through the gateway data reporting interface after the device is configured. It should be noted that some BLE chips do not support sending broadcasts when directly connected, while some do; specific confirmation is needed from the chip manufacturer.
2.2.2 Direct Connection Authentication Login
The direct connection status between the device and the phone will be called back to the gap_event_handler function:
static void gap_event_handler(mible_gap_evt_t evt, mible_gap_evt_param_t* param){ switch (evt) { case MIBLE_GAP_EVT_CONNECTED:// Successfully connected at the lower level break; case MIBLE_GAP_EVT_DISCONNECT:// Connection at the lower level disconnected break; default: break; }}Before the device and phone can communicate directly, login authentication must be completed, and the authentication callback is the mi_schd_event_handler function:
void mi_schd_event_handler(schd_evt_t *p_event){ switch (p_event->id) { case SCHD_EVT_ADMIN_LOGIN_SUCCESS : // Direct connection login successful break; case SCHD_EVT_ADMIN_LOGIN_FAILED : // Direct connection login failed break; default:break; }}2.2.3 Direct Connection Spec Communication
The direct connection communication interface is declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
// Direct connection spec communication initialization. set_cb, get_cb, action_cb are the direct connection spec operation callback functions. The buflen represents the buffer length required by the firmware side when the plugin gets multiple properties at once. Assuming the plugin can get a maximum of 5 properties at once, it is recommended that buflen ≥6 (header consumption) + 5*12 (property content) + 6 (encryption header) = 72. If there are string type properties, the length of the string property value should be added to this, for example, if the numeric string length is 10, then buflen ≥82static inline int miio_gatt_spec_init(property_operation_callback_t set_cb, property_operation_callback_t get_cb, action_operation_callback_t action_cb, uint16_t buflen)
// When directly connected, the device actively reports properties to the phone pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_properties_changed(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, property_value_t *newValue)
// When directly connected, the device actively reports events to the phone pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_event_occurred(uint16_t siid, uint16_t eiid, arguments_t *newArgs)2.2.4 Direct Connection Transparent Transmission Communication
When the product requires data transmission through a custom transparent transmission service, it is recommended to add the stdio transparent channel configured by Xiaomi to reduce service configuration issues:
// stdio transparent service initialization, the callback function is the channel data reception function. The plugin must encrypt data when sending, and the data will be automatically decrypted and pushed to the application layer before the callback.int stdio_service_init(stdio_rx_t rx_handler)
// Send data through the transparent channel, len≤14Byte, the interface will automatically encrypt the data before sendingint stdio_tx(void *data, uint8_t len)Stdio Profile Definition:
Service UUID: 6D-69-2E-6D-69-6F-74-2E-62-6C-65-00-00-01-00-00
RX UUID: 6D-69-2E-6D-69-6F-74-2E-62-6C-65-00-01-01-00-00
TX UUID: 6D-69-2E-6D-69-6F-74-2E-62-6C-65-00-02-01-00-002.3 OTA
The upgrade function SDK for the chip/module itself has been integrated and supported. The firmware side can enable the USE_MIBLE_OTA macro definition. The corresponding upgrade status callback function is app_dfu_callback.
static void app_dfu_callback(mible_dfu_state_t state, mible_dfu_param_t *param){ switch (state) { case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_START: MI_LOG_INFO("fragment size is %d\n", param->start.fragment_size); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_UPGRADE_STATUS: MI_LOG_INFO("upgrade status is %x\n", param->upgrade_status.req); param->upgrade_status.rsp = param->upgrade_status.req; break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_TRANSFER: MI_LOG_INFO("last fragment index is %d\n", param->trans.last_index); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_VERIFY: MI_LOG_INFO("verify result is %d\n", param->verify.value); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_SWITCH: MI_LOG_INFO("switch to new firmware\n"); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_CANCEL: MI_LOG_INFO("the sequence is canceled\n"); break; default: MI_LOG_INFO("state of DFU is unknown %d\n", state); break; }}When uploading firmware to the developer platform, it is essential to strictly follow the platform documentation for each step to check for normalcy. If the chip/module log shows<span>Not found TAG HEAD(MAGIC NUM)</span>, it indicates that there is a problem with the firmware upload/configuration. It is important to note: common reasons include wild versions, version disorder, and not configuring support for signatures and the minimum version of https.
