In terms of display technology, 2016 is a significant year. With the continued popularity of 4K and the emergence of new features like HDR, the viewing experience that televisions can present will be further enhanced. In the mobile phone sector, the increase in screen resolution has also led to more refined display effects.
However, while we are ready to embrace new technologies, the battle between two types of display panels continues: LCD and OLED. The former is currently the most popular type of display panel, and the LED TVs we commonly see actually use LCD panels with LED backlighting. OLED is a completely different type of panel, primarily used in certain mobile phones and televisions.
Some people refer to OLED as the trend of the future, but is it really better than LED LCD panels?
Differences
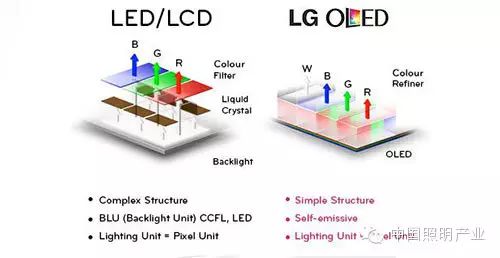
LED LCD panels use backlighting to illuminate pixels, while OLED pixels can emit light independently. This allows OLED panels to achieve brightness control on a pixel-by-pixel basis, which is something LED LCD cannot do.
In some cheap TVs and LCD screen mobile phones, the LED backlighting used in LED LCD is actually positioned on the side of the display rather than the back, and the light emitted passes through the red, green, and blue pixels to reach our eyes. Therefore, the brightness control of LED LCD panels is limited. When in a dark environment, you will find that the black displayed is not pure black.

Contrast
OLED panels do not emit any light when displaying pure black, so their contrast can reach infinity, while a good quality LCD panel may have a contrast ratio of only 1000:1. The “dynamic” contrast ratio marked on LCD TVs is generally much higher than this value because it refers to the TV’s ability to adjust backlight levels based on screen content, not the actual contrast ratio.
Some LED LCD panels can actually achieve contrast ratios close to OLED, such as direct-lit LED. This type of panel has LED backlighting directly placed behind the LCD, allowing for more precise brightness control. However, this type of panel is generally used only in high-end TVs, and the results can vary.
It is worth noting that direct-lit LED TVs can only control a certain LED “area” or group, and still cannot achieve pixel-level control like OLED. When watching a 21:9 movie on a 16:9 TV, direct-lit LED can handle the black borders well, but when dealing with more complex tasks, its performance may not be as good, such as displaying bright objects against a pure black background, where you may see a halo effect due to the mismatch between the backlight area and the screen content.

Display Quality
In terms of overall performance, both OLED and LCD are capable of presenting excellent picture quality. HDR is the main feature promoted in the television field in 2016, and to establish relevant standards, the television industry has introduced a new “Ultra HD Premium” label. It is noteworthy that both LCD and OLED TVs have been awarded this label. This means that both display technologies are capable of presenting top-notch picture quality.
Due to their excellent contrast, OLED displays are the best choice for watching content in a dark room. Considering that plasma TVs have exited the historical stage, this point is particularly important. For enthusiasts pursuing extreme picture quality, OLED displays are also an excellent choice, not just in the television sector. Samsung’s recently released Galaxy S7 and S7 edge both use OLED panels, and their display quality may also be among the best in smartphones.

Popularity
If OLED quality is so outstanding, why are OLED TVs not yet widespread? This is mainly because the production difficulty of this panel is very high. So far, only three companies have the capability to produce full-size commercial OLED TVs: Samsung, LG, and Panasonic. However, this group is expected to expand further this year. It is rumored that Philips is currently developing OLED TVs, which are expected to be officially released this year.
Samsung’s OLED TV model is KE55S9C, with an initial price of £7000 (approximately 64847 RMB). At such a high price, this TV should provide you with a perfect experience, but its blue LEDs raise some concerns — their lifespan is shorter than that of green and red LEDs.
By using white LEDs and color filters, LG has successfully addressed this issue in its OLED TVs. LG is also making significant efforts to popularize OLED. Although OLED TVs are still not affordable for mainstream consumers, LG’s attempts are evident.
Currently, LG’s cheapest OLED TV is the 55EC930V, priced at around £1299 (approximately 12034 RMB). Although the product quality is good, it has become somewhat outdated as it does not support 4K. However, if you want to buy a 4K OLED TV, be prepared for a budget of at least £2000.
As for LCD TVs, you can currently buy a 4K LCD TV for less than £500, while the cheapest 4K OLED TV costs £2499 (approximately 23150 RMB, LG 55EG960V). Although the price of the latter is still relatively high, it has decreased significantly compared to the cheapest 4K OLED model from a year ago (LG 65EC970V).
Although the price of OLED TVs remains relatively high, the continued investment from technology manufacturers will significantly lower costs. By the end of this year, we may see sufficiently affordable 4K OLED TVs appearing on the market.
Advantages of LCD
One of the main advantages of LCD panels is their lower cost. Looking at the current market, you will see quite a number of low-cost devices equipped with high-quality LCD panels, such as Motorola’s Moto E. Of course, the low cost of LCD has quickly lowered the prices of 4K TVs.
At the same resolution, LCD screens often appear clearer than OLED, mainly because display manufacturers have adopted strategies to address the issues of OLED panels.
For OLED panels, different colored LEDs not only have different lifespans but also different brightness levels. Compared to LCD displays that use conventional red, green, and blue sub-pixel patterns, OLED often needs to be more “dynamic”.
For example, the pixels of the Galaxy Note 4 are not made up of three conventional sub-pixels, but rather consist of two pixels through a red-green-blue-green configuration. Their shapes are also different: the red and blue sub-pixels are diamond-shaped, while the green ones are oval.
This pixel arrangement is called PenTile, which can make OLED with fewer pixels appear somewhat blurry. Due to the increase in resolution, this effect has largely disappeared in recent smartphones. LG’s OLED TVs do not need to use this technology because they use color filters instead of colored LEDs.
Viewing Angles
OLED panels have near-perfect viewing angles, although they often exhibit slightly different hues when viewed from the side. For example, the Galaxy Note 4 appears somewhat bluish. The viewing angle of LCD panels mainly depends on the display technology used. For instance, many low-end monitors, laptops, and phones use TN panels, which have poor viewing angles, while IPS panels have significantly improved color reproduction and viewing angles, making them the choice for most smartphones, most monitors, and some TVs.
Color Reproduction
The latest LCD panels can produce extremely natural colors. When correctly calibrated, both IPS and VA panels can achieve high levels of color accuracy — the iPhone 6s is an excellent example — but TN panels often appear somewhat washed out.
OLED vs LED LCD: Which Screen Technology Is Superior?
OLED has the potential for better color performance than the best LCD panels, but the challenge lies in how to harness this capability. These panels can reproduce a more natural color spectrum than the film/software production standards, but if not calibrated correctly, they can appear overly saturated.
Future Development
Panel manufacturers are trying their best to break through the limitations of LCD capabilities. OLED’s task in the coming years is to lower costs, while LCD will focus on technological development.
Quantum dots can be considered one of the most attractive LCD display technologies in recent times. They do not use white LEDs, but rather blue LEDs and different sizes of “quantum dots,” which can convert light into different colors by changing the wavelength.
Some Kindle Fire HD tablets showcased by Amazon at this year’s CES used this technology, and Samsung’s flagship SUHD TV series also features these trendy nanoparticles. Quantum dots are one of the main ways for LCD displays to meet UHD Premium standards and satisfy HDR requirements.
Conclusion
Whether you are planning to buy a mobile phone, monitor, laptop, or television, if your budget is limited, you will ultimately choose a product equipped with an LCD display.
For manufacturers, this is a relatively easy technology to handle. However, in terms of image quality, LCD can be more troublesome, especially when compared to OLED. Fortunately, in recent years, technologies like IPS have come to the rescue.
The production of OLED is very difficult, and this is reflected in the prices of related products. However, whether for mobile phones or televisions, OLED panels can present the most eye-catching image quality. With long-term investments from technology companies, this screen technology will not be a passing trend.
Source: Tencent Digital
