

What is NB-IoT
NB-IoT = Narrow Band Internet of Things
NB-IoT is a low-power wide-area communication technology built on cellular networks.
NB-IoT Module
A module that carries the NB-IoT chip and can complete communication functions.
The four main features of NB-IoT technology:

Mainstream Module Manufacturers
Currently, the modules on the market mainly use chips from Huawei Boundica and Qualcomm.
The following are some major module manufacturers:
Quectel (836430)

The company is located in Shanghai and is a global leader in GSM/GPRS, WCDMA/HSPA(+), LTE, and GNSS module supply, as well as the world’s first NB-IoT module manufacturer compliant with the 3GPP R13 standard.
China Mobile IoT

The company is located in Shanghai, specializing in the operation of IoT-specific networks, designing and producing IoT-specific modules and chips, and developing and operating the IoT open platform OneNET.
ZTE IoT

The company has R&D centers in Shenzhen and Xi’an, independently developing IoT communication products and solutions, continuously providing innovative solutions for domestic and foreign partners.
Lierda (832149)

The company is located in Hangzhou, a national key high-tech enterprise, dedicated to promoting technology and market development in the IoT embedded industry with strong technical strength.
H3C

The company is located in Beijing, a global leader in new IT solutions, dedicated to the R&D, production, consulting, sales, and services of new IT solutions and products.
Guanghetong Wireless (300638)

The company is located in Shenzhen, the first listed provider of wireless communication modules and solutions in China, always focusing on the development of the IoT and consumer electronics fields.
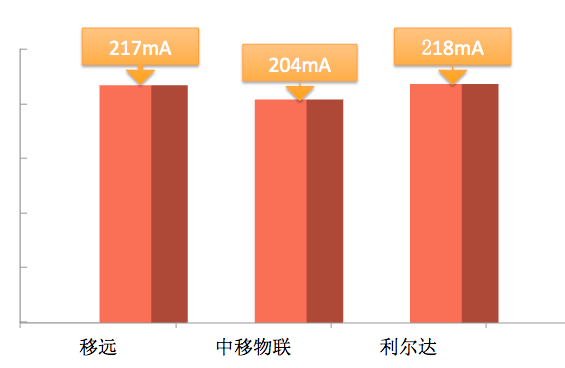
This test used NB-IoT modules from Quectel, China Mobile IoT, and Lierda to complete specific power consumption tests; at the same time, the 2G module from Guanghetong Wireless was tested for power consumption comparison experiments.

Key Energy-Saving Technologies
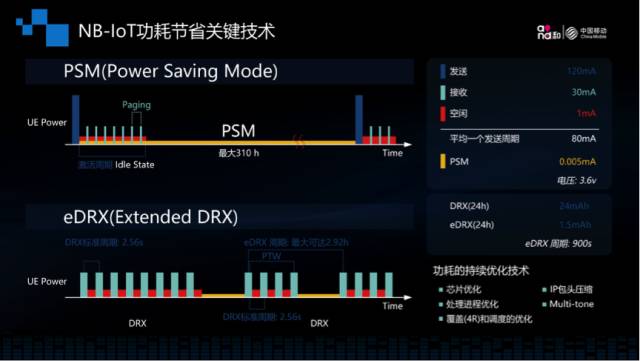
PSM (Power Saving Mode) is a mode that allows the UE to turn off the signal transmission and reception and access layer-related functions after entering idle state for a period of time, thereby reducing power consumption from antennas, RF, signaling processing, etc.
eDRX (Extended Discontinuous Reception) is an enhancement of the original DRX technology, supporting longer paging cycles.
Test Module Display
01
NB-IoT Module

02
2G Module


China Mobile Zhejiang IoT Laboratory
Test Capability Overview
NB-IoT Base Station
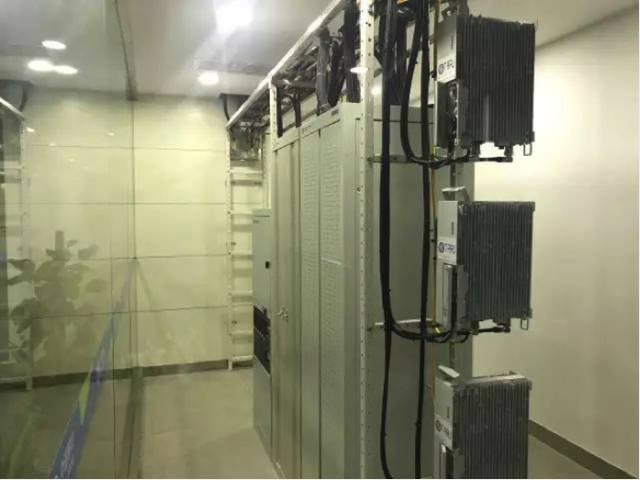

Function Description:
The IoT laboratory has built a small NB-IoT base station to facilitate manufacturers to conduct relevant NB-IoT function tests, network signal parameter configurations, and problem location. The NB-IoT network environment in the laboratory is consistent with the external commercial NB-IoT network, allowing manufacturers to directly commercialize through testing.
DC Current Analyzer
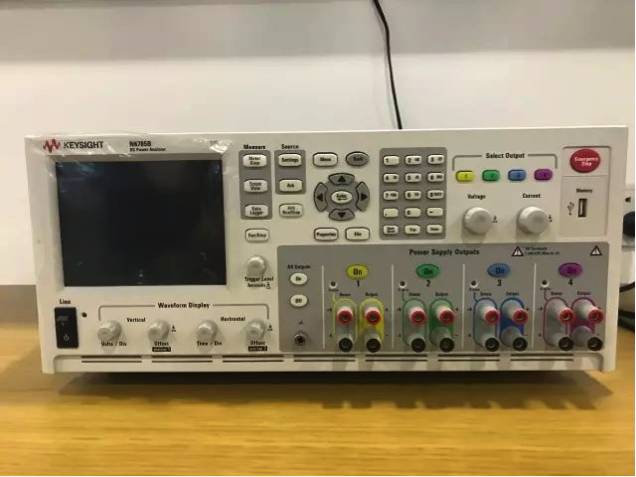

Function Description:
For the power consumption verification tests of NB-IoT low-power performance, the laboratory has high-priced purchased the Keysight N6705B power analyzer. The wide range of power supply output, long-term data recording, and high-precision current measurement have enabled the power consumption testing of NB-IoT.
Power Consumption Testing Method

Testing Environment
Location: Mobile IoT Laboratory
Voltage: Power analyzer 3.8V power supply
Test Sub-board: Using a specially made sub-board module in the laboratory to ensure consistency of peripheral circuits
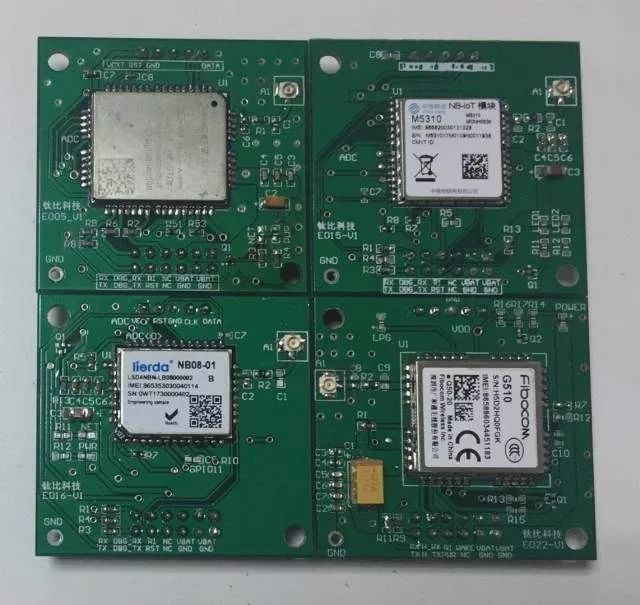

Firmware Version Information:
Quectel Module: V100R100C10B657SP1
China Mobile IoT Module: V100R100C10B657SP1
Lierda Module: V100R100C10B657SP1
2G Module: G510_V0D.00.47
Note: The 2G module in the experiment used the default configuration for testing
Testing Content
Peak Current Testing for Module Networking
Average Current Testing in IDLE State
Average Current Testing in PSM
Average Current Testing for a Complete Packet Sending Task
Testing Steps
1. Power on the module being tested, start recording the current waveform, and begin testing;
2. The testing module successfully attaches to the network;
3. The module does not send or receive data, enters IDLE state, and waits for T3324 timeout, entering PSM mode;
4. Send uplink data, the module wakes up from PSM low power mode, then enters IDLE state, with no data interaction, and finally re-enters PSM sleep mode;
5. From the recorded current waveform, extract the peak current/average current for each mode, which can further calculate the power consumption for each mode;
Evaluation Results
Dimensions
Module
Length/mm
Width/mm
Thickness/mm
BC95
19.9
23.6
2.2
M5310
19.0
18.4
2.2
NB08
20
16
2.2
2G Module
20.2
22.2
2.5
All four modules have the characteristic of small size, which can maximally meet the demand for small-sized module products in terminal devices.
Power Consumption
In this power consumption test, all modules used a 3.8V power supply, and the power consumption data was obtained by averaging three repeated experiments.
Peak Current Comparison for Networking
Average Current Comparison in IDLE State
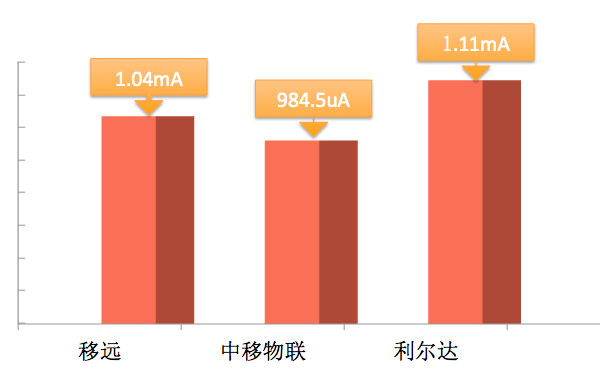
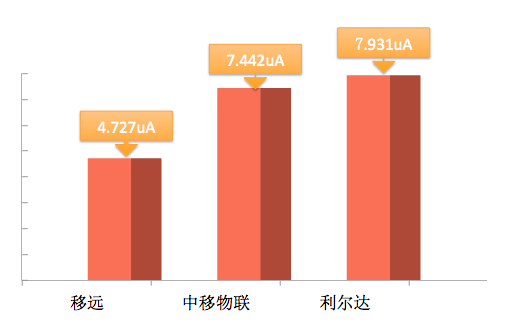
Average Current Comparison in PSM State
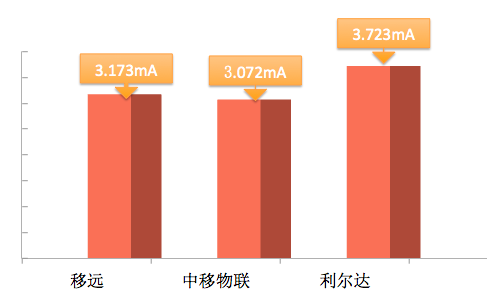
Average Current Comparison for a Complete Packet Sending Task
Measured Result Charts
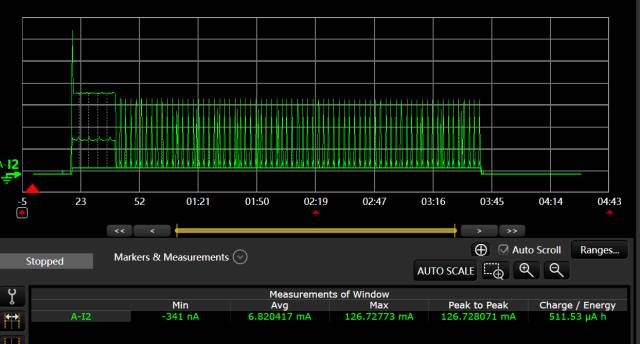
The above image shows the testing process of the Quectel module observed from the DataLogger of the N6705B DC power analyzer. The NB-IoT module is in PSM sleep mode, sends uplink data, exits PSM mode, connects to the network, sends UDP packets, and after 20s of no data interaction, enters IDLE mode. The duration of this state is controlled by the Active timer (T3324=3min), and after 3min of no data interaction, it re-enters PSM mode.
NB-IoT vs GPRS Power Consumption Comparison
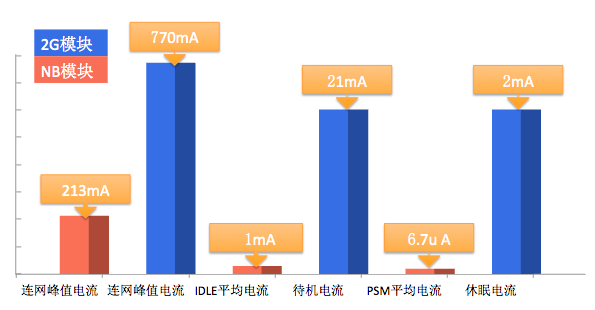
Note: The data for the NB-IoT modules is the average of three modules


Conclusion
Based on the Zhejiang Mobile IoT Open Laboratory, we completed this NB-IoT module power consumption test. By analyzing the power consumption of the selected three NB-IoT modules and the GPRS module under various working states, it can be seen that NB-IoT has significant advantages in low power consumption, whether in peak current during networking or in PSM sleep mode, the power consumption is far lower than that of traditional 2G modules.
The Zhejiang Mobile IoT Open Laboratory is equipped with high-end power analyzers, which facilitate precise and complete power consumption analysis. At the same time, it has built a full-link environment for NB-IoT coverage testing, allowing manufacturers to verify the signal sensitivity of NB-IoT terminal products and other functional performance tests.
Everyone is welcome to visit for communication and testing!
To apply, please reply “application form” on the public account interface, fill it out as required, and submit it to the laboratory email[email protected].

Scan to Follow Us