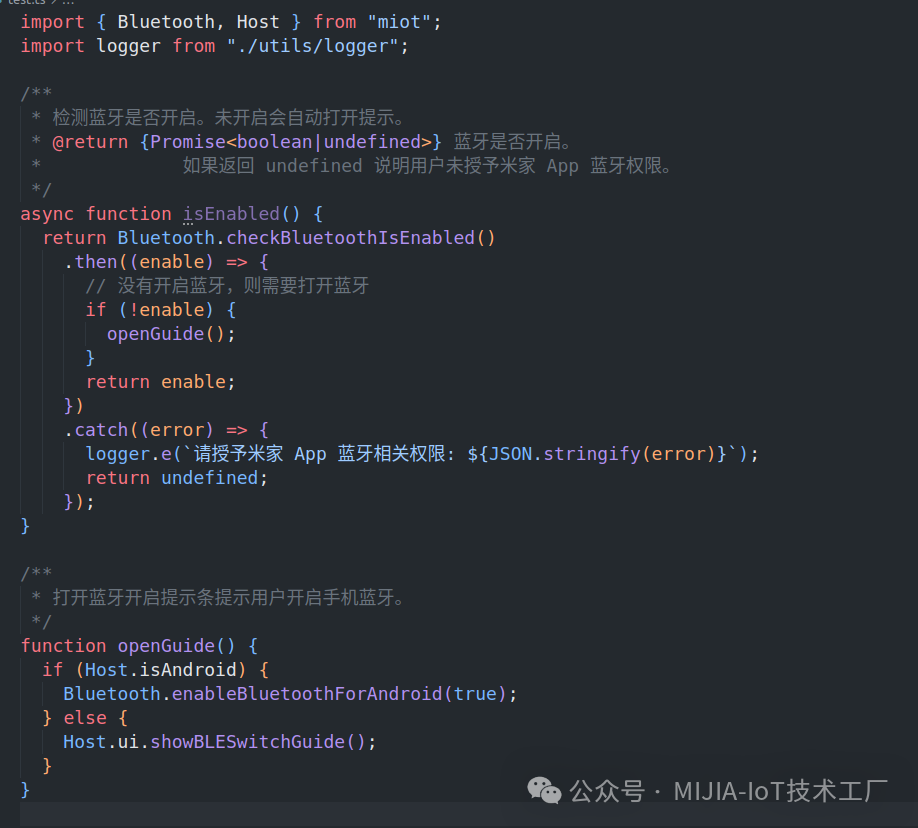
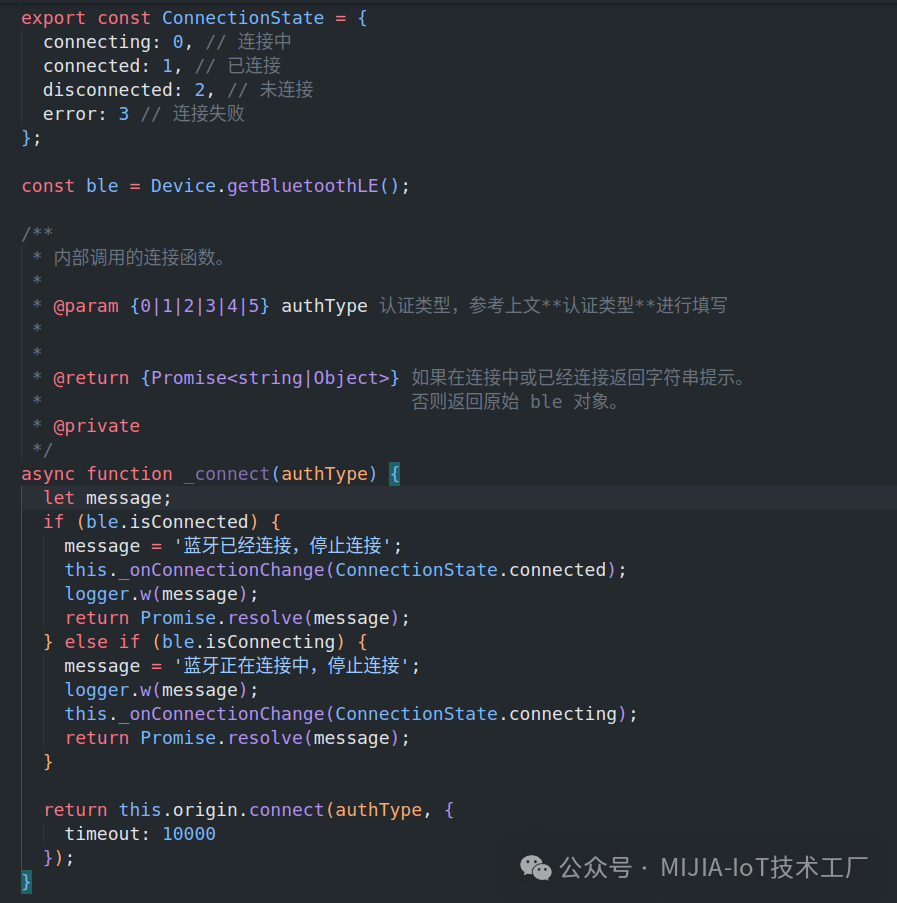
3. Extension Program Development3.1 Connecting BLE DevicesAfter successfully connecting the Mi Home App and the device via Bluetooth, the App will use a specific encryption method for secure authentication with the device. Different devices have different types of security authentication. During the development of the Bluetooth device extension program, there will be many functions that require passing authentication type parameters (authType or bleAuthType). Currently, the most commonly used types are 1, 4, and 5, with standard BLE devices being type 4.
