Updated smartphone SoC processor rankings as of April 22, 2025, with a reasonable distribution of CPU and GPU performance scores, combined with the latest version of the system, and appropriate adjustments made to some smartphone SoC rankings, continuously optimizing the performance ladder.
The April update features the Snapdragon 8s Gen4, manufactured using TSMC’s second-generation 4nm process (N4P), utilizing a “1+7” big core CPU architecture, consisting of 1 3.2GHz Cortex-X4 super core, 3 3.0GHz Cortex-A720 big cores, 2 2.8GHz Cortex-A720 middle cores, and 2 2.0GHz Cortex-A720 efficiency cores.
The CPU performance of the Snapdragon 8s Gen4 has significantly improved, with single-core performance slightly inferior to the Snapdragon 8 Gen3, but greatly surpassing the Dimensity 8400 and 8s Gen3. Multi-core performance is close to that of the 8 Gen3, showing significant progress compared to the previous generation 8s Gen3. In the Geekbench 6 test, the single-core score reached 2232 points, while the multi-core score was 7308 points. In terms of GPU, the Adreno 825 performed excellently in the Aztec 1440P off-screen test, with a significant increase in peak performance and energy efficiency far exceeding the previous generation 8s Gen3.
The Snapdragon 8s Gen4 can be seen as an optimized version of the small 8 Gen3! This month, the Redmi Turbo4 Pro and iQOO Z10 Turbo Pro debuted with this chip.
Below is the latest mainstream consumer smartphone processor performance ladder for 2025; for reference when choosing a smartphone; data source: Geekbench single-threaded, multi-threaded scores, and GFXBench Manhattan graphics frame rate rankings, as well as game frame rates, energy consumption, and overall user experience rankings.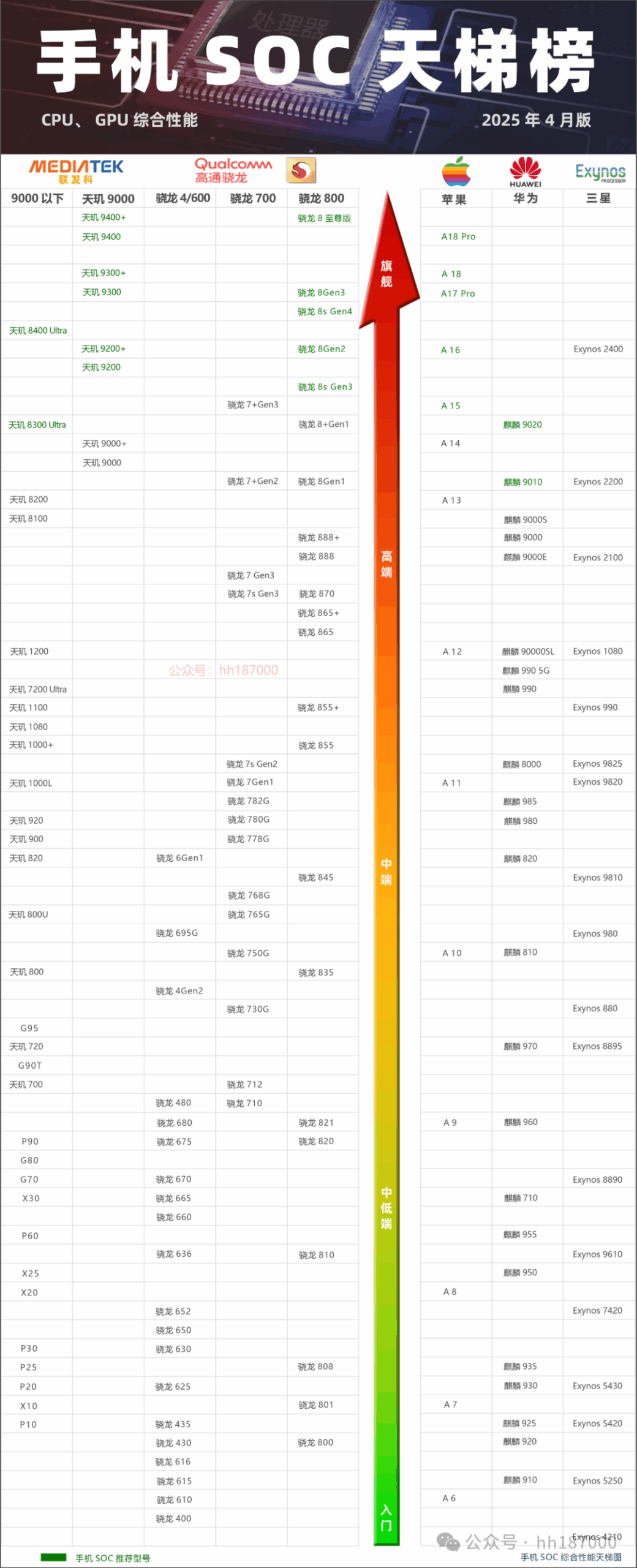 We have conducted testing and statistical organization of mainstream smartphone processors and continuously optimized the performance ladder.Here is a brief introduction to smartphone processors: A smartphone processor (also known as SoC, commonly referred to as CPU, in English System on Chip, translated as system-level chip) is the core component that consumers pay the most attention to when purchasing a smartphone. It is the control center of the entire phone and the command center for the logical part. The microprocessor achieves control by running software stored in memory and calling databases within memory. All data processing must go through the CPU, and the management of various parts of the phone relies on the unified and coordinated command of this microprocessor headquarters.
