
✦
Course Outline
✦

1
Course Introduction
The rapid development of mobile internet is inseparable from the smartphone operating system, and among different mobile operating systems, the Android system dominates globally. Android is an open-source operating system based on Linux, mainly used for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android Studio is an IDE developed by Google for Android developers.
This course is a theory and practice-oriented course. In order to achieve the expected teaching effect and objectives, the teaching content listed in the outline can be taught through typical example explanations using multimedia electronic courseware, necessary on-site practical demonstrations, appropriate classroom exercises, computer experiments that complement theoretical courses, and timely tutoring and Q&A. This outline has clearly defined key content and general understanding and comprehension in the teaching content of each chapter.
2
Teaching Objectives
Using an exploratory and innovative perspective, learn and master the application program development of the Android operating system from basic to advanced, understand the composition and principles of the Android framework, master the use of Android resources, component and user interface development, and be familiar with Android’s data access, multimedia development, and network communication. At the same time, cultivate students’ ability to master basic innovative methods, have an attitude and awareness of pursuing innovation, think independently, analyze problems, and solve practical problems using computer programming; and cultivate students’ project development capabilities, teamwork spirit, and self-learning abilities to adapt to the requirements of an information society while acquiring new knowledge and technologies in computer science.
3
Assessment Format and Grade Calculation
This course is a school examination course, and the final assessment is a closed-book written exam. The composition of the total evaluation score for the course is: the final exam score accounts for 60% of the total evaluation score, practical work accounts for 20%, and homework accounts for 20%.
4
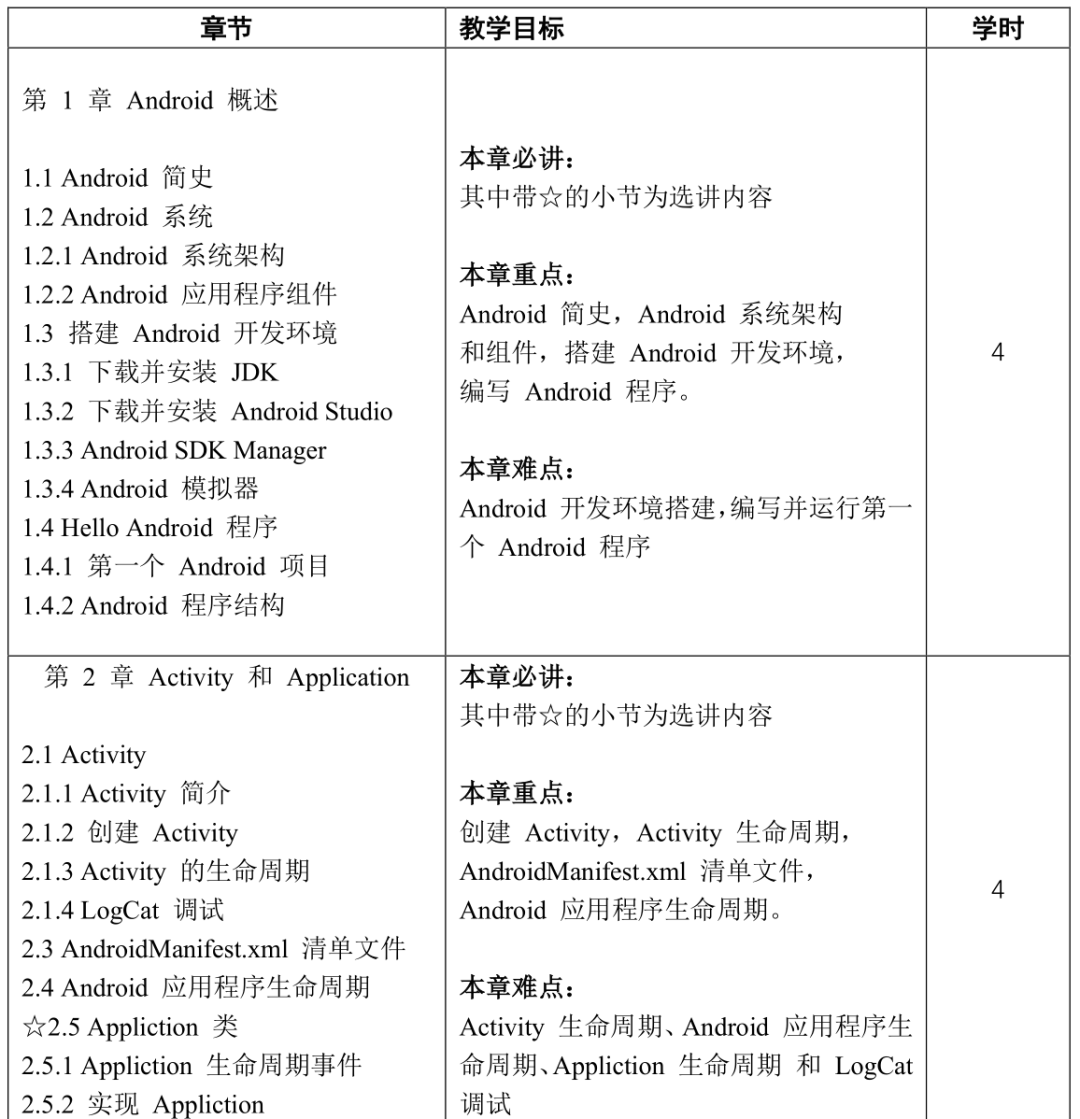
