
Introduction: With the widespread adoption of AI technology, enterprises face a critical question: Where should AI processing take place—on edge devices or in the cloud? This article will delve into the main differences between Edge AI and Cloud AI, their respective advantages, and how enterprises can make choices in different scenarios, even combining both for optimal results.
Edge AI vs Cloud AI: Which is Better for Enterprise Workloads?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a core force driving digital transformation in enterprises, widely applied in various fields from customer service to predictive maintenance. As AI technology becomes more prevalent, enterprises face a critical question: Where should AI processing take place—on edge devices or in the cloud? This article will explore the main differences between Edge AI and Cloud AI, their respective advantages, and how enterprises can make choices in different scenarios, even combining both for optimal results.

Edge AI: Enabling Intelligent Decision-Making Locally
Edge AI is a technology that deploys AI algorithms directly on local hardware or edge devices, such as IoT sensors, mobile devices, or local servers. Unlike traditional cloud AI, Edge AI does not require data to be transmitted to the cloud for processing; instead, it analyzes and makes decisions directly at the source of data generation. Its main features include:
Real-time processing capability: Edge AI can process data at the moment of generation, providing immediate feedback and decision support. This is crucial for applications that require rapid responses, such as obstacle avoidance decisions in autonomous vehicles or real-time control of factory robots.
Low latency: Since data processing is done locally, it avoids the delays associated with network transmission, allowing Edge AI to achieve minimal latency. This is significantly advantageous for time-sensitive applications, such as financial transaction monitoring or real-time monitoring of medical devices.
Offline operation capability: Edge AI can operate in environments with limited or no network connectivity. This is particularly suitable for remote areas or applications with unstable networks, such as equipment monitoring on offshore oil platforms or environmental monitoring in remote mountainous regions.
Real-world Application Cases
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: In smart factories, Edge AI supports predictive maintenance by analyzing machine behavior data in real-time. It can quickly identify abnormal states of equipment, issue early warnings, and schedule maintenance, thus avoiding significant losses due to equipment downtime. For example, by installing sensors on production equipment and deploying Edge AI algorithms, parameters such as vibration and temperature can be monitored in real-time, triggering alerts and providing maintenance suggestions upon detecting anomalies.
Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous driving systems have extremely high requirements for latency; even a slight delay can lead to serious safety issues. Edge AI can process sensor data, such as camera images and radar signals, locally in the vehicle, making quick decisions like automatic braking and obstacle avoidance. This enables autonomous vehicles to navigate safely in complex traffic environments without relying on real-time responses from the cloud.
Retail and Monitoring: Smart cameras supporting Edge AI can analyze video streams in real-time, immediately detecting theft, changes in foot traffic, or stock levels. For instance, in shopping malls, smart cameras can monitor customer shopping behavior in real-time, automatically identifying unusual activities and promptly notifying security personnel; simultaneously, they can count the number of items on shelves in real-time, alerting for restocking, thus improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Cloud AI: Powerful Computing and Data Processing Capabilities
Cloud AI is a technology that delivers AI processing and models through cloud infrastructure. Enterprises send data to centralized cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, where powerful computing resources analyze and respond to the data. The main features of Cloud AI include:
Centralized data storage: Cloud AI can centralize data from different sources in the cloud, facilitating unified management and analysis. This is very convenient for enterprises that need to process massive amounts of data, such as financial transaction data or user behavior data from e-commerce websites.
Scalable processing capabilities: Cloud platforms provide powerful computing resources that can be flexibly scaled according to the actual needs of enterprises. Whether processing large-scale data analysis tasks or training complex AI models, Cloud AI can provide sufficient computational support.
Suitable for batch processing and big data analysis: Cloud AI is particularly well-suited for tasks that require substantial computational resources and time, such as batch processing analysis of massive datasets or training large neural networks. It can efficiently handle large-scale datasets, providing deep insights and decision support for enterprises.
Real-world Application Cases
Enterprise Analytics: Cloud AI has significant advantages in enterprise data analysis. For example, CRM platforms can leverage Cloud AI to analyze vast amounts of customer data, predict customer behavior, assess customer value, and formulate precise marketing strategies. E-commerce websites can use Cloud AI to analyze user browsing and purchasing behavior, optimizing product recommendation algorithms to improve user conversion rates and sales.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Applications such as virtual assistants, translation tools, and AI-driven customer service robots rely on complex language models like GPT. These models typically require substantial computational resources to operate, and Cloud AI provides an ideal environment for running them. For instance, intelligent customer service robots can utilize Cloud AI’s natural language processing capabilities to understand user questions in real-time and provide accurate answers, enhancing customer service efficiency and quality.
AI Model Training: Training large neural networks requires significant computational resources and data support. Cloud AI offers powerful GPU clusters and vast data storage, enabling AI developers to efficiently train complex AI models. For example, training image recognition models and speech recognition models typically occurs on cloud platforms to fully leverage their computational power.
