SWD stands for Serial Wire Debug Interface. Sometimes you may encounter terms like: JTAG-DP, SW-DP, SWJ-DP, which are interfaces for external hardware boxes. Among them, SWJ-DP was added in ADI v6.0: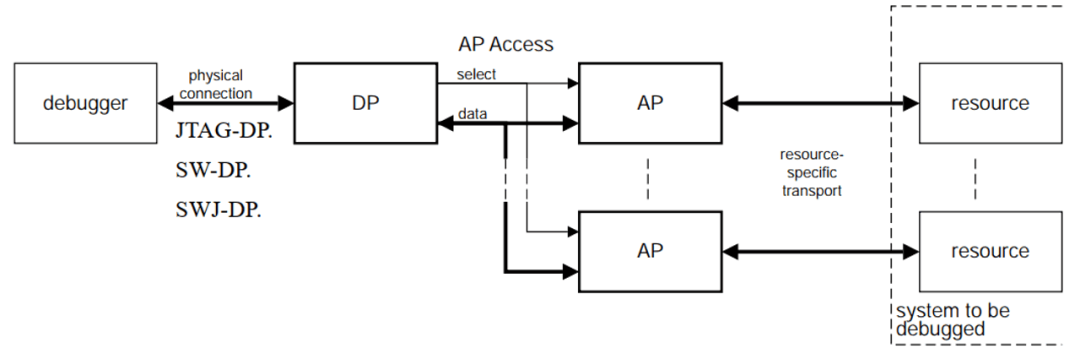 In summary:
In summary:
| Physical Interface | JTAG Interface? | SWD Interface? | Specification |
| JTAG-DP | Yes | ADI v5.0/v6.0 | |
| SW-DP | Yes | ADI v5.0/v6.0Serial Wire (Serial Interface) | |
| SWJ-DP | Yes | Yes | ADI v6.0Serial Wire/JTAG (Compatible with both Serial and JTAG interfaces) |
Why are there these differences? See the following PIN definitions (ADI v6.0):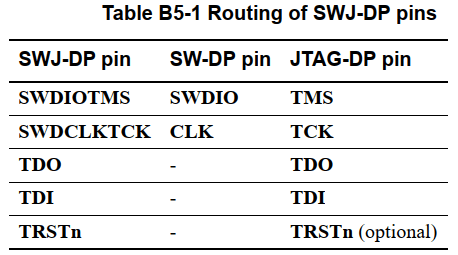 Thus, we see that SW-DP has only two PINs, while SWJ-DP has the same PINs as JTAG, but supports both SW-DP and JTAG operating modes. The reduction in PINs is to save space.Now, let’s focus on SWD. So how does this protocol work?Since it uses two wires, it is similar to I2C, with one clock line and one data line. The bit stream of 11001001 on the data line follows a protocol, similar to sending a request first and then receiving a reply. This request-reply interaction model is sometimes easier to understand than the JTAG shift bit.See the timing diagram below:
Thus, we see that SW-DP has only two PINs, while SWJ-DP has the same PINs as JTAG, but supports both SW-DP and JTAG operating modes. The reduction in PINs is to save space.Now, let’s focus on SWD. So how does this protocol work?Since it uses two wires, it is similar to I2C, with one clock line and one data line. The bit stream of 11001001 on the data line follows a protocol, similar to sending a request first and then receiving a reply. This request-reply interaction model is sometimes easier to understand than the JTAG shift bit.See the timing diagram below: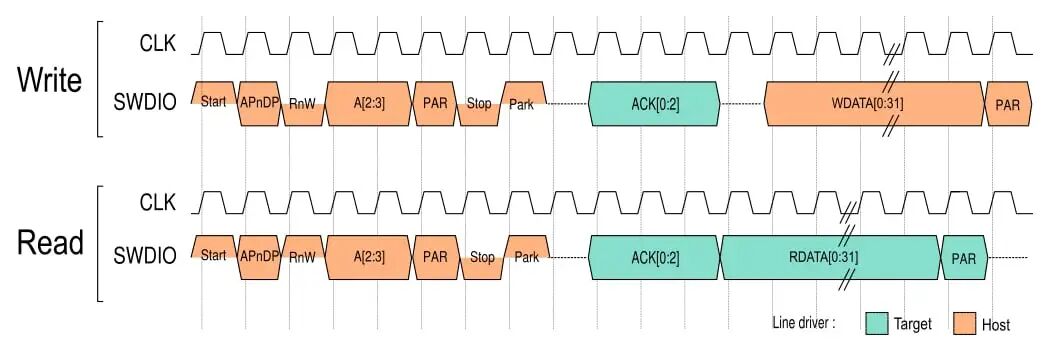 SWD communication is divided into