Click on the “Business Card” above to follow our public account
You can obtain programming materials from the menu bar
| Hello, I am Coder-Wen Xiaobai,a post-95 Java backend developer. |
1. Introduction
In the process of developing business systems, we inevitably use databases. During application development, database connection information is often configured in plain text in the <span>yaml</span> configuration file, which poses a risk of password leakage. So, is there a way to avoid this? The solution is to encrypt the database password during configuration and then decrypt it when reading, thus preventing the leakage of sensitive information.
2. SM4 Algorithm
There are many popular encryption algorithms on the market, and this time we will introduce the domestically produced encryption algorithm SM4.
The SM4 encryption algorithm is a block cipher encryption algorithm. For detailed information, please refer to Baidu Encyclopedia:
SM4: https://baike.baidu.com/item/SM4.0?fromModule=lemma_search-box

3. Database Configuration Information Encryption and Decryption
1. Import Relevant Encryption and Decryption Dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bouncycastle</groupId>
<artifactId>bcprov-jdk15to18</artifactId>
<version>1.76</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.25</version>
</dependency>2. Write the Encryption and Decryption Utility Class
import cn.hutool.crypto.SmUtil;
import cn.hutool.crypto.symmetric.SM4;
public class SM4Utils {
/**
* SM4 is a symmetric encryption algorithm, requiring a key for encryption and decryption.
* <p>
* System.out.println(Arrays.toString("@Jhx2024#$%^&*!+".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
* Note that the length of the string key must be 16 characters.
*/
private static final byte[] keys = new byte[]{64, 74, 104, 120, 50, 48, 50, 52, 35, 36, 37, 94, 38, 42, 33, 43};
/**
* Create an SM4 encryption and decryption object.
*/
private static final SM4 sm4 = SmUtil.sm4(keys);
/**
* Set an identifier to indicate that strings starting with @SM4@- are encrypted and need to be decrypted.
*/
public static final String SM4_PREFIX = "@SM4@-";
/**
* Encrypt a string.
*
* @param value
* @return
*/
public static String encryptStr(String value) {
// Add a prefix to the encrypted string for easy identification.
return SM4_PREFIX + sm4.encryptBase64(value);
}
/**
* Decrypt a string.
*
* @param encryptValue
* @return
*/
public static String decryptStr(String encryptValue) {
// When decrypting, remove the encryption identifier.
return encryptValue.startsWith(SM4_PREFIX) ? sm4.decryptStr(encryptValue.substring(SM4_PREFIX.length())) : encryptValue;
}
}Note: The length of the string key must be 16 characters, otherwise an error will occur:
Exception in thread "main" cn.hutool.crypto.CryptoException: InvalidKeyException: SM4 requires a 128 bit key
at cn.hutool.crypto.symmetric.SymmetricCrypto.encrypt(SymmetricCrypto.java:277)
at cn.hutool.crypto.symmetric.SymmetricEncryptor.encrypt(SymmetricEncryptor.java:139)
at cn.hutool.crypto.symmetric.SymmetricEncryptor.encryptBase64(SymmetricEncryptor.java:159)
at com.learn.util.SM4Utils.encryptStr(SM4Utils.java:34)
at com.learn.SnowFlakeDemoApplication.main(SnowFlakeDemoApplication.java:17)
Caused by: java.security.InvalidKeyException: SM4 requires a 128 bit key
at org.bouncycastle.jcajce.provider.symmetric.util.BaseBlockCipher.engineInit(Unknown Source)
at javax.crypto.Cipher.init(Cipher.java:1246)
at javax.crypto.Cipher.init(Cipher.java:1186)
at cn.hutool.crypto.CipherWrapper.initMode(CipherWrapper.java:116)
at cn.hutool.crypto.symmetric.SymmetricCrypto.initMode(SymmetricCrypto.java:415)
at cn.hutool.crypto.symmetric.SymmetricCrypto.encrypt(SymmetricCrypto.java:274)
... 4 more3. Testing the SM4 Utility Class
- • Test Code
String str = "hello, world"; System.out.println("Original string: " + str); str = SM4Utils.encryptStr(str); System.out.println("Encrypted string with default SM4 key: " + str); str = SM4Utils.decryptStr(str); System.out.println("Decrypted string with default SM4 key: " + str);
• Test Result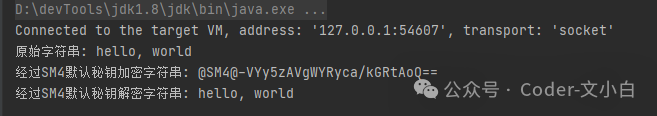
4. Encrypting and Decrypting Database Configuration Information
1. Modify Database Configuration Information
Encrypt the database configuration information,<span>the encrypted information needs to be generated using our custom SM4Utils utility class</span>:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/uid
username: '@SM4@-tWyNqklSTiV5W3gN4dTQ2g=='
password: '@SM4@-tWyNqklSTiV5W3gN4dTQ2g=='At this point, when starting the project, there will definitely be an error when loading the database information:
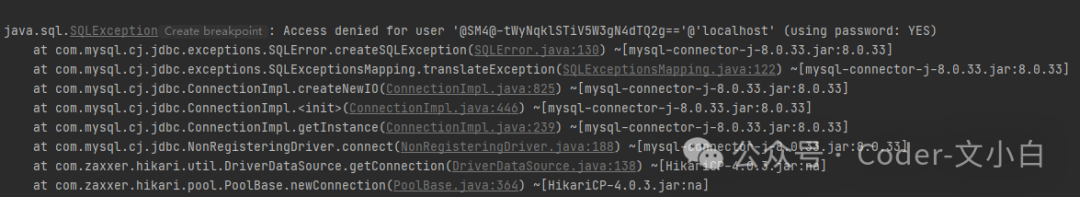
2. Custom Data Source Decryption
For the encrypted database configuration information, custom decryption is required, so a custom DataSource object needs to be created:
import com.learn.util.SM4Utils;
import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource;
public class MyHikariDataSource extends HikariDataSource {
@Override
public String getUsername() {
// Decrypt the username.