Comparing Edge AI and Cloud AI
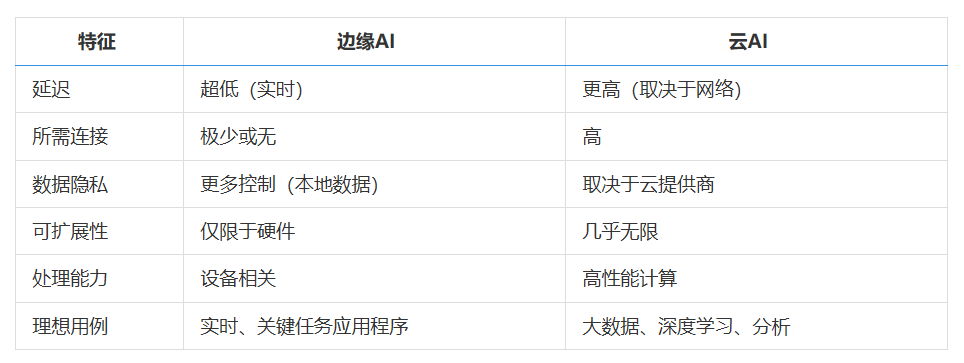
Security and Compliance: Key Considerations for Data Privacy
1. Security Advantages of Edge AI
Edge AI has significant advantages in data privacy and security, especially in highly regulated industries such as healthcare and finance. Since data is processed and stored locally, there is no need to transmit it to the cloud, greatly reducing the risk of data breaches. For example, in healthcare, sensitive patient data can be processed and analyzed on local devices, with only anonymized and encrypted data transmitted to the cloud for further analysis and storage, ensuring patient data privacy and security.
2. Compliance Challenges of Cloud AI
Cloud AI must strictly adhere to various data protection regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). These regulations impose strict requirements on data collection, storage, transmission, and processing, especially when it comes to cross-border transmission of personal data. Enterprises must ensure that their Cloud AI solutions comply with relevant regulations, or they may face hefty fines and legal risks. For instance, financial enterprises using Cloud AI for data analysis must ensure that customer personal information is adequately protected during transmission and storage, in compliance with relevant financial regulatory requirements.
Hybrid AI: Merging the Advantages of Edge and Cloud
1. The Rise of Hybrid Architectures
As enterprises’ demands for AI technology become increasingly diverse, more and more enterprises are adopting hybrid AI architectures. This architecture combines the advantages of Edge AI and Cloud AI, allowing for urgent data processing on edge devices for quick decision-making while synchronizing with the cloud for long-term storage and model updates. For example, drones can use Edge AI to process captured image data in real-time to quickly identify targets or anomalies, while periodically sending this data to the cloud for training improved AI models and conducting deeper analysis.
2. Advantages of Hybrid Architectures
Hybrid AI architectures provide enterprises with greater flexibility, allowing them to balance latency, cost, and scalability across different application scenarios. For instance, in industrial production, Edge AI can monitor the operational status of production equipment in real-time and quickly respond to anomalies, while Cloud AI can analyze historical data to optimize production processes and predictive maintenance strategies. Through this hybrid architecture, enterprises can fully leverage the low-latency advantages of Edge AI and the powerful computing capabilities of Cloud AI without compromising performance, achieving optimal AI application results.
Cost Considerations: Balancing Initial Investment and Long-Term Expenses
1. Cost Characteristics of Edge AI
The initial hardware investment for Edge AI is relatively high, requiring the deployment of high-performance computing hardware and storage devices on local devices. However, since data processing is done locally, it reduces the demand for network bandwidth, resulting in lower ongoing bandwidth costs. Additionally, the operational costs of Edge AI are relatively stable, primarily depending on the maintenance and upgrade costs of local devices. For applications that require high real-time performance and data privacy, despite the higher initial investment, Edge AI can save enterprises significant network bandwidth and data transmission costs in the long run.
2. Cost Characteristics of Cloud AI
Cloud AI operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing enterprises to pay based on actual usage. This model offers high flexibility, as enterprises do not need to make substantial upfront hardware investments and can adjust resource usage according to business needs. However, if enterprises need to process large amounts of data or frequently call AI services, the costs of Cloud AI can become quite expensive. Additionally, the operational costs of Cloud AI include data storage fees, network transmission fees, and maintenance fees from cloud service providers. Therefore, enterprises need to carefully evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) based on data volume, processing needs, and uptime requirements when choosing Cloud AI.
Choosing Between Edge AI and Cloud AI: A Guide for Enterprises
When to Choose Edge AI
If enterprises face the following situations, Edge AI may be the better choice:
Need for real-time decision-making: When application scenarios have extremely high response time requirements, such as autonomous vehicles or real-time control of industrial equipment, Edge AI can quickly process data locally and make decisions, avoiding safety risks or efficiency losses due to network latency.
