🎈✨Introduction: 😎Dear friends, as network engineers, do you often feel confused by various protocols? Today, I am here to provide you with a super detailed list of 35 commonly used protocols for network engineers, making it easy for you to master them and no longer feel lost! 👏
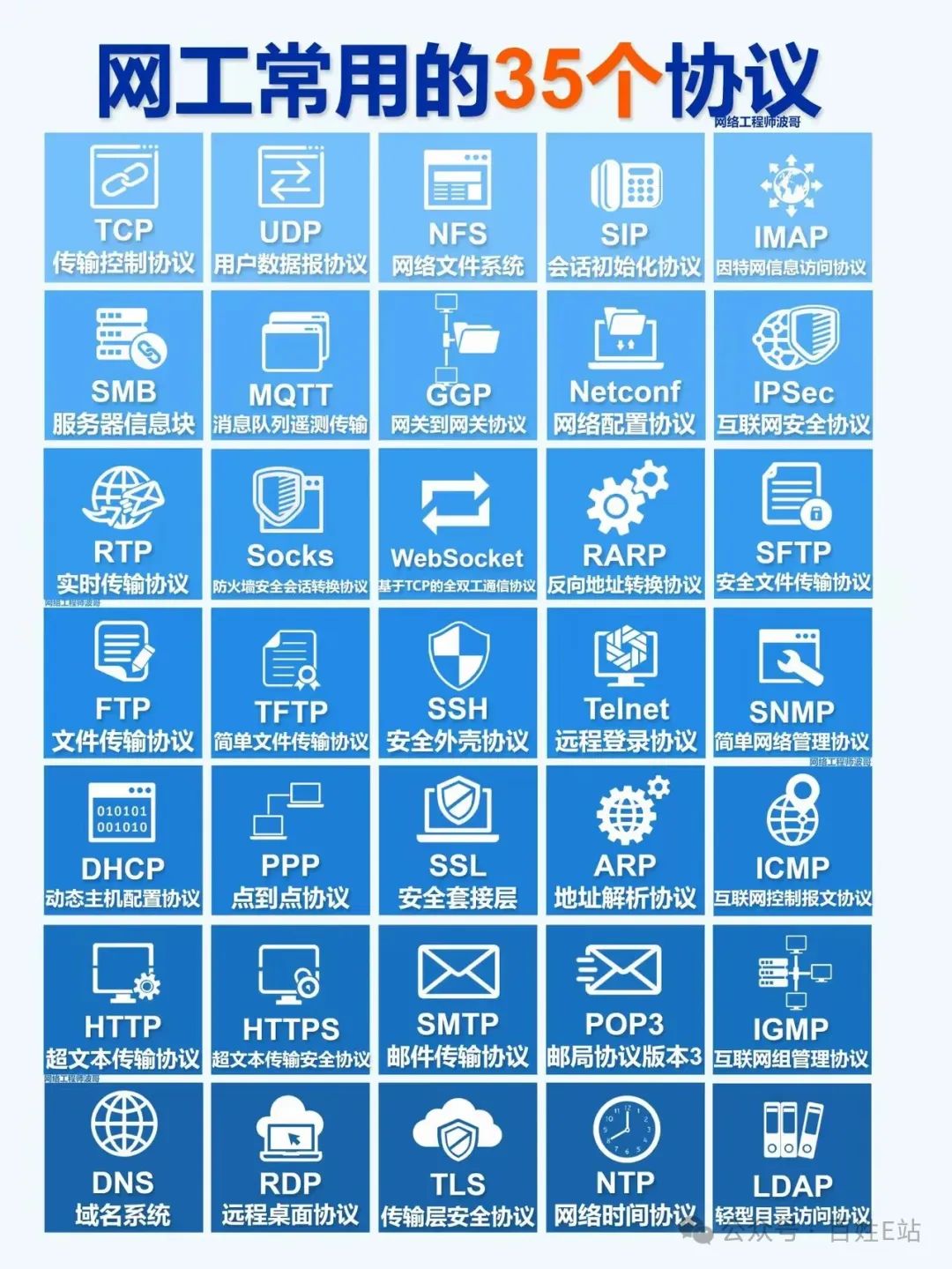
Body:
1. – TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Like a delivery person, it is responsible for reliably delivering data from one place to another. 2. – UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Like an impatient courier, it delivers data quickly but may risk packet loss. 3. – NFS (Network File System): Allows you to share files between different computers, like placing files in a large warehouse for everyone to access at any time. 4. – SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): Used to establish and manage multimedia sessions, such as phone calls and video conferences. 5. – IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Helps you manage and view emails in your mailbox, making your email life more organized. 6. – SMB (Server Message Block): Commonly used for sharing files and printers in a local area network. 7. – MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): Suitable for data transmission between IoT devices, compact and flexible. 8. – GGP (Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol): Used for routing and data forwarding on the Internet. 9. – Netconf (Network Configuration Protocol): Used for configuration management of network devices, allowing you to easily set various network configurations. 10. – IPSec (Internet Protocol Security): Like a bodyguard for the network, providing security for data transmission. 11. – RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol): Specifically used for transmitting real-time multimedia data, such as video live streaming and audio calls. 12. – Socks (Socket Secure): Helps you bypass firewall restrictions to access restricted network resources. 13. – WebSocket (Full-duplex Communication Protocol Based on TCP): Enables bidirectional real-time communication between browsers and servers, just like chatting with friends at any time. 14. – RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol): Used to convert hardware addresses to IP addresses, allowing network devices to communicate with each other. 15. – SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol): Provides a more secure file transfer service based on the SSH protocol. 16. – FTP (File Transfer Protocol): A traditional file transfer protocol, although less secure than SFTP, it is still widely used. 17. – TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol): A very simple file transfer protocol, commonly used for device initialization and configuration. 18. – SSH (Secure Shell Protocol): Can establish a secure channel over an insecure network for remote login and file transfer operations. 19. – Telnet (Remote Login Protocol): Allows you to remotely log into other computers over the network, as if you were sitting in front of that computer. 20. – SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): Used for managing and monitoring network devices, allowing you to easily understand the network’s operational status. 21. – DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Automatically assigns IP addresses, subnet masks, gateways, and other information to devices in the network, very convenient. 22. – PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol): Commonly used for dial-up Internet access and establishing wide area network connections. 23. – SSL (Secure Sockets Layer): Provides encryption and authentication services for network communication, ensuring secure data transmission. 24. – ARP (Address Resolution Protocol): Converts IP addresses to hardware addresses, allowing network devices to find each other. 25. – ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): Used for network diagnostics and troubleshooting, like a doctor that helps you identify problems in the network. 26. – HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Used for transmitting hypertext data between web browsers and web servers, such as web pages. 27. – HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): Adds encryption and authentication features to HTTP, making web page transmission more secure. 28. – SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Used for sending and receiving emails, just like postal service letter delivery. 29. – POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): Used to download emails from the mail server to the local client. 30. – IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol): Used to manage multicast groups, allowing efficient transmission of multicast data over the network. 31. – DNS (Domain Name System): Converts domain names to IP addresses, allowing you to easily access websites through domain names. 32. – RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol): Allows you to remotely access the desktop of another computer over the network, operating as if you were sitting in front of that computer. 33. – TLS (Transport Layer Security): Similar to SSL, used to provide encryption and authentication services for network communication. 34. – NTP (Network Time Protocol): Used to synchronize the time of various devices in the network, ensuring time accuracy. 35. – LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol): Used to store and manage information about users, groups, devices, etc., facilitating network management and access.
Notes: – When learning and using protocols, pay attention to security issues to avoid data leaks and network attacks. – Different protocols are suitable for different scenarios, so choose the appropriate protocol based on actual needs. – When configuring network devices, carefully read the device documentation and instructions to ensure correct configuration.
Summary: 😘Dear friends, the 35 commonly used protocols for network engineers introduced today are just the tip of the iceberg; there are many other protocols waiting for you to explore and learn. I hope everyone can gain a deeper understanding of protocols through today’s learning, laying a solid foundation for future work and study. 💪
Interactive Guidance: 🎉Dear friends, if you find this article helpful, please like, bookmark, and follow me! 🤗 If you have any other questions or suggestions, feel free to leave a comment! 😘