We have conducted testing and statistical organization of mainstream smartphone processors and continuously optimized the performance ladder.Here is a brief introduction to smartphone processors: A smartphone processor (also known as SoC, commonly referred to as CPU, in English System on Chip, translated as system-level chip) is the core component that consumers pay the most attention to when purchasing a smartphone. It is the control center of the entire phone and the command center for the logical part. The microprocessor achieves control by running software stored in memory and calling databases within memory. All data processing must go through the CPU, and the management of various parts of the phone relies on the unified and coordinated command of this microprocessor headquarters. Strictly speaking,computer CPUs and smartphone CPUs are completely different, smartphone CPUs should be called smartphone SoCs.Smartphone SoCs integrate a series of functional modules including CPU, GPU, RAM, modem, navigation, and mobile baseband. With the continuous improvement of integrated circuit production technology and process levels, the functions of microprocessors in smartphones have become increasingly powerful, such as integrating advanced digital signal processors (DSP) within the microprocessor. Therefore, the performance of the smartphone processor determines the performance of the entire phone. In contrast, computer CPUs are not as complex; they are simply central processing units without integrating other functional modules, and the memory, graphics processors (GPUs), and network interfaces in computers are independent.
Strictly speaking,computer CPUs and smartphone CPUs are completely different, smartphone CPUs should be called smartphone SoCs.Smartphone SoCs integrate a series of functional modules including CPU, GPU, RAM, modem, navigation, and mobile baseband. With the continuous improvement of integrated circuit production technology and process levels, the functions of microprocessors in smartphones have become increasingly powerful, such as integrating advanced digital signal processors (DSP) within the microprocessor. Therefore, the performance of the smartphone processor determines the performance of the entire phone. In contrast, computer CPUs are not as complex; they are simply central processing units without integrating other functional modules, and the memory, graphics processors (GPUs), and network interfaces in computers are independent.
Key components integrated in smartphone SoC chips
1. CPU: Responsible for processing computational tasks. The most important part of the smartphone processor, responsible for task computation and control, its strength directly relates to smartphone performance. It is easy to understand that all instructions are processed and issued by it.2. GPU: Responsible for image rendering. The graphics processor, equivalent to the graphics card in a laptop. The GPU is crucial for gaming experience; generally, the stronger the performance, the higher the game frame rate.3. Baseband: A circuit in the smartphone, primarily responsible for demodulating, deinterleaving, despreading, and decoding wireless signals in mobile networks. It is responsible for communication capabilities, and the quality of mobile signal is directly related to this.4. ISP: Image Signal Processor, mainly used for image processing in smartphone imaging systems. Mainstream smartphone SoC chips from Qualcomm, MediaTek, Kirin, etc., integrate ISP modules. For most people, the presence of ISP may not be highly noticeable, but it is an indispensable part of the smartphone.5. DSP: Digital Signal Processor, a chip that integrates specialized computing capabilities. DSPs are designed for embedded systems such as mobile base stations, where floating-point operations are not required, only integer operations. However, with the advent of 5G networks, the computational burden on base stations is increasing, making floating-point operations essential.6. NPU: Responsible for artificial intelligence computations. Functions such as facial recognition and portrait segmentation address the long-standing issue of poor video quality in night scenes due to insufficient computing power of ISP and general processors, as well as information loss in traditional imaging links.7. Other integrated functional components. Therefore, this is why the most important factor when choosing a smartphone is the smartphone chip! Because it is not just about performance!