Limited network connectivity: In some remote areas, offshore platforms, or applications with unstable networks, Edge AI can operate offline, ensuring normal operation and data processing of devices without being affected by network conditions.
Data privacy is crucial: For industries involving sensitive data, such as healthcare and finance, Edge AI can process and store data locally, reducing the risk of data breaches and better meeting data privacy and compliance requirements.
Predictable and localized workloads: If an enterprise’s data processing needs are relatively stable and primarily focused on local devices, Edge AI can provide a more efficient and cost-effective solution, avoiding unnecessary data transmission and waste of cloud resources.
When to Choose Cloud AI
If enterprises face the following situations, Cloud AI may be the better choice:
Need for powerful AI model training and analysis: When enterprises need to process large-scale datasets, train complex neural networks, or conduct deep data analysis, the powerful computing capabilities and rich data storage resources of Cloud AI can provide strong support, helping enterprises quickly complete model training and data analysis tasks.
Workloads involve large datasets: For enterprises that need to process massive amounts of data, such as e-commerce, finance, and telecommunications, Cloud AI can efficiently store and process this data, providing powerful data analysis and mining capabilities to support enterprise decision-making.
Need for rapid AI scaling: When enterprises need to quickly deploy and scale AI applications across multiple locations, the scalability advantages of Cloud AI can help enterprises respond quickly to business needs and flexibly adjust resource allocation for rapid AI application expansion.
Integration with SaaS or cloud-native applications: If enterprises are already using SaaS (Software as a Service) or cloud-native applications, Cloud AI can seamlessly integrate with these applications, providing more efficient data sharing and collaboration capabilities, helping enterprises achieve a more complete digital transformation.
Industry Insights: Future Trends and Enterprise Strategies
Industry Trends
According to McKinsey, by 2025, up to 75% of enterprise data will be created and processed outside traditional data centers or the cloud. This trend indicates that Edge AI will become one of the important directions for future enterprise digital transformation. With the proliferation of IoT devices and the development of 5G technology, more and more data will be generated and processed on edge devices, and Edge AI will play a crucial role in real-time decision-making, data privacy protection, and network bandwidth optimization. However, cloud computing still has irreplaceable advantages in deep learning, centralized orchestration, and large-scale processing. Therefore, in the future, enterprises will increasingly adopt hybrid AI architectures that combine Edge AI and Cloud AI to meet diverse business needs.
Enterprise Strategy Recommendations
There is no one-size-fits-all solution between Edge AI and Cloud AI. Enterprises must weigh factors such as latency, scalability, privacy, and cost based on their business needs, technical conditions, and budget to formulate the most suitable AI strategy. Here are some strategic recommendations:
Assess business needs: Enterprises should analyze their business scenarios and data processing needs in depth, clarifying which application scenarios require real-time decision-making and which require powerful computing and data analysis capabilities, thus determining the applicability of Edge AI and Cloud AI.
Consider data privacy and compliance: For industries involving sensitive data, enterprises need to prioritize data privacy and compliance requirements, choosing AI solutions that can meet relevant regulatory requirements. Edge AI has advantages in data privacy protection, but in some cases, Cloud AI can also meet compliance requirements through encryption, anonymization, and other technical means.
Balance costs and benefits: Enterprises need to comprehensively consider the cost characteristics of Edge AI and Cloud AI, including initial investments, operational costs, and long-term benefits. By conducting detailed cost analysis and benefit assessments, they can choose the most cost-effective AI solutions.
Adopt hybrid architectures: For most enterprises, hybrid AI architectures may be the best choice. Enterprises can process urgent data on edge devices for quick decision-making while synchronizing data to the cloud for long-term storage and model updates. This architecture can fully leverage the advantages of both Edge AI and Cloud AI, achieving optimal AI application results.
Conclusion: The Future of Artificial Intelligence is Distributed
As AI technology continues to evolve, enterprises face an increasing number of choices. Edge AI and Cloud AI each have their advantages and are suitable for different application scenarios. Edge AI excels in real-time performance, data privacy, and offline operation capabilities, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid decision-making and privacy protection; while Cloud AI has significant advantages in powerful computing capabilities, scalability, and big data processing, making it suitable for handling large-scale datasets and complex AI model training tasks. Enterprises must weigh various factors based on their business needs, technical conditions, and budget to choose the most suitable AI solutions.
In the future, the development trend of artificial intelligence will be distributed. Enterprises will increasingly adopt hybrid AI architectures that combine Edge AI and Cloud AI to achieve the best balance of performance, cost, and privacy protection. This distributed AI architecture will provide enterprises with greater flexibility and innovation capabilities, driving deeper development of digital transformation. Therefore, enterprises need to plan and layout in advance, formulating AI strategies that adapt to future developments to gain a competitive edge in the fierce market.
Source: Internet