| type | Description |
| -1 | Automatic detection, not supported on Android |
| 0 |
Ordinary Xiaomi Bluetooth protocol device |
| 1 |
Xiaomi Bluetooth device with security chip (e.g., lock products) |
| 2 | Shared security chip Xiaomi Bluetooth device |
| 3 |
Ordinary BLE Bluetooth device (no mibeacon, no Xiaomi FE95 service) |
| 4 | Standard Auth standard Bluetooth authentication protocol |
| 5 | Mesh device |
| 6 | Shared lock device |
3.2 BLE Device Communication
Xiaomi has provided a reference demo for the entire operation of the extension directly connected to the BLE Spec. After downloading the demo, unzip the document to the projects folder and modify the config.js file in the root directory of the project to run.
Name: com.miot.blespec.zip
Address: https://kpan.mioffice.cn/webfolder/ext/RYmWzTb0bXg%40
Password: Xhd4
For Bluetooth direct connection and BLE API, please refer to the official documentation:https://github.com/MiEcosystem/miot-plugin-sdk/wiki/02-%E8%93%9D%E7%89%99%E6%A8%A1%E5%9D%97
3.3 Firmware Upgrade
Since the firmware version of the BLE device depends on the data read and reported to the cloud after connecting to the phone, the SDK’s firmware upgrade detection occurs after the extension program and device are successfully connected. Therefore, it is necessary to attempt to connect to the device every time the extension program enters the device upgrade page to ensure that the SDK’s firmware upgrade detection can be triggered.
Code to be added in the index.js file in the root directory of the project:
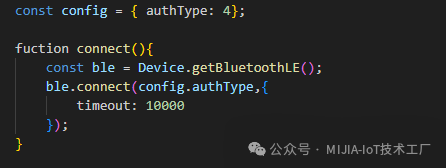
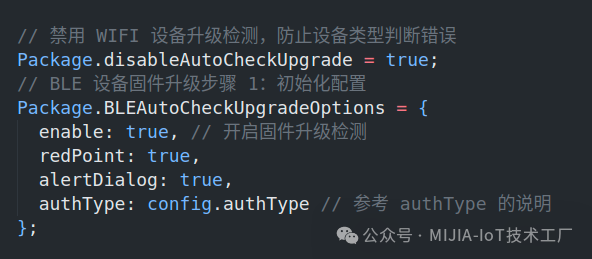
Configure the extraOptions property of the CommonSetting component:
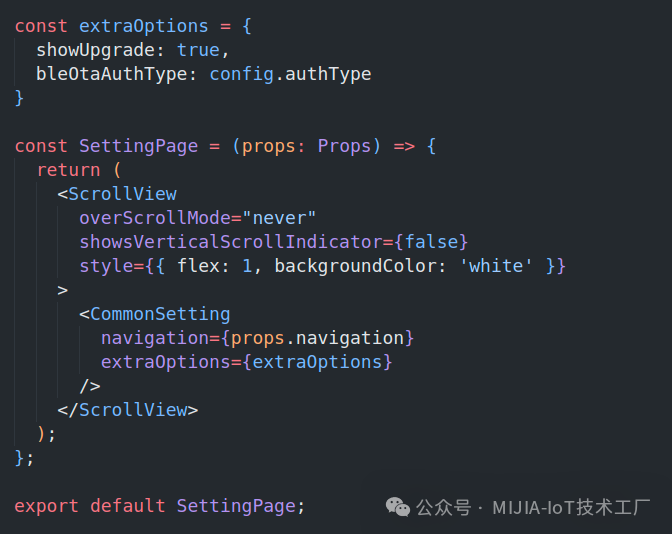
4. Conclusion
Mi Home BLE devices support the development of multiple chips/modules. Although there may be differences in the development environment for different chips/modules, the interfaces and functions related to Mi Home are universal. Therefore, everyone can refer to this article to implement related functional development during the development process. If you encounter any related issues, feel free to leave a comment for discussion!!!




