Health Monitoring of Smartwatches

Introduction
As people pay more attention to healthy living, smart health monitoring systems have gradually gained widespread attention and application. Smartwatches are widely used to monitor various health indicators in daily life, but what are their principles?






Heart Rate Measurement





Heart
Rate
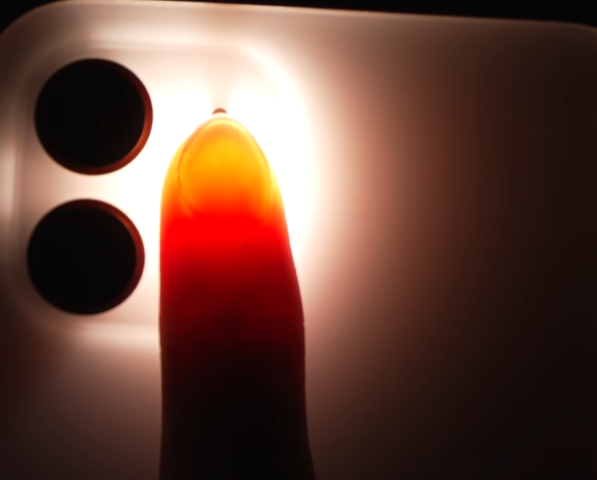
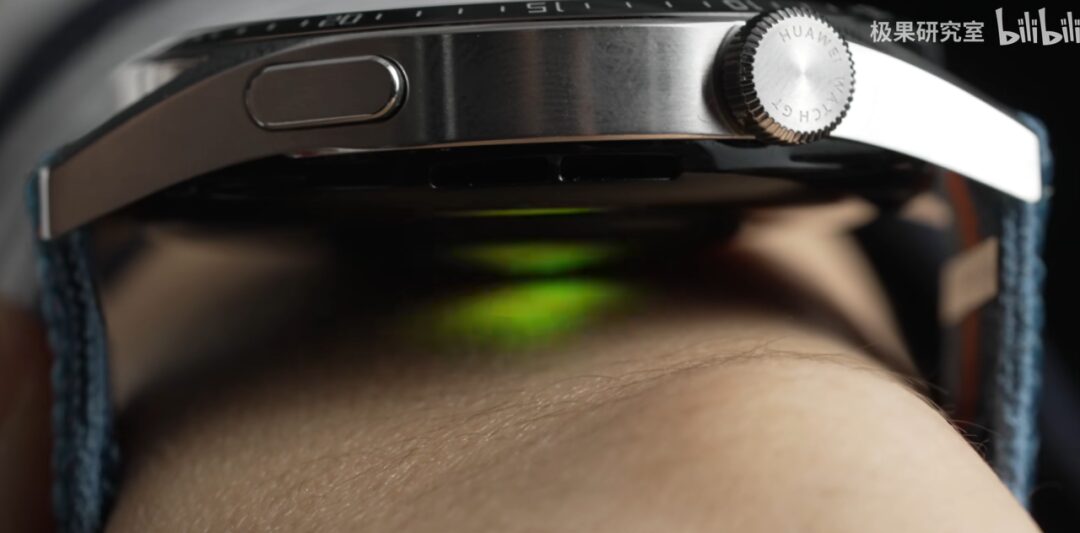





Heart Rate
The heart’s beating causes the blood vessels in the wrist to contract, measuring the heart rate by monitoring the frequency of light and dark changes. However, the light used by the watch is mostly green light, primarily due to the power consumption constraints of the watch; the LED used for lighting is best energy-efficient. However, the skin depth that can be penetrated on the wrist is relatively shallow, and the blood vessels here are quite thin, with the blood volume changing with each heartbeat being quite small. Therefore, the wavelength of this LED should be in the range where the human body has the highest absorption rate, so even minor activities of the skin can cause significant changes in the light signal. Hence, the lights used in wristbands for measuring heart rate are green. Some watches consider the differences in users’ skin tones and textures and may use both red and green colors for measurement.


