Follow+Star Public Number, don’t miss wonderful content

Source of material | Network
What is rsync?
rsync (remote sync) is a tool used for file synchronization. It can be used for file synchronization between two local directories, as well as between local devices and remote devices.
The difference between rsync and scp is that: rsync checks the existing files on both the sender and receiver, only transferring the changed parts (the default rule is that the file size or modification time has changed).
Using rsync
Here, we will demonstrate using a PC and a development board.
Note: Both parties involved in the transfer must have rsync installed.
Our development board does not have rsync, so let’s compile one together.
Download the rsync source code:
https://download.samba.org/pub/rsync/
Unzip, enter rsync-3.2.3, and create a tmp folder:
tar -xvf rsync-3.2.3.tar.gz
cd rsync-3.2.3/
mkdir tmp
Enter the following command to generate the cross-compilation Makefile:
./configure --prefix=$PWD/tmp --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
You might encounter the following error:
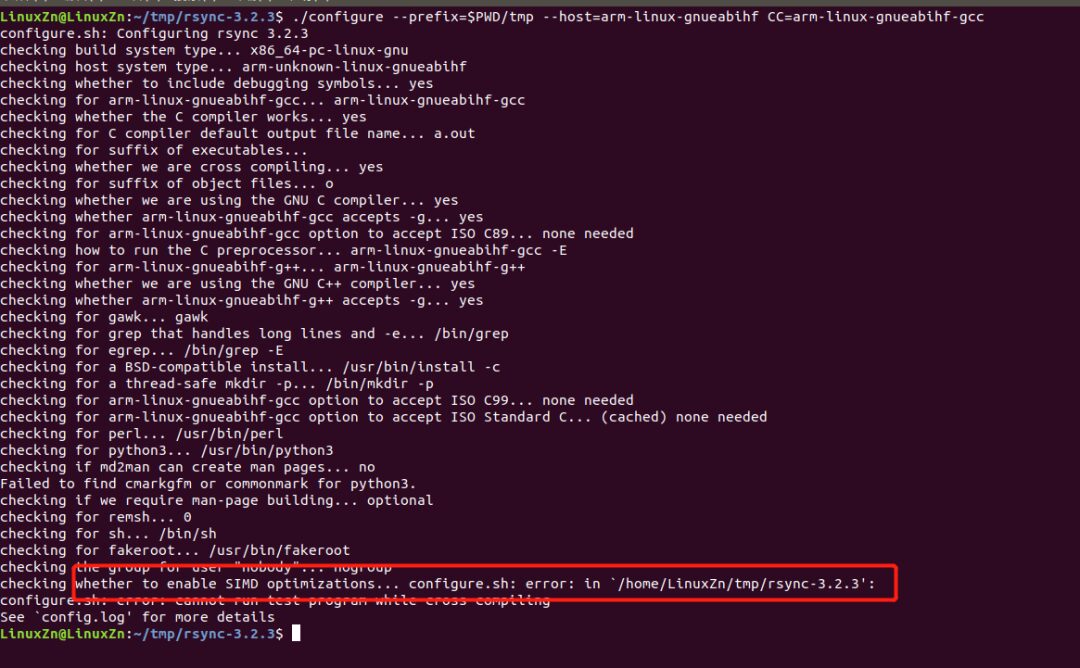
Modify according to the prompt. The general idea is that SIMD is enabled, and we don’t need to care about what SIMD is; we can just disable it.
Output the command ./configure --help to check the configuration parameters, and you can see how to disable SIMD:

Input:
./configure --prefix=$PWD/tmp --disable-simd --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
Still getting an error:
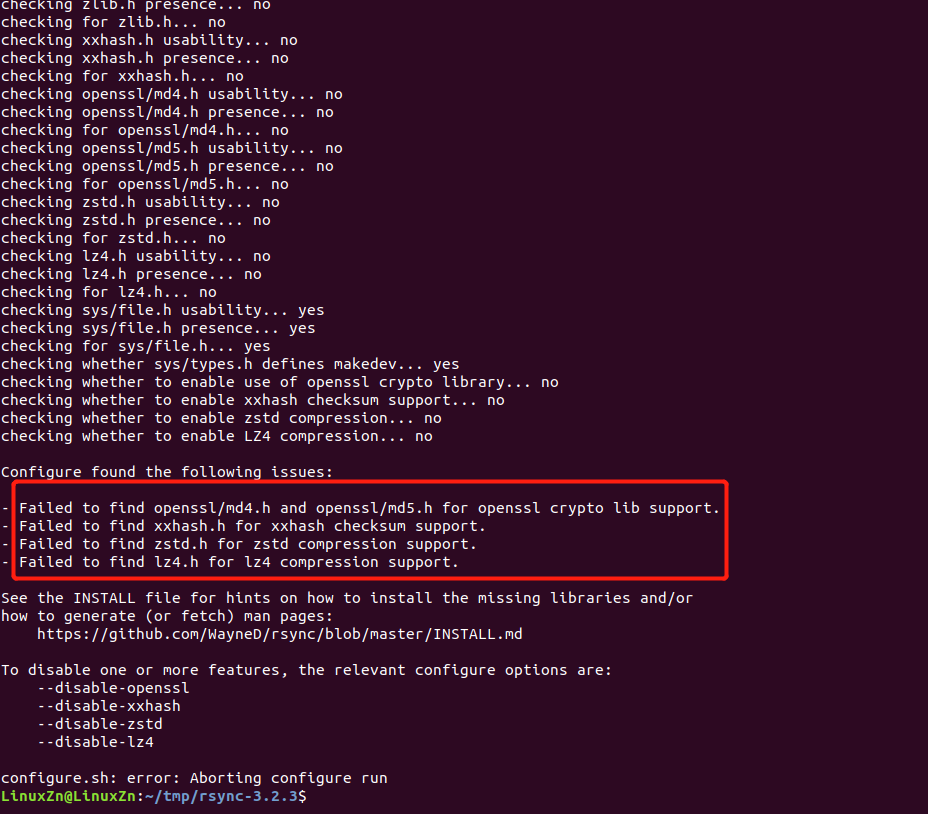
Modify the configure command again according to the prompt:
./configure --prefix=$PWD/tmp --disable-simd --disable-openssl --disable-xxhash --disable-zstd --disable-lz4 --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf CC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
At this point, it shows rsync 3.2.3 configuration successful:
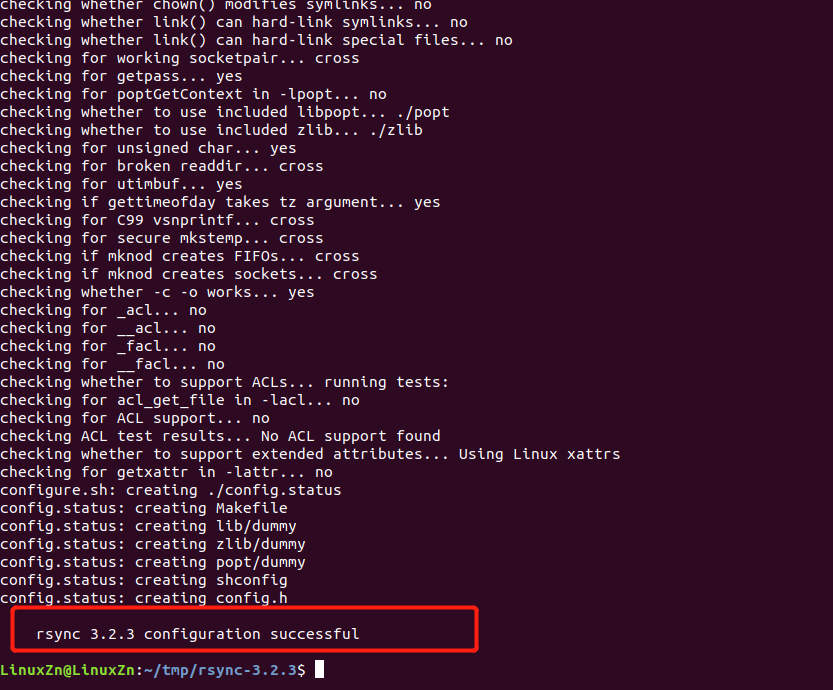
The Makefile file can now be generated.
Note: If there are still errors, configure according to the prompts.
PS: For support on the Makefile file, you can refer to the previous article: Common Basic Knowledge of Makefile!
Then compile and install:
make
make install
In the tmp folder, you will find:
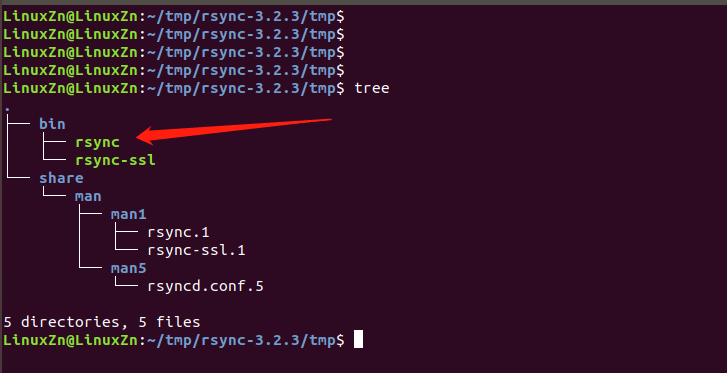
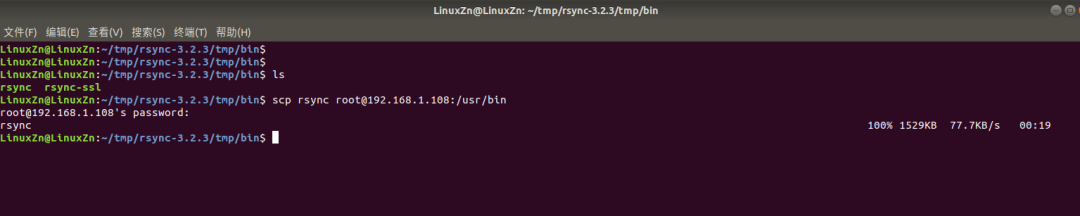
Among them, the rsync executable file is what we need to use on our board, so transfer it to the board’s /usr/bin directory:
scp rsync [email protected]:/usr/bin
Next, let’s do a simple demonstration of using rsync:
Create 100 files on the board first:
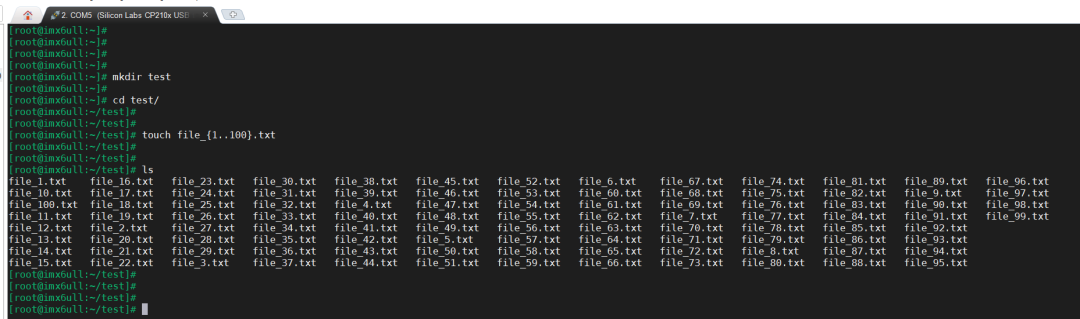
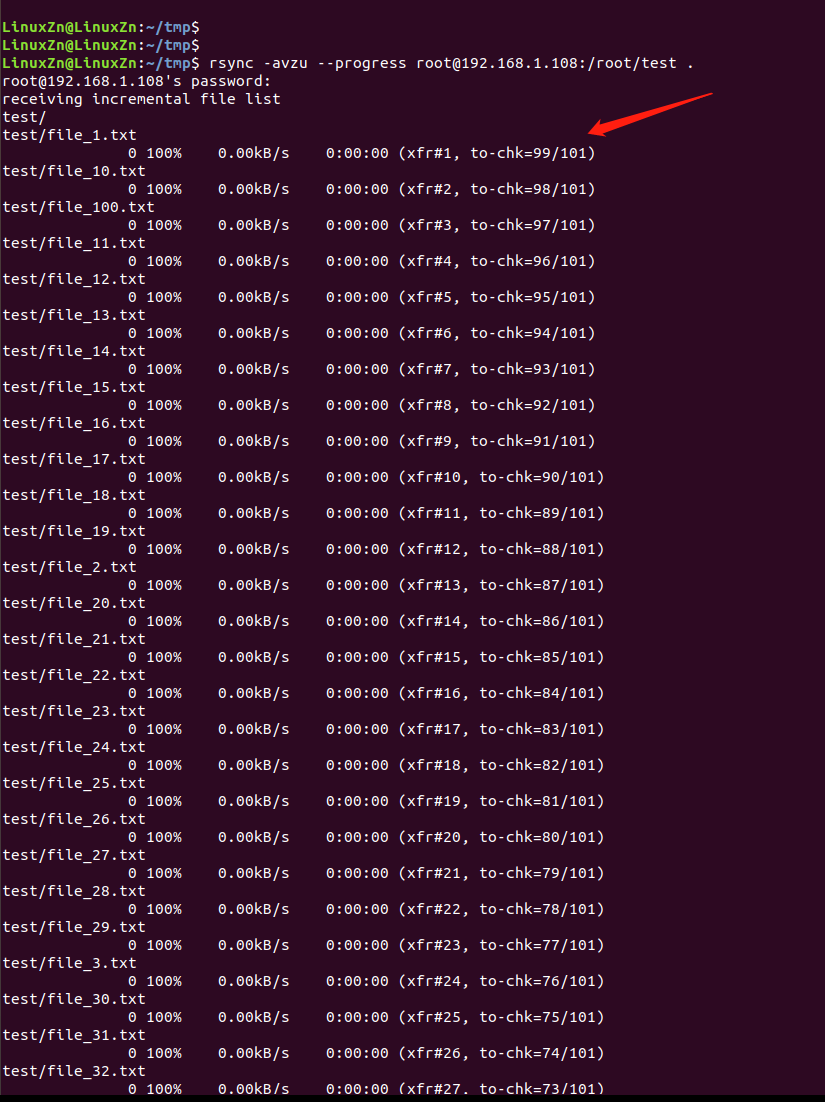
Synchronize these files from the board to the local PC:
rsync -avzu --progress [email protected]:/root/test .
-a: Archive mode, saves all metadata, such as modification time, permissions, owners, etc. -v: Outputs details. -z: Specifies data compression during synchronization. -u: Skips files with updated modification times in the target directory during synchronization. –progress: Displays progress.
The board creates another 100 files:
Synchronize again from the PC:
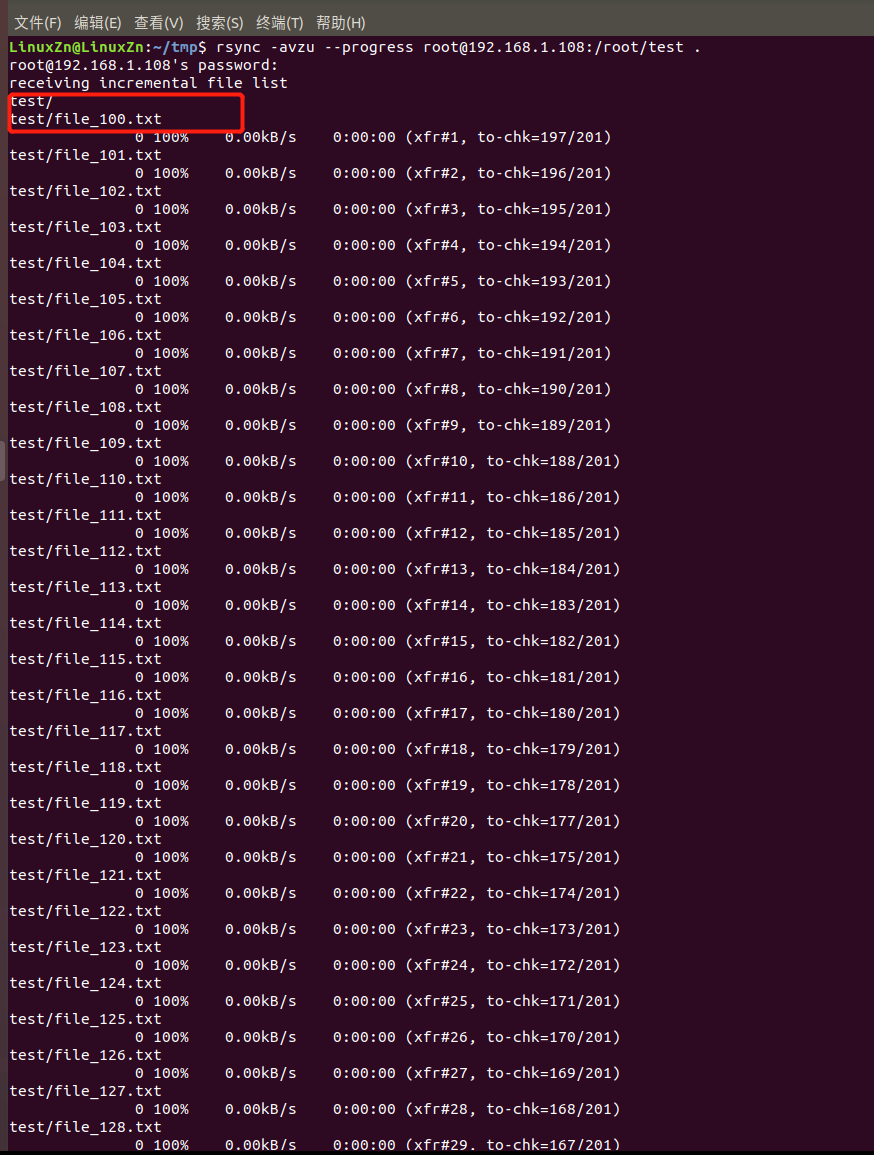
You can see that the files continue to transfer, and those that have already been transferred will not be transferred again.
This concludes our simple sharing about the rsync tool.
Are there other similar tools?
———— END ————

● Column “Embedded Tools”
● Column “Embedded Development”
● Column “Keil Tutorial”
● Selected Tutorials on Embedded Column
Follow the public account reply “Join Group” to join the technical exchange group according to the rules, reply “1024” to see more content.
