1. What is CAN Bus?

2. Characteristics of CAN Bus
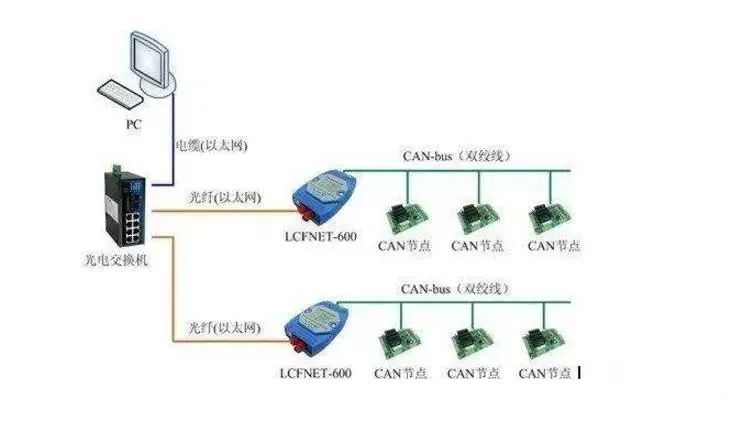
3. Principles of CAN Bus
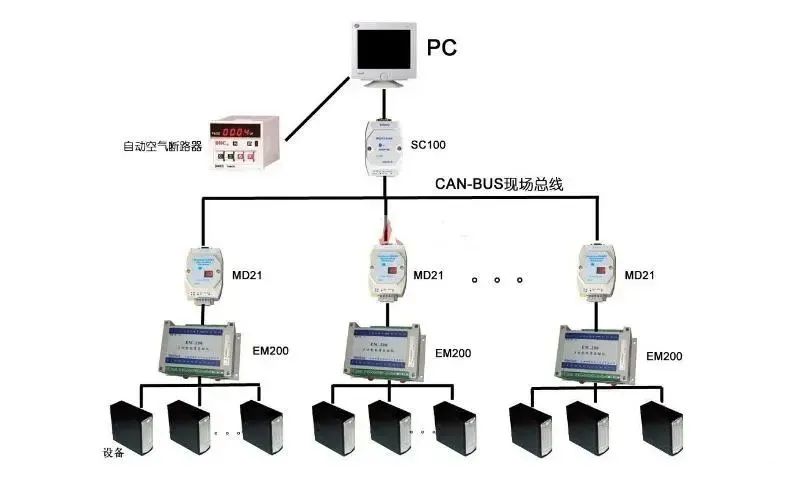
4. Applications of CAN Bus
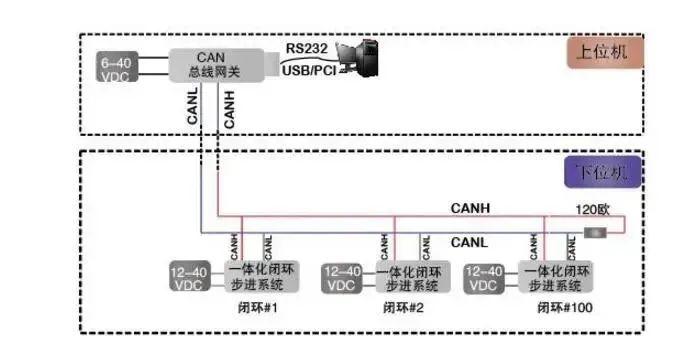
5. Is CAN Bus a Digital Signal or an Analog Signal?
6. Differences Between Analog Signals and Digital Signals
(Image source from the Internet)
Click the mini-program below to see more maintenance cases
