This article is part of a series that includes “What is PLC?” and “Working Modes, Execution Operations, and Principles of Mitsubishi PLC” (click the blue text to view previous articles). Together, these three articles explain the basic knowledge of PLC. This article mainly discusses the classification of PLC, expansion options, programming languages, and performance indicators. Below, these four aspects will be explained one by one.
Classified by the components of Mitsubishi PLC’s hardware structure. They are divided into integrated, modular, and hybrid types.
The integrated type has internal CPU module, memory, I/O modules, various interface modules, and battery modules; a common representative model of this PLC is FX3S. The maximum number of I/O points is 30, making it a small PLC.
Note: This type cannot add I/O and special function modules for expansion, only expansion boards and adapter extensions can be added.
The modular type consists of different modules such as CPU, I/O, and power supply. It is easy to assemble and maintain. A common representative model of this PLC is the Q series. Its I/O points can reach thousands, making it a medium to large PLC;
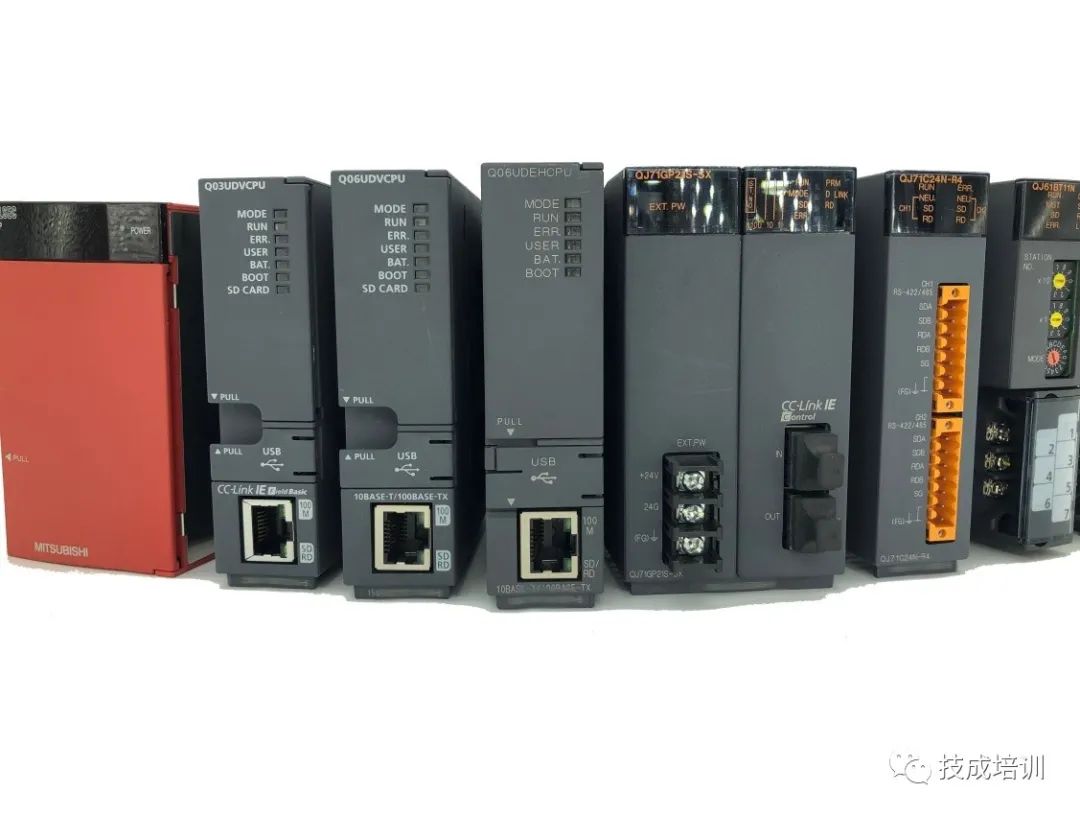

The hybrid type combines the characteristics of both integrated and modular types, offering flexible applications at a reasonable price; common representative models include FX3U and FX5U. Its maximum I/O points can reach 512, making it a medium to small PLC;

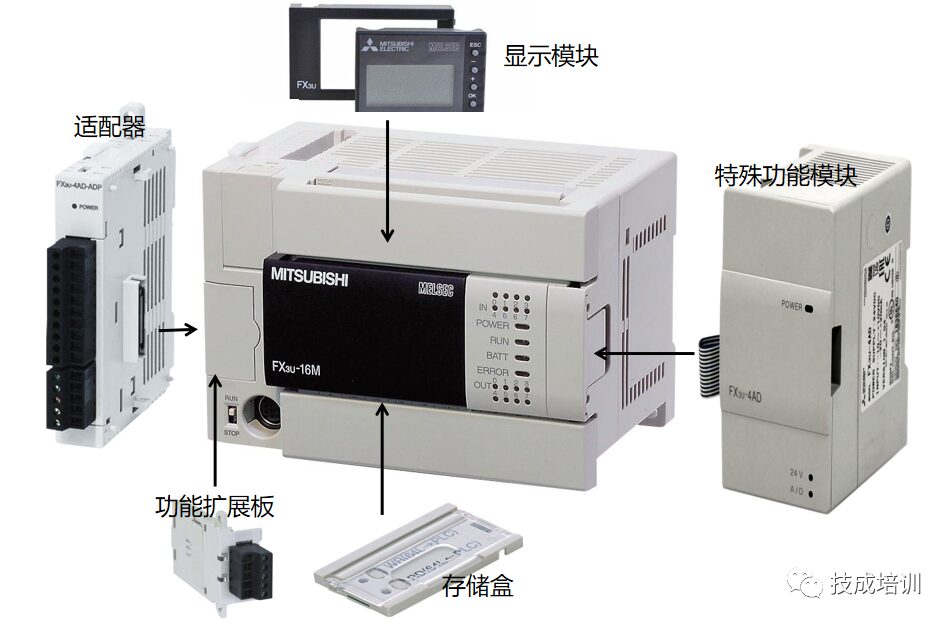
The hybrid type has characteristics of both integrated and modular types, and its expandable options include:
Function extension boards, expansion modules, expansion units, special function modules, special function units, special adapters.
Expansion modules: do not include power supply (FX2N-16EX-ES/UL);
Expansion units: include power supply, but no CPU (FX2N-32ET-ESS/UL);
Function extension boards: can only accommodate one 422, 485, USB, 8AV, etc. BD board (FX3U-485-BD);
Special function modules: installed on the right side of the PLC (FX3U-4AD, etc.);
Special function units: include power supply (FX2N-20GM);
Special adapters: installed on the left side of the PLC (FX3U-4ADP-MB);
Memory boxes: can be added when the PLC memory capacity is insufficient (FX3U-FLPOM-16, 16000 steps);
Display modules: installed directly above the PLC (FX3U-7DM);

