On Linux systems, using systemd allows for easy control of the frps server’s startup, shutdown, background configuration, and automatic startup on boot. Below are the specific operational steps:
1. Install systemd
If systemd is not yet installed on your Linux server, you can use a package manager such as yum (for CentOS/RHEL) or apt (for Debian/Ubuntu) to install it:
# Install systemd using yum (CentOS/RHEL)
sudo yum install systemd
# Install systemd using apt (Debian/Ubuntu)
sudo apt install systemd2. Create the frps.service file
Use a text editor (such as vim) to create a <span>/etc/systemd/system</span> directory with a <span>frps.service</span> file to configure the frps service:
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/frps.service
3. Write the content
In the <span>frps.service</span> file, write the following content:
[Unit]
Description=frp server
After=network.target syslog.target
Wants=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/path/to/frps -c /path/to/frps.toml
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetReplace <span>/path/to/frps</span> with the actual path to frps, and <span>/path/to/frps.toml</span> with the path to the frps configuration file.
4. Manage the frps service using systemd commands
# Start frps
sudo systemctl start frps
# Stop frps
sudo systemctl stop frps
# Restart frps
sudo systemctl restart frps
# Check frps status
sudo systemctl status frps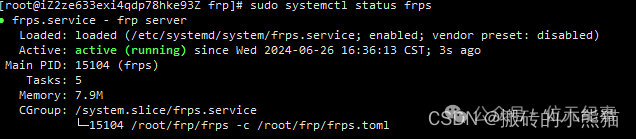
5. Set frps to start on boot
sudo systemctl enable frpsConclusion
By following the above steps, you can manage the frps service on Linux systems using systemd, including starting, stopping, restarting, checking status, and configuring it to start automatically on boot. This makes the management of frps more convenient and automated.