
To reduce the environmental impact of automobiles, we must focus on making gas vehicles more “environmentally friendly”. In other words, we need to optimize the efficiency of the engine. The good design of the electronic ignition system is the best guarantee for control, safety, and optimization of combustion.
Inductive Discharge Ignition System (IDI)
To better understand the vehicle’s electronic ignition system, we have created a simplified ignition system diagram, along with a detailed explanation of the IDI system:
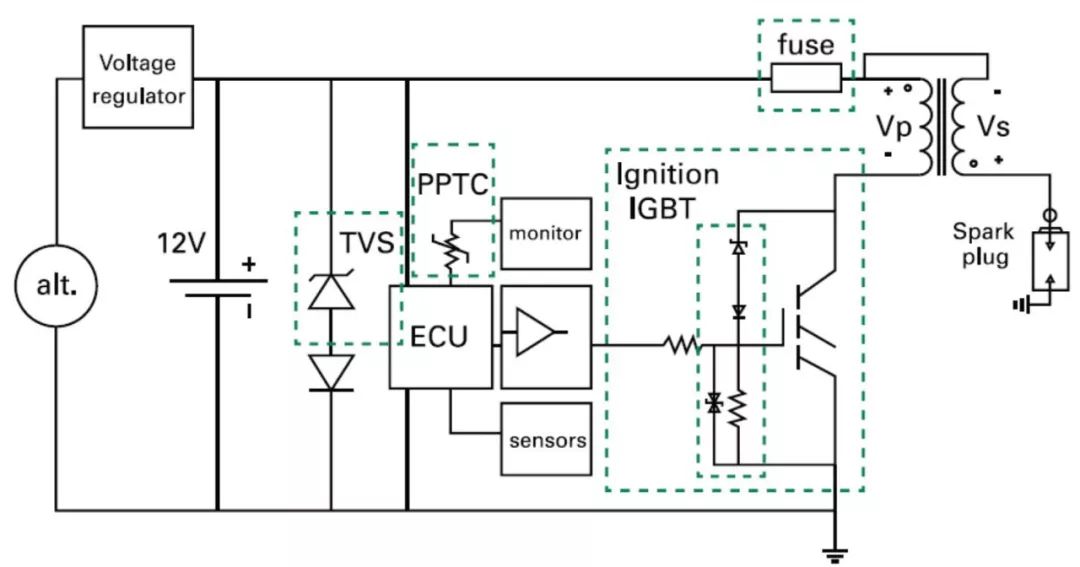
Inductive Discharge Ignition System
Before discussing IDI in detail, please remember: the spark events in the combustion chamber of a gasoline engine are controlled by the ignition system.
The core of the ignition system is the Ignition Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (Ignition IGBT). Its reliability, accuracy, and proper operation determine the efficiency of the entire system.
When the ignition IGBT is turned on, it closes the circuit of the ignition coil grounding. As the current in the primary winding of the ignition coil gradually increases, energy is stored in the primary side inductor and transformer core.
When the ignition IGBT is turned off, the rapid change in current rate (di/dt) will induce a high voltage spike across the collector-emitter of the ignition IGBT. The energy stored in the transformer core causes a voltage surge on the secondary side inductor, triggering a spark event. Additionally, the energy from leakage inductance must be absorbed by the ignition IGBT.
Protection of the Ignition System
The high voltage spikes in the collector-emitter may damage the ignition IGBT. Therefore, the ignition IGBT must be clamped at 350-450V. Furthermore, the gate must prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) spikes.
In the case of overcurrent, the fuse will disconnect the electronic components from the battery. This fuse regularly undergoes periodic pulses and must have a high melting thermal value (I²t) to extend its life. Due to the switching operations of the transformer, the voltage across the fuse may be very high. These fuses should be able to withstand harsh environments and higher operating temperatures.
Another important component of the ignition system is the TVS diode.The ignition system is connected to the automotive battery providing different loads. Inductive loads in the AC generator or even transients may cause voltage spikes along the power lines. These transmission spikes can cause electronic device failures or severe damage to the ignition electronic system. The TVS diode protects the circuit from these events.
In some types of ignition systems, the normal operating status of the ignition system should be monitored and feedback sent to the control unit. If the monitoring device is physically separated from the control unit, a resettable fuse can provide assistance. In this case, if overcurrent flows through the feedback cable, the electronic control unit (ECU) will be protected.
(Image source from the internet)
Click the mini-program below to see more repair cases
