The Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 processors utilize a 32-bit architecture, with internal registers in the register set, a 32-bit data path, and bus interfaces, employing Thumb-2 technology that supports both 16-bit and 32-bit instructions. They feature the following characteristics:
-
Three-stage pipeline design
-
Harvard bus architecture (I-BUS, D-BUS)
-
32-bit addressing
-
AMBA bus interface
-
NVIC interrupt controller, supporting up to 240 interrupt requests and 8-256 interrupt priorities
-
Support for various OS features, such as tick timers and shadow stack pointers
-
Sleep mode and low power consumption
-
MPU
-
Bit-field features (support for bit data access in two specific memory regions)
Instructions:
-
General data processing: + – x ÷
-
Memory access instructions
-
Bit-field processing instructions
-
Multiply-accumulate and saturation instructions
-
Instructions for jumps, conditional jumps, and function calls
-
System control instructions that support OS
-
Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD)
-
Floating-point instructions
ARM primarily provides:
-
Design of units such as logic gates and memory
-
Peripherals and AMBA basic components (Cortex-M System Design Kit CMSDK, ARM Corelink)
-
Other debug components for connecting debugging systems in multiprocessor designs (ARM Coresight IP)
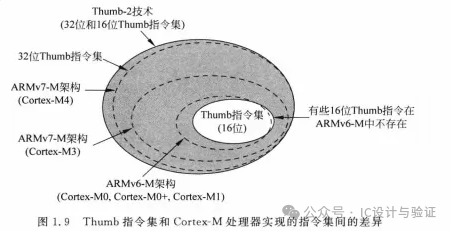
Thumb ISA Architecture
Since the processor supports both 16-bit and 32-bit instructions in the Thumb-2 instruction set, there is no need to switch between Thumb state (16-bit instructions) and ARM state (32-bit instructions). According to the Thumb-2 encoding, if the [15:11] bits are encoded as 0b11101, 0b11110, or 0b11111, then it is a 32-bit instruction.