three phases: packet request, acknowledgment, and data transfer. During the packet request phase, the host platform sends a request to the DP and must then issue an acknowledgment response. If the packet request is a data read or write request and there is a valid acknowledgment, the system enters the data transfer phase, during which data is written to or read from SWDIO. After data transfer, the host is responsible for initiating the packet request again or driving the SWD interface during idle cycles (setting the SWDIO clock to low). Parity checks are applied during the packet request and data transfer phases.Whether SWD is used depends on what the chip’s DAP interface is. Many modern chips (such as STM32, ARM Cortex series) support both JTAG and SWD.The image below shows a JTAG to SWD adapter, allowing JTAG hardware debugging boxes to be used with chips that have SWD interfaces:
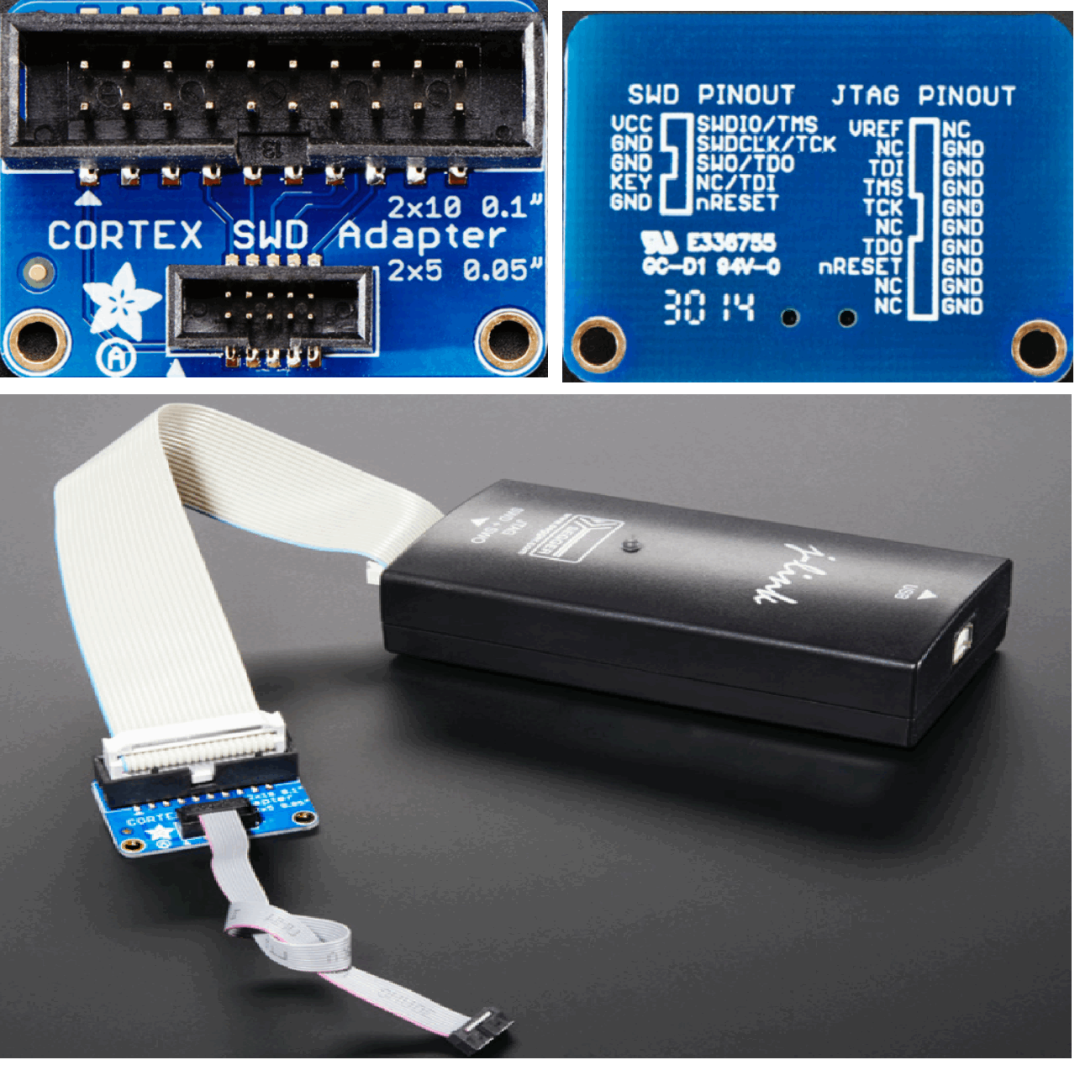
SWD communication is divided into three phases: packet request, acknowledgment, and data transfer. During the packet request phase, the host platform sends a request to the DP and must then issue an acknowledgment response. If the packet request is a data read or write request and there is a valid acknowledgment, the system enters the data transfer phase, during which data is written to or read from SWDIO. After data transfer, the host is responsible for initiating the packet request again or driving the SWD interface during idle cycles (setting the SWDIO clock to low). Parity checks are applied during the packet request and data transfer phases.Whether SWD is used depends on what the chip’s DAP interface is. Many modern chips (such as STM32, ARM Cortex series) support both JTAG and SWD.The image below shows a JTAG to SWD adapter, allowing JTAG hardware debugging boxes to be used with chips that have SWD interfaces: