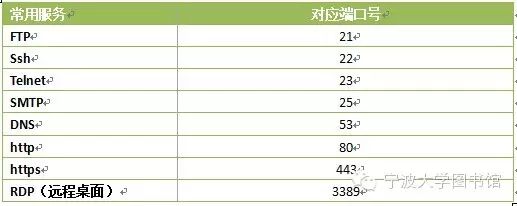
In network technology, a port generally has two meanings: first, it refers to the physical interface (hardware) between computers and other devices. For example, interfaces like RJ-45 ports and SC ports used to connect other network devices such as switches and routers. Second, it refers to the logical virtual ports (software), which typically refer to ports in the TCP/IP protocol, with port numbers ranging from 0 to 65535, such as port 80 for web browsing services and port 21 for FTP services.
Every host on the Internet has a unique address (IP), but the same host may provide more than one service simultaneously, such as FTP services, WWW services, etc. Each service occupies a port on that host. In Internet applications, different services are distinguished by “IP address + port number”.
There are two types of ports in software: one is TCP ports and the other is UDP ports. When computers communicate with each other, there are two methods: one is a method where information can be confirmed to have arrived after sending, which typically uses the TCP protocol; the other is a method where after sending, it does not check whether the information has arrived, which typically uses the UDP protocol. The ports provided for these two types of protocols are divided into TCP ports and UDP ports.
Port numbers can be classified into three main categories:
1. Well-known ports: from 0 to 1023, which are tightly bound to certain services. 2. Registered ports: from 1024 to 49151, which are loosely bound to certain services. These port numbers are generally not fixed to any specific service, and many services can use these ports. 3. Dynamic or private ports: from 49152 to 65535, which, by definition, belong to the range of “dynamic ports”, and no ports can be officially registered for use. Theoretically, these ports should not be allocated for services. In practice, machines usually allocate dynamic ports starting from 1024.
Common services corresponding to port numbers: