Li, J., Zhong, P., Yang, M., Zhu, F., Chen, J., Xu, B., Liu, W. (2019). Dynamic and Intelligent Modeling Methods for Joint Operation of a Flood Control System. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management. 145, 0401904410. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001110
Li, J., Zhong, P., Yang, M., Zhu, F., Chen, J., Liu, W., Xu, S. (2020). Intelligent identification of effective reservoirs based on the random forest classification model. Journal of Hydrology. 591, 125324.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125324
Keywords: reservoir groups; flood control joint scheduling; effective reservoirs; intelligent reasoning; self-organizing modeling
Real-time flood control scheduling of reservoir groups is an important non-engineering measure for flood disaster reduction. Traditional joint optimization scheduling of reservoir groups is based on the conceptualization of the flood control system in the study area, establishing an overall model that reflects the topological structure of the flood control system of the reservoir group, and seeking efficient solution methods for the overall model. However, as the scale of flood control engineering systems expands, the contradiction between solving high-dimensional, nonlinear joint scheduling models and the high timeliness of flood control scheduling decisions remains a pressing issue that needs to be addressed in real-time joint scheduling of reservoir groups.
This paper utilizes dynamic information such as the spatiotemporal distribution of heavy rainfall and changes in reservoir flood control capacity, employing artificial intelligence for dynamic modeling. By minimizing the scale and complexity of the mathematical model, it aims to reduce the dimensionality and decision-making difficulty of real-time flood control joint scheduling of reservoir groups from a physical perspective. The study first introduces the concept of “effective reservoirs” and comprehensively considers factors such as real-time water conditions, reservoir status, the flood control effect of reservoirs on flood control sections, and the hydraulic connections between reservoirs to establish an identification index system for effective reservoirs. Then, based on the “equivalent” principle, the effective reservoir samples from historical floods are determined using a stepwise reduction method, which in turn establishes the index threshold values. On this basis, an intelligent identification method for effective reservoirs based on reasoning machine principles is proposed, and a dynamic mixed scheduling model for effective reservoir joint scheduling and non-effective reservoir individual scheduling is self-organized based on the identification results of effective reservoirs.
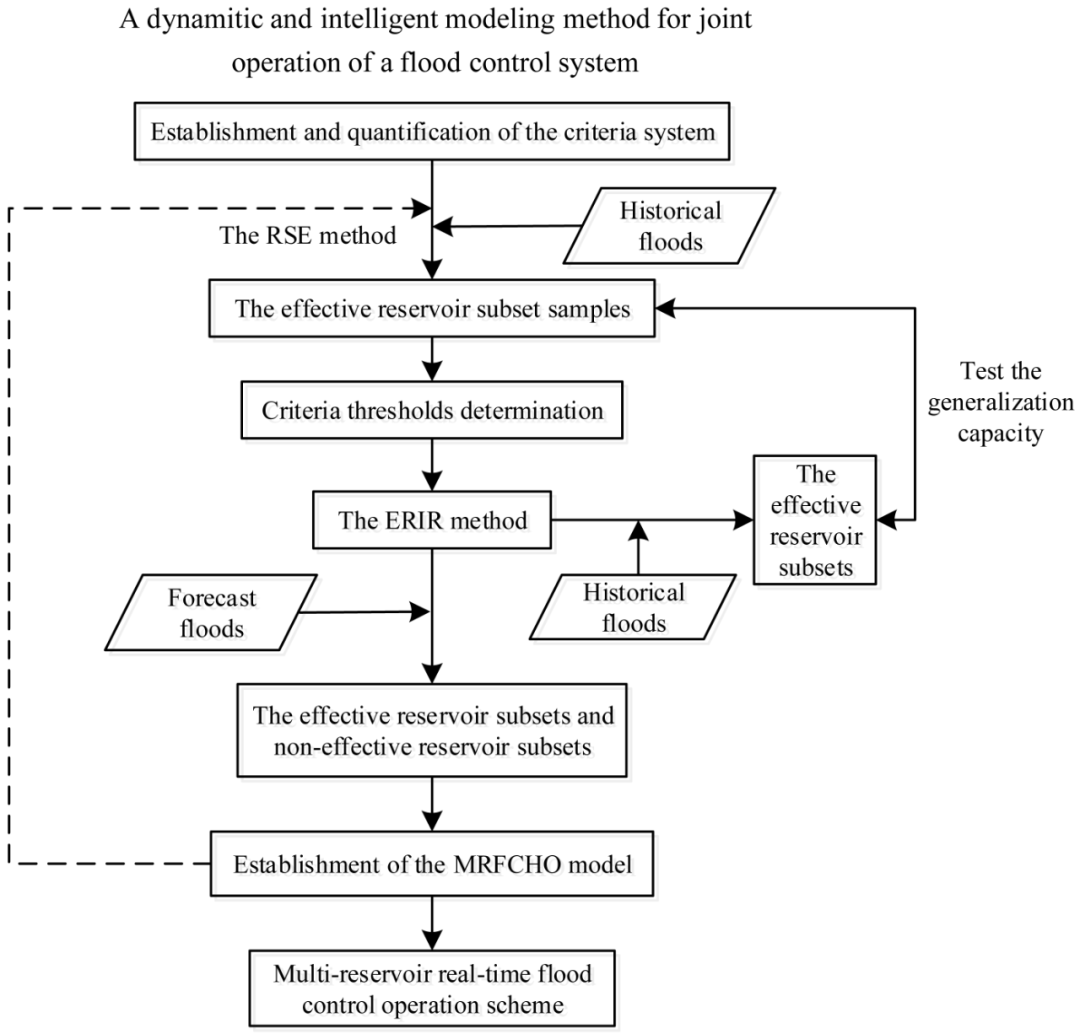
Figure 1: Research Framework
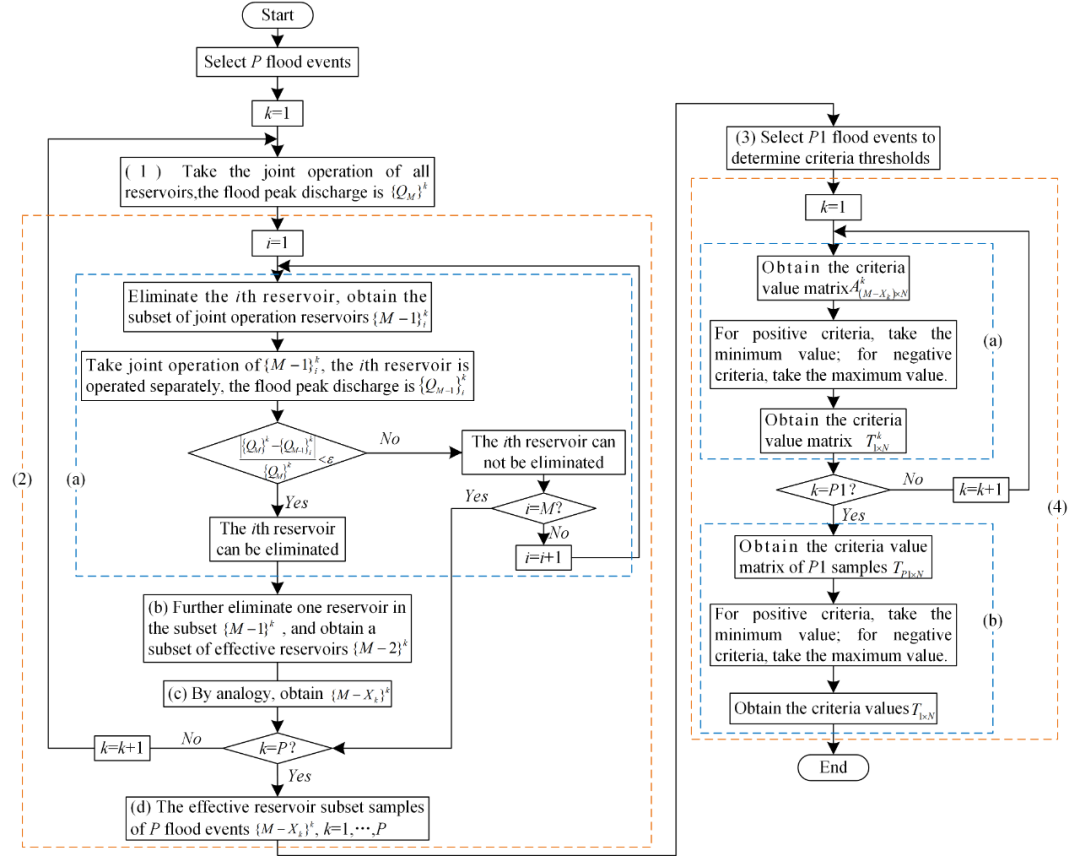
Figure 2: Process for Determining Effective Reservoir Samples and Index Thresholds
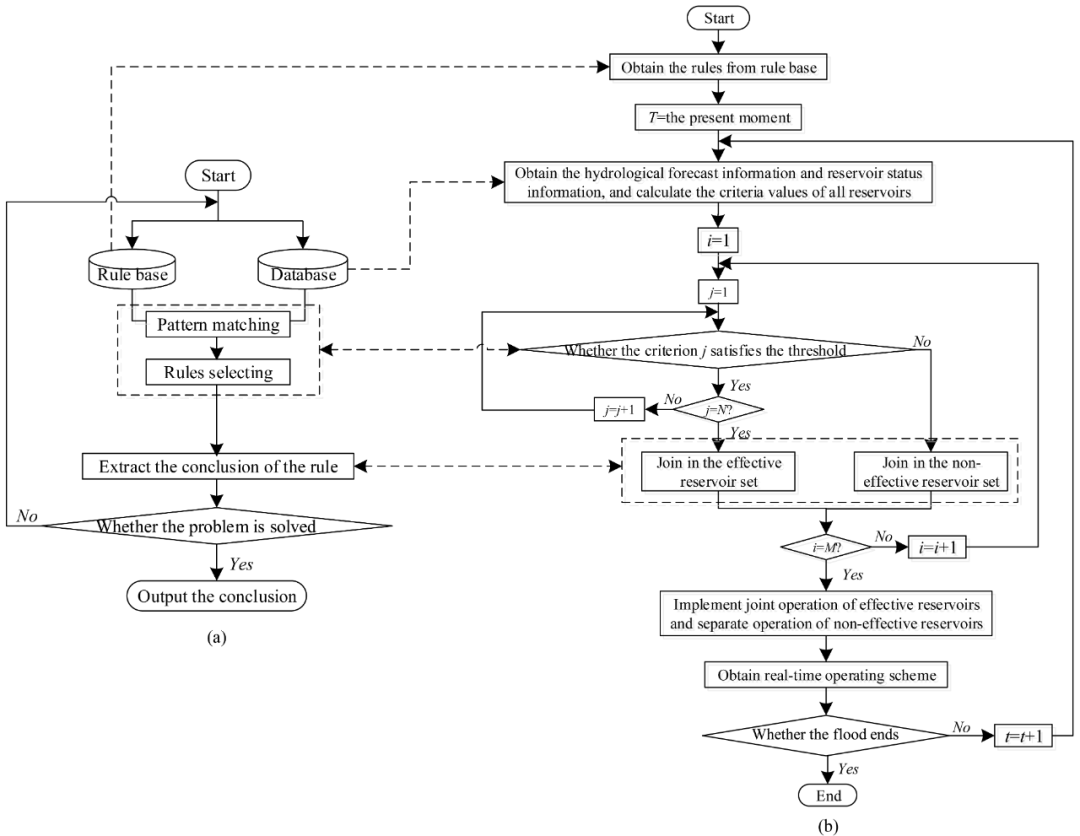
Figure 3: Working Mode of Reasoning Machine and Intelligent Identification Flow of Effective Reservoirs
We applied the proposed self-organizing modeling method to the flood control system above the Lutaizi section in the Huai River Basin. Case studies show that: (1) The reasoning method proposed in this paper can accurately identify the subset of effective reservoirs in real-time based on water, rain, and operational information, with the number of effective reservoirs accounting for less than 50% of all reservoirs; (2) The effective reservoirs have a significant compensatory effect on the Lutaizi section, with the flow processes formed by the dynamic mixed scheduling model and the overall joint scheduling model being similar, with peak flow differences within 0.5%; (3) Due to the significant reduction in the number of reservoirs participating in joint scheduling, the difficulty of model solving and decision-making for real-time flood control scheduling is significantly reduced.
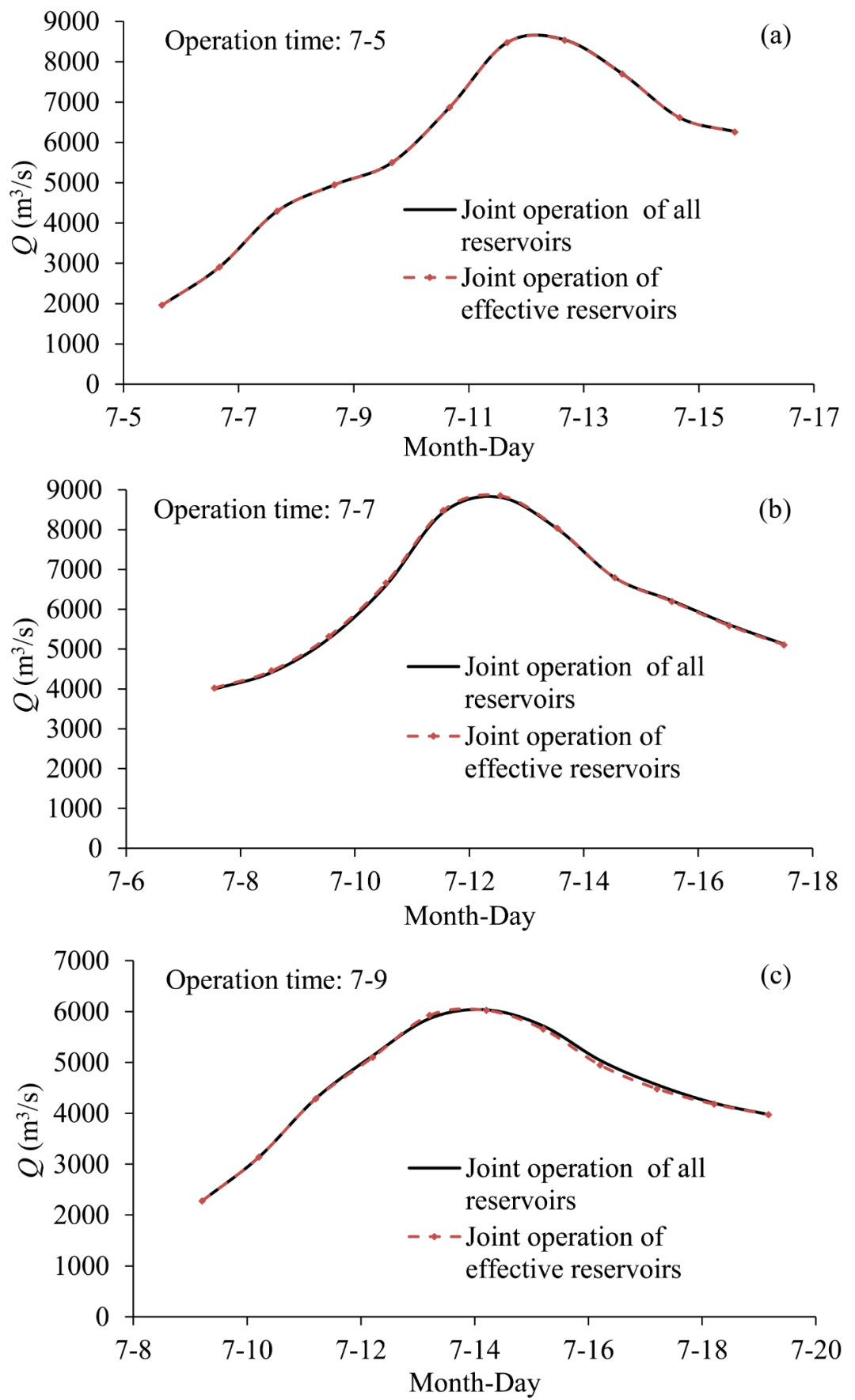
Figure 4: Flow Processes of Public Flood Control Sections During Different Scheduling Periods
Author Biography:
Li Jieyu, PhD student in Hydrology and Water Resources at Hohai University, class of 2017, under the supervision of Professor Zhong Pingan. His main research directions include dynamic intelligent modeling of real-time flood control scheduling of reservoir groups, risk analysis, etc. He has published academic papers as the first author in authoritative journals in the field of hydrology and water resources such as Journal of Hydrology.
Contact Information:: [email protected]
——————————————–
Written by: Li Jieyu | Edited by: Wang Qian | Proofread by: Lin Jingyu
[Next: Human Activities and Lake Groups]
——————————————–
Click “Read Original” for the original download link
Get the latest hydrological news quickly at Hydro90, join the hydro90 WeChat group, and communicate freely with the editor and water (literature) friends!
(Please add the editor’s WeChat for group recommendation, note “join group”)