return SM4Utils.decryptStr(super.getUsername());
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
// Decrypt the password.
return SM4Utils.decryptStr(super.getPassword());
}
}3. Modify Database Configuration
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/uid
username: '@SM4@-tWyNqklSTiV5W3gN4dTQ2g==' # Encrypted using SM4Utils.encryptStr method
password: '@SM4@-tWyNqklSTiV5W3gN4dTQ2g==' # Encrypted using SM4Utils.encryptStr method
type: com.learn.db.MyHikariDataSource # Specify the custom DataSource classNote: I am using the default HikariDataSource data source of Spring Boot, so the custom DataSource inherits from the HikariDataSource class. If using another data source, such as Druid, simply inherit from the Druid DataSource class.
4. Start Testing

Start without errors, business is normal, transformation is complete.
4. Extension – Support for Encrypting and Decrypting All Configuration Properties
From the above approach to database encryption and decryption, it can be seen that<span>this logic also applies to reading all properties in Spring Boot</span>.
1. Import jasypt-spring-boot-starter Dependency
Jasypt provides encryption support for property sources in Spring Boot applications.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ulisesbocchio</groupId>
<artifactId>jasypt-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>2. Implement Custom Encryptable Property Detector
package com.learn.pro;
import com.learn.util.SM4Utils;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyDetector;
public class MyEncryptablePropertyDetector implements EncryptablePropertyDetector {
/**
* Determine if the string needs to be decrypted.
*
* @param s
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isEncrypted(String s) {
if (s != null) {
return s.startsWith(SM4Utils.SM4_PREFIX); // Check for SM4 encryption identifier
}
return false;
}
/**
* Get the string after removing the encryption identifier.
*
* @param s
* @return
*/
@Override
public String unwrapEncryptedValue(String s) {
return s.substring(SM4Utils.SM4_PREFIX.length());
}
}3. Custom Password Resolver
package com.learn.pro;
import com.learn.util.SM4Utils;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyResolver;
public class MyEncryptablePropertyResolver implements EncryptablePropertyResolver {
private MyEncryptablePropertyDetector encryptablePropertyDetector;
public MyEncryptablePropertyResolver(MyEncryptablePropertyDetector encryptablePropertyDetector) {
this.encryptablePropertyDetector = encryptablePropertyDetector;
}
@Override
public String resolvePropertyValue(String s) {
/**
* Determine if decryption is needed, if so return the decrypted value.
*/
if (encryptablePropertyDetector.isEncrypted(s)) {
return SM4Utils.decryptStr(s);
}
return s;
}
}4. Activate Custom Assembly Class
package com.learn.pro;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyResolver;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyJasyptConfig {
@Bean
public MyEncryptablePropertyDetector encryptablePropertyDetector() {
return new MyEncryptablePropertyDetector();
}
@Bean
public EncryptablePropertyResolver encryptablePropertyResolver() {
return new MyEncryptablePropertyResolver(encryptablePropertyDetector());
}
}5. Testing
Here we define a property for encryption testing,<span>the encrypted information needs to be generated using our custom SM4Utils utility class</span>:
sm4:
test: "@SM4@-1LnppEtMiTgGtTJ4shhYMg==" # SM4Utils.encryptStr("hello, SM4!")Test Code:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
@Value("${sm4.test}")
private String sm4Test;
private static DemoApplication demoApplication;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
demoApplication = this;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("\nGetting property sm4.test = " + demoApplication.sm4Test);
}
}Test Result:
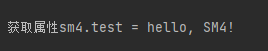
Thus, a general encryption and default decryption function for Spring Boot configuration files is completed.