Blood Oxygen Concentration


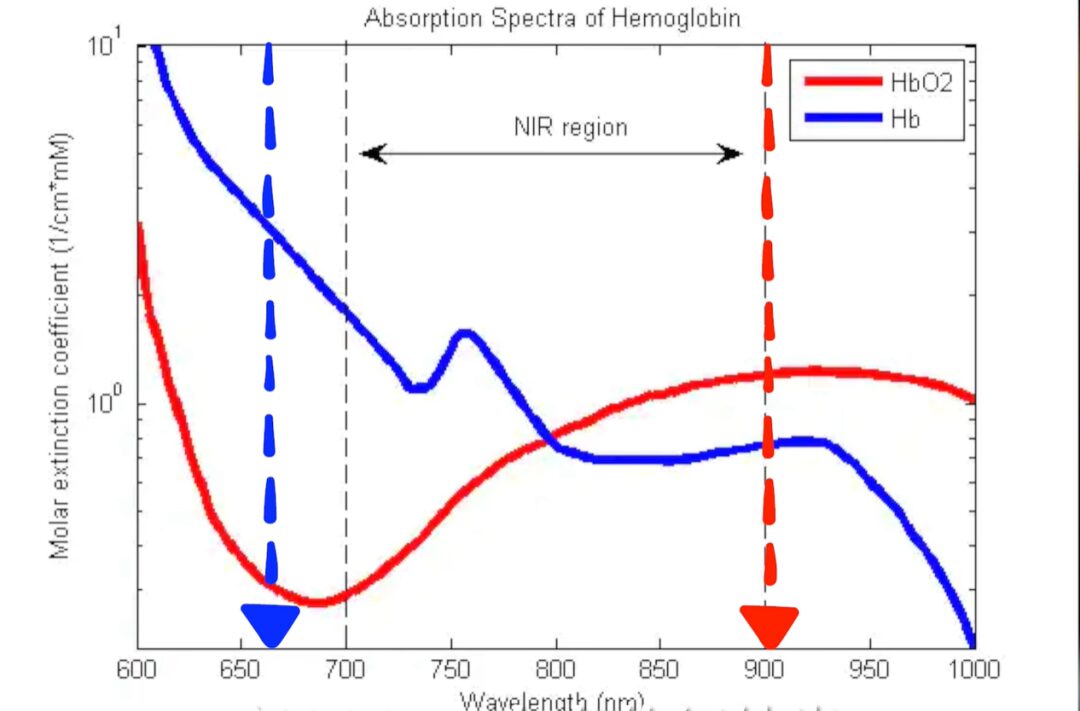
The Absorption Rates of Oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) and Deoxyhemoglobin (Hb) to Red and Infrared Light

Method
The direct measurement of blood oxygen saturation is done by collecting blood samples from the arteries, using a blood gas analyzer to obtain results. Currently, the principle behind blood oxygen monitoring in smartwatches is based on the different absorption rates of oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) and deoxyhemoglobin (Hb) to red and infrared light. The watch shines red and infrared light onto the skin, compares the results returned from both, and finally calculates the blood oxygen level through algorithms. If you wear an Apple Watch, you will notice the wrist glowing red when the lights are off and the body is still, indicating that blood oxygen detection is in progress.