Currently, the five most well-known mainstream chip manufacturers are Qualcomm, Huawei, Samsung, MediaTek, and Apple. The flagship chips from these five companies are:
-
Qualcomm representative models: Snapdragon 8 Supreme Edition, Snapdragon 8 Gen3, 8s Gen4, Snapdragon 8 Gen2;
-
Huawei representative models: Kirin 9020, Kirin 9010, Kirin 9000S, Kirin 9000, etc.;
-
Samsung representative models: Exynos 2400, Exynos 1580, Exynos 2200, etc.;
-
MediaTek representative models: Dimensity 9400 (+), Dimensity 9300 (+), Dimensity 9200, etc.;
-
Apple representative models: A18 Pro, A17 Pro, A16, etc.
 Apple: In terms of CPU performance and experience,Apple‘s A-series processors have consistently been in the top tier of high-end flagships over the years, combined with the advantages of the excellent iOS system, offering a good advantage in smoothness compared to the Android platform, and with high energy efficiency, making them relatively more power-saving than Android devices, with the flagship representative beingA18 Pro. A new iPhone can maintain a high level of smoothness even after several years of use.Qualcomm: As the most popular in the Android camp, Qualcomm’s chip models are very comprehensive, covering high, mid, and low-end series models. The latest Snapdragon 8 Supreme Edition is the mainstream choice for Android flagships this year, with the Xiaomi 14, OnePlus 13, and other flagship models debuting with this SoC. In previous years, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen1 and Snapdragon 888 faced criticism for power consumption and heating issues. As long as Qualcomm’s power consumption does not falter, it remains the preferred chip for major Android manufacturers.Huawei: As a well-known domestic smartphone manufacturer, Huawei mainly uses its own Kirin processors, with the highest-end updated to the Kirin 9000 series (9020, 9010). Due to U.S. sanctions, it has fallen behind Apple and Qualcomm’s second-generation chips in performance, but it is believed that Huawei will rise again in the future.MediaTek: In recent years, MediaTek has made a strong comeback, despite being criticized in earlier years for its performance. However, since upgrading the Dimensity series, it has been making significant progress. Last year’s Dimensity 9300 could compete head-to-head with Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen3, and this year’s Dimensity 9400 is also a top choice for Android flagships, fully entering the high-end flagship market.Samsung: Samsung’s processors have relatively low popularity, mainly because Samsung phones have nearly exited the domestic market, and Samsung processors are mainly used in Samsung’s Korean models, while Samsung’s domestic phones are equipped with Qualcomm processors.
Apple: In terms of CPU performance and experience,Apple‘s A-series processors have consistently been in the top tier of high-end flagships over the years, combined with the advantages of the excellent iOS system, offering a good advantage in smoothness compared to the Android platform, and with high energy efficiency, making them relatively more power-saving than Android devices, with the flagship representative beingA18 Pro. A new iPhone can maintain a high level of smoothness even after several years of use.Qualcomm: As the most popular in the Android camp, Qualcomm’s chip models are very comprehensive, covering high, mid, and low-end series models. The latest Snapdragon 8 Supreme Edition is the mainstream choice for Android flagships this year, with the Xiaomi 14, OnePlus 13, and other flagship models debuting with this SoC. In previous years, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen1 and Snapdragon 888 faced criticism for power consumption and heating issues. As long as Qualcomm’s power consumption does not falter, it remains the preferred chip for major Android manufacturers.Huawei: As a well-known domestic smartphone manufacturer, Huawei mainly uses its own Kirin processors, with the highest-end updated to the Kirin 9000 series (9020, 9010). Due to U.S. sanctions, it has fallen behind Apple and Qualcomm’s second-generation chips in performance, but it is believed that Huawei will rise again in the future.MediaTek: In recent years, MediaTek has made a strong comeback, despite being criticized in earlier years for its performance. However, since upgrading the Dimensity series, it has been making significant progress. Last year’s Dimensity 9300 could compete head-to-head with Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen3, and this year’s Dimensity 9400 is also a top choice for Android flagships, fully entering the high-end flagship market.Samsung: Samsung’s processors have relatively low popularity, mainly because Samsung phones have nearly exited the domestic market, and Samsung processors are mainly used in Samsung’s Korean models, while Samsung’s domestic phones are equipped with Qualcomm processors.