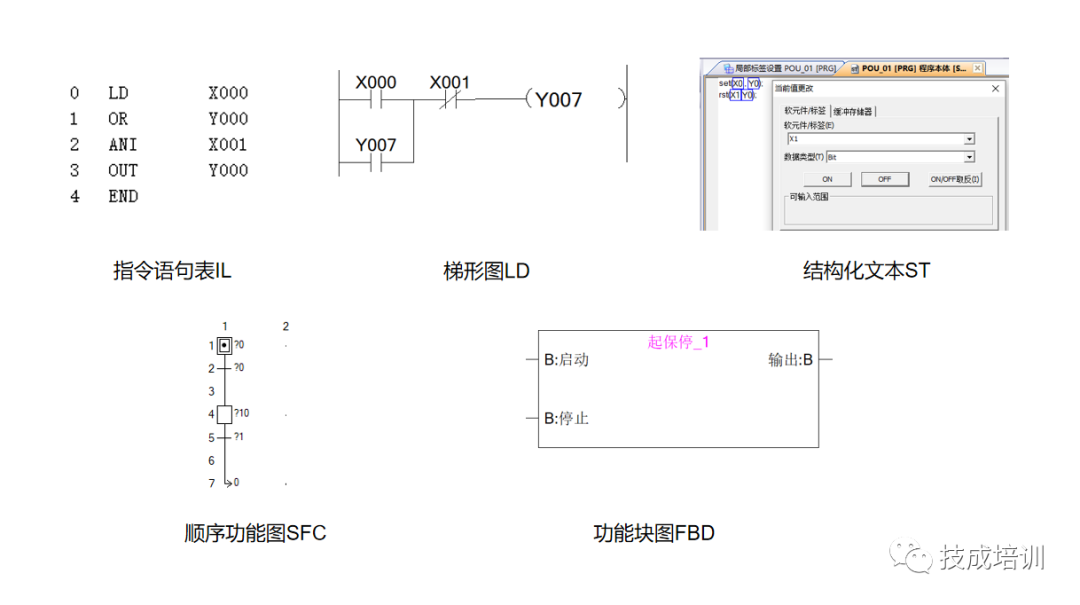
Mitsubishi PLC supports five types of programming languages:
Instruction List (IL): programmed using a handheld programmer, which has poor readability and is rarely used.
Ladder Diagram (LD): the primary language to learn, intuitive and practical;
Sequential Function Chart (SFC): also known as state transition diagram;
Function Block Diagram (FBD): particularly suitable for large scale and complex control systems, allows custom function blocks like start/stop function blocks;
Structured Text (ST): a high-level programming language with a syntax similar to C language; it has poor intuitiveness and operability; requires high proficiency from programmers;
What is the role of PLC performance indicators?
The PLC performance indicators can be found in the hardware manual and provide reference for selecting PLC for projects.
The following uses the FX3U hardware manual to showcase five important performance indicators.
The maximum number of I/O points that the PLC control system can connect to. This can be checked in the hardware manual (as shown in the image).
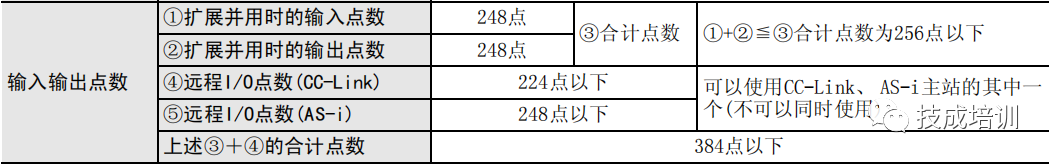
The memory capacity for storing application programs. Measured in K steps. Each instruction in the written program occupies a certain number of steps. Performance can be checked in the hardware manual (as shown in the image).
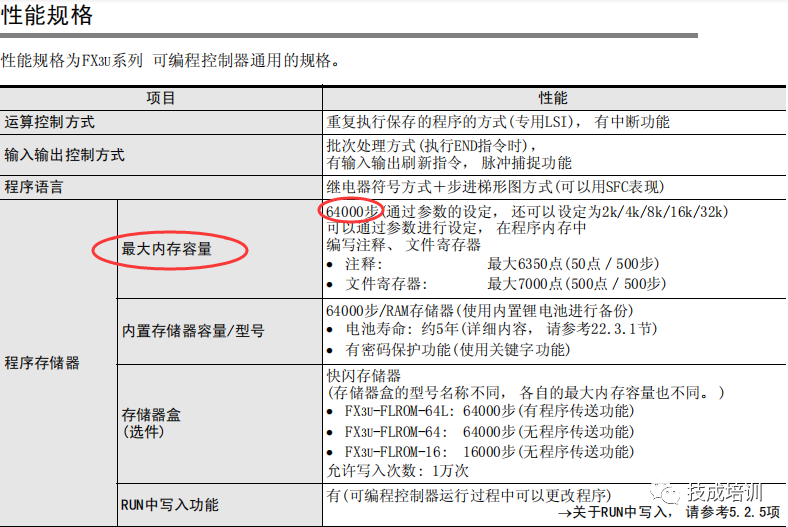
This performance parameter may not affect beginners in learning PLC programming. However, in certain projects with high precision requirements or a large number of program steps, faster scan processing speed becomes critical. This performance parameter must be considered. The PLC scan speed can be checked in the hardware manual (as shown in the image). This is the performance parameter found in the FX3U hardware manual. The basic instruction time is 0.065us/instruction; with a large number of program instructions, the cumulative time of basic instructions can be significant. In cases where high precision is required, faster scan cycles become essential, making this performance parameter particularly important.

