EPS ECU consists of a microcontroller for control, integrated circuits for monitoring (sometimes also microcontrollers), motor drive circuits (driving and conversion circuits), relays that switch motor paths and power paths, and interface circuits that receive external signals.
The function of the motor drive circuit is to implement PWM control of the power component MOSFET.
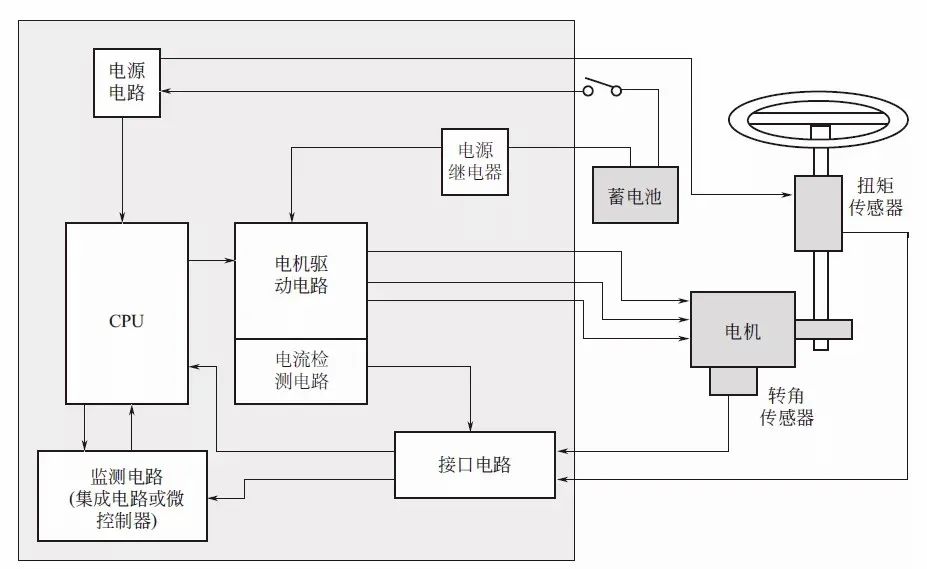
Example of EPS ECU Circuit (Brushless) ▲
The printed circuit board of EPS ECU is shown in the figure below, consisting of coils required to eliminate interference in the power line, electrolytic capacitors required to absorb current fluctuations, and power relays required to switch the power supply.Since the size of the printed circuit board must not be too large, some types of printed circuit boards are equipped with semiconductor relays.
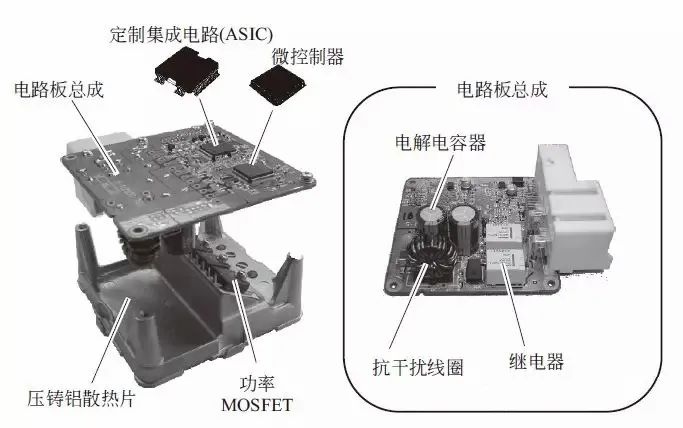
Example of EPS ECU Composition (Brushed) ▲
EPS assist control is shown in the figure below, which can be divided into basic assist control, assist auxiliary control, motor current control, and failure protection handling.Different manufacturers have different control methods, and common control methods will be explained here.
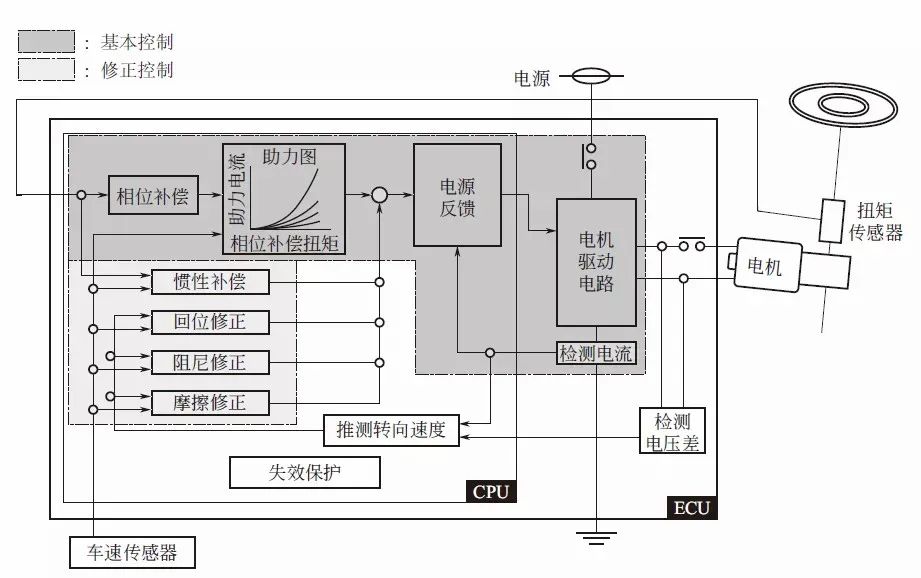
To compensate for the response delay of the system to the torque sensor signal, phase compensation should be implemented.Based on the value after phase compensation, the assist amount is determined.These controls are closely related to vehicle characteristics and are mostly set in graphical form.Additionally, assist amount can be adjusted based on vehicle speed, applying speed sensitivity characteristics.Then, the final assist command value is passed to the current control section by adding the auxiliary control amount.