Electrocardiogram


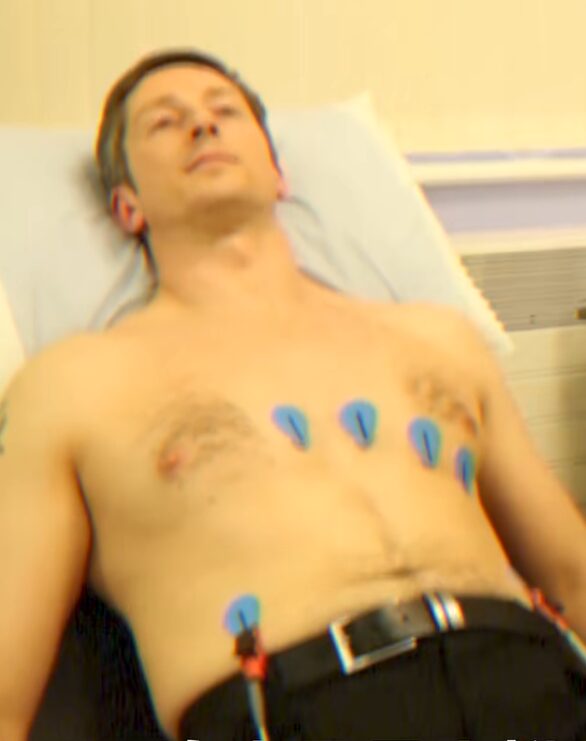
Electrocardiogram
Smartwatches are equipped with built-in electrocardiogram sensors. This sensor is an electrode capable of measuring electrocardiogram signals. This electrode connects through the skin to the user’s heart, recording the electrical signals during heartbeats and transmitting these signals to the smartwatch’s processor.
Electrocardiogram

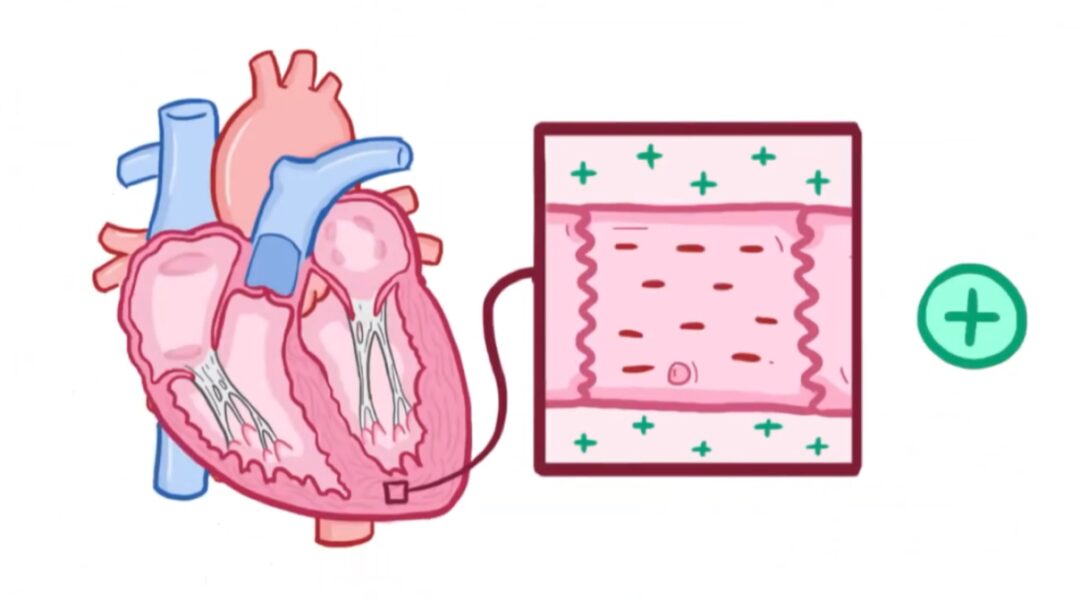

Electrocardiogram
Then, the smartwatch’s processor needs to process the signals collected by the sensor. The processing usually includes digital signal filtering, noise reduction, amplification, and sampling steps. These processes help the smartwatch obtain more accurate and reliable electrocardiogram signals. To achieve the collection and processing of electrocardiogram monitoring information in smartwatches, PPG technology is used, which stands for (photoplethysmography) that uses an LED light source and a detector to measure the attenuated light reflected and absorbed by blood vessels and tissues, recording the pulsation state of the vessels and measuring the pulse wave.

e
n
d