The output types of Mitsubishi FX series PLC include relay output type MR, transistor output type MT, and thyristor output type MS.
Commonly used are MR and MT types. For beginners, it is recommended to choose the transistor output type. The transistor output type supports sending high-speed pulses, driving stepper and servo motors. In project control, if the output has a large load or the on/off frequency is less than 6 times per minute, it is recommended to use the relay output type. Its maximum load is 2A/point and has strong anti-interference capability.
Relay type MR performance parameters (as shown in the image).
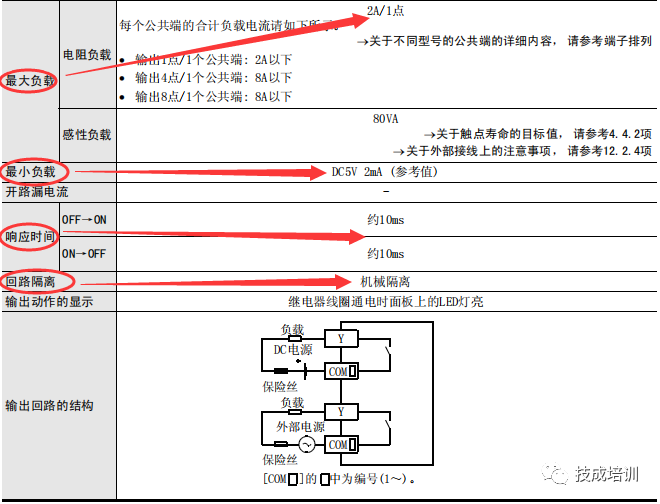
Transistor type MT performance parameters (as shown in the image) are divided into leakage type and source type.
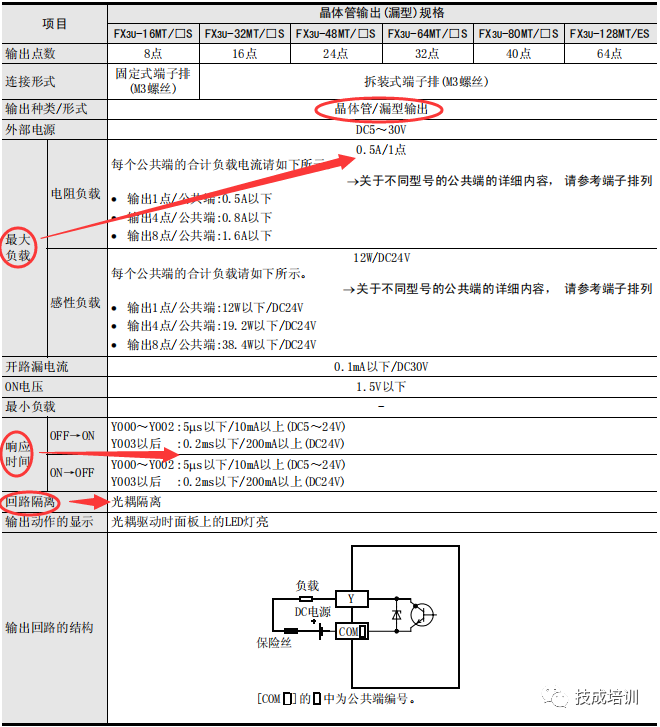
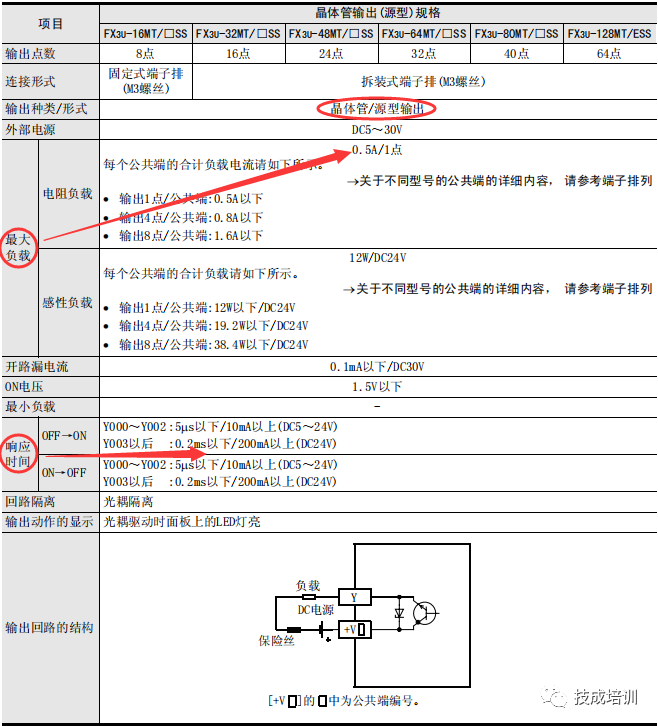
The more instructions a PLC supports, the more convenient it becomes for programmers during coding. For example, the FX2N PLC does not support certain positioning instructions like DRVI, DRVA, etc. Whereas the FX3U PLC supports CRC checks, which the FX2N PLC does not. The list of instructions supported by each PLC model can be found in the corresponding programming manual (as shown in the image).

The above four sections cover all the content of this article. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment for discussion. If this has helped you in learning PLC, please like and follow, thank you!
Source: Jicheng Training Network, Author: Zheng Xiaowei, unauthorized reproduction is prohibited~
We have prepared an essential electronic package for electrical engineers
Scan the QR code below
to receive the materials for free
↓↓↓

(Scan to receive for free)

Collect | 2024 Selected Industrial Control Technology Articles Summary, here comes the dry goods!
Previous Recommendations
A failed PLC engineer interview, was I too inexperienced?
Sharing valuable insights! New file creation, opening, archiving, and recovery in the博图库!
This electrician’s wiring is impressive, they must be a senior technician!
Switch cabinets too complex? Let me help you understand switch cabinets in five minutes!
Explanation of Mitsubishi FX PLC scan cycle, even beginners can understand!
Essential 64 Siemens eBooks for automation learning | Free to receive
[Case Study] S7-1200 PLC Analog Control of Frequency Converter, all new engineers should take a look!