(2) Assist Auxiliary Control
The steering wheel is not only controlled by the driver’s steering operation; when the road applies torque to the tires, the steering wheel may also rotate.Therefore, in addition to conventional basic assist control, assist auxiliary control should also be implemented.The main assist auxiliary controls include:“Inertia compensation” to smooth assist when excluding the motor’s inertia torque influence;corresponding return correction when the steering wheel returns due to restoring torque after turning;“Damping correction” to stabilize the steering wheel when letting go;and corresponding friction correction due to assist delay caused by friction in the motor or mechanism.
The correction amount is the same as the assist graph and is a value that changes based on vehicle characteristics, all of which should be determined after matching.
(3) Motor Current Control
To enable the motor to track the above motor current command value in real-time, it is necessary to control the motor’s current.Typically, after detecting the motor current, the corresponding difference of the command value is corrected, i.e., feedback control.Additionally, based on half the cycle of the assist command value, the motor circuit control cycle is set.Basically, for the difference between the command value and the current detection value, PI (Proportional Integral) control can be implemented, converting it into a voltage command value, and this voltage command is converted into the PWM duty cycle, controlling the motor by switching MOSFET through this duty cycle.
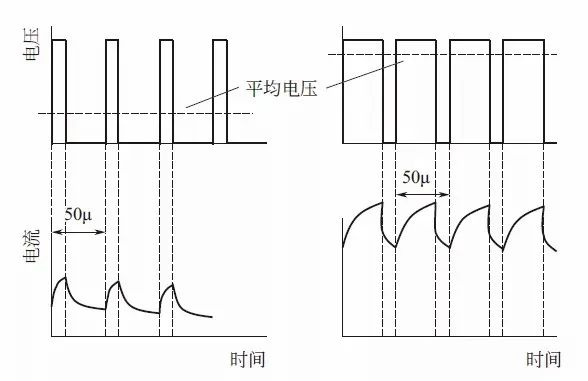
Moreover, when using brushless motors, motor current control is usually vector control for obtaining motor angle signals, and the d-axis and q-axis of the vector also need to undergo feedback PI control.
In addition to feedback control, some motor current controls also adopt observer control and model matching control.
To provide assist that is about ten times the driver’s steering force, EPS must quickly detect any abnormalities in assist and take accurate measures (see table below).
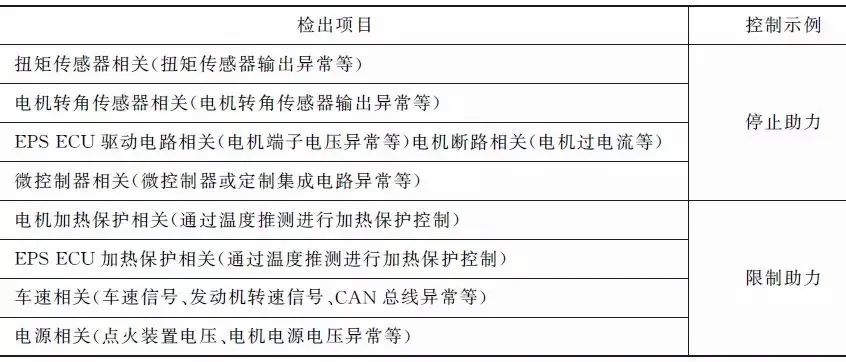
EPS should avoid not only abnormal overheating but also steering lock where the steering wheel cannot turn and free play where the steering wheel rotates freely.When an abnormal condition is detected, the system must be shut down.
Therefore, most EPS adopt a interlock method that monitors whether the direction of the driver’s steering torque matches the direction of the assist.However, EPS that works in conjunction with other systems has already been put into practical use, and the direction of assist may not necessarily match the direction of the steering torque, so in such systems, a method that monitors the control calculation itself is used.
(Image source from the internet)
Click the mini-program below to see more repair cases