LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): also known as liquid crystal display. Widely used in embedded, mobile, and PC applications.
-
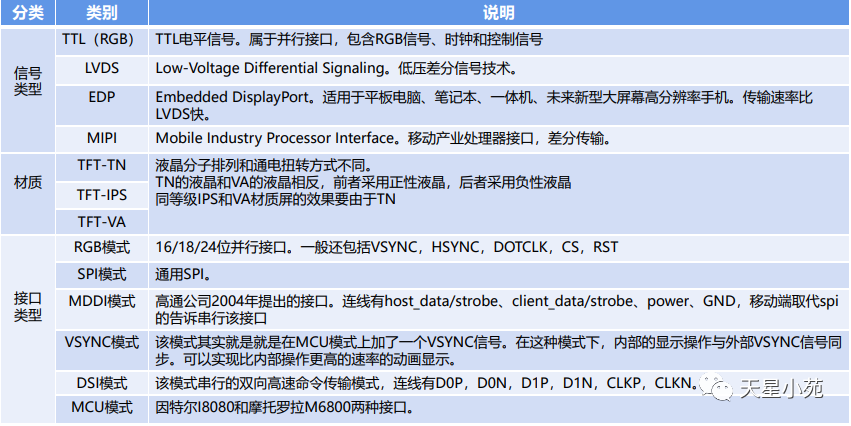
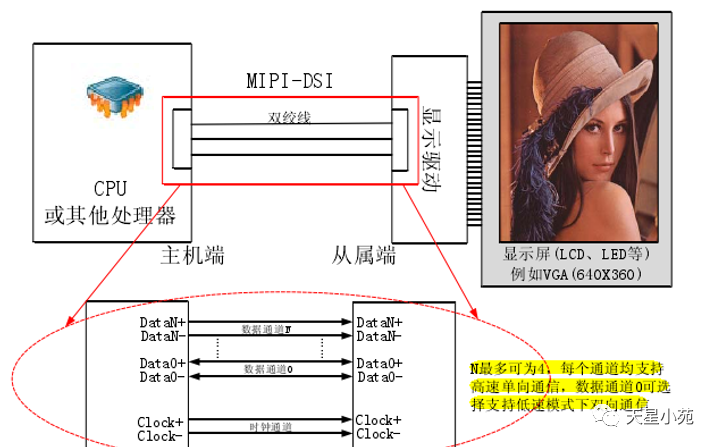
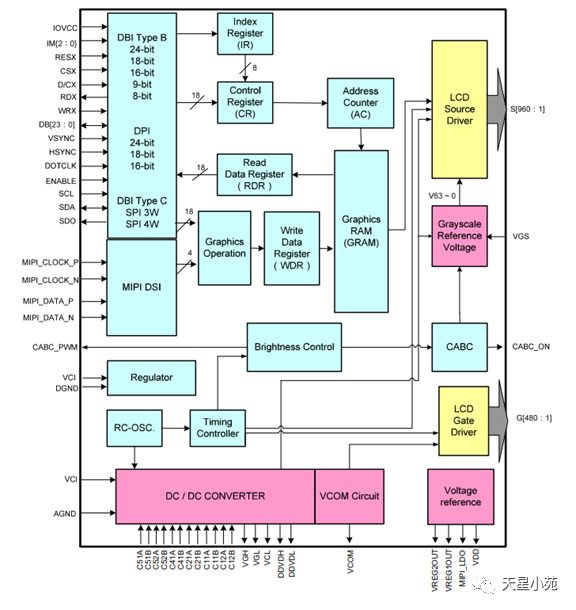
Divided into several categories based on signal type: TTL/LVDS/EDP/MIPI -
Classified by material (for TFT-LCD): TFT-TN/TFT-IPS/TFT-VA. -
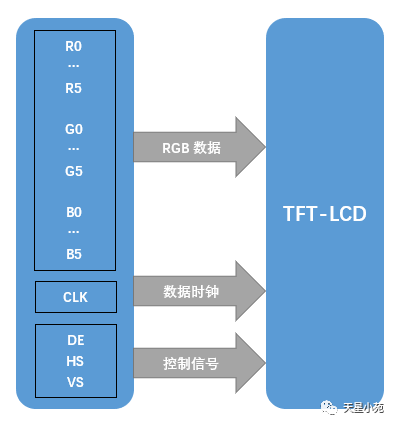
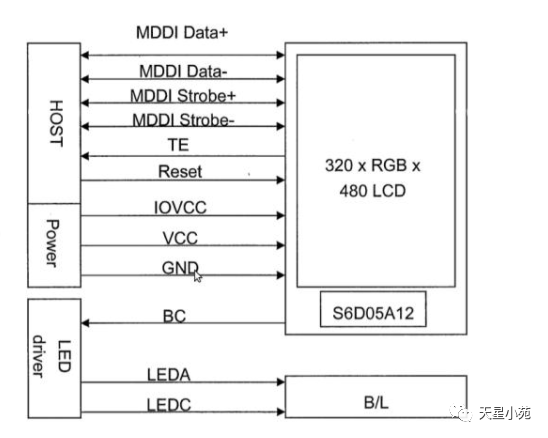
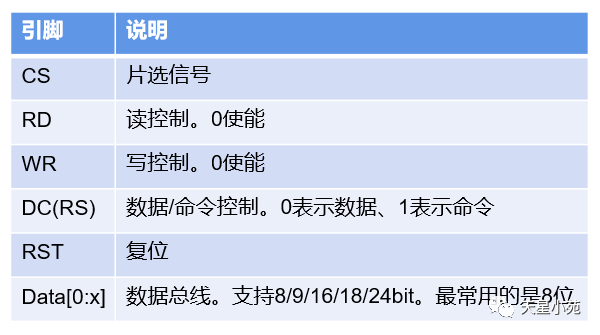
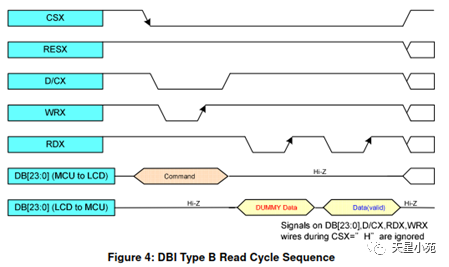
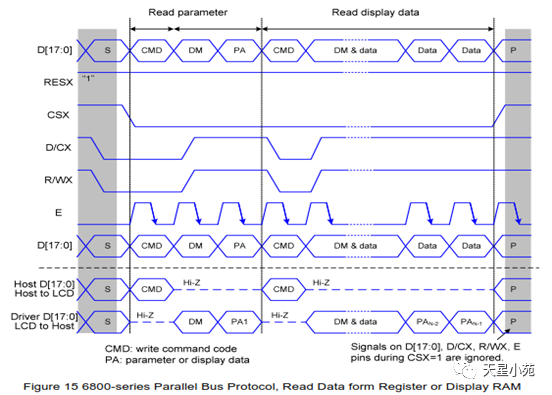
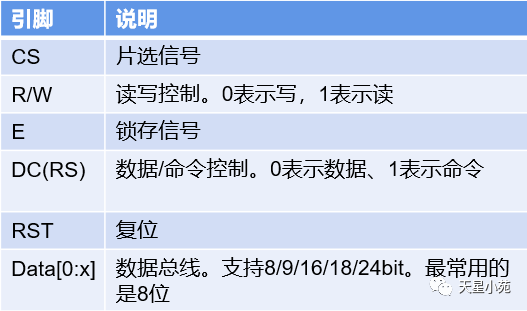
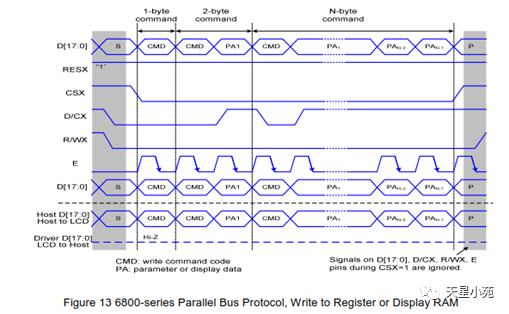
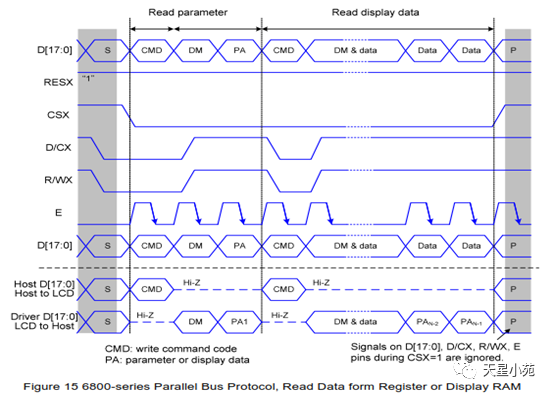
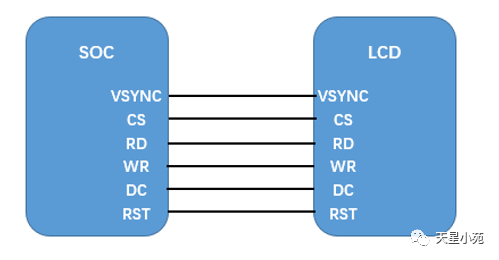
Interface types include: RGB mode, SPI mode, MDDI mode, VSYNC mode, DSI mode, MCU mode, etc. 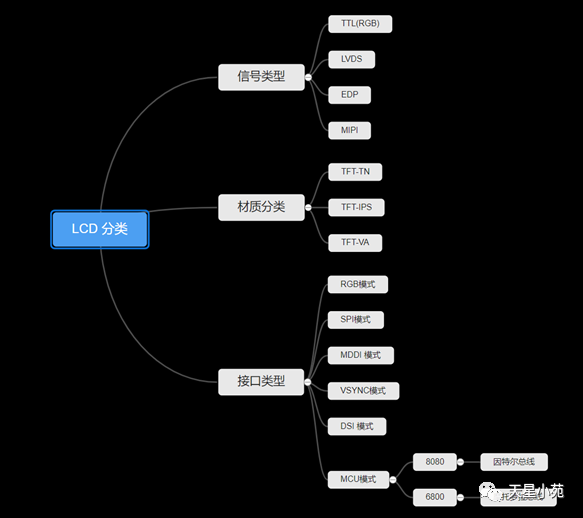
Scan the QR code to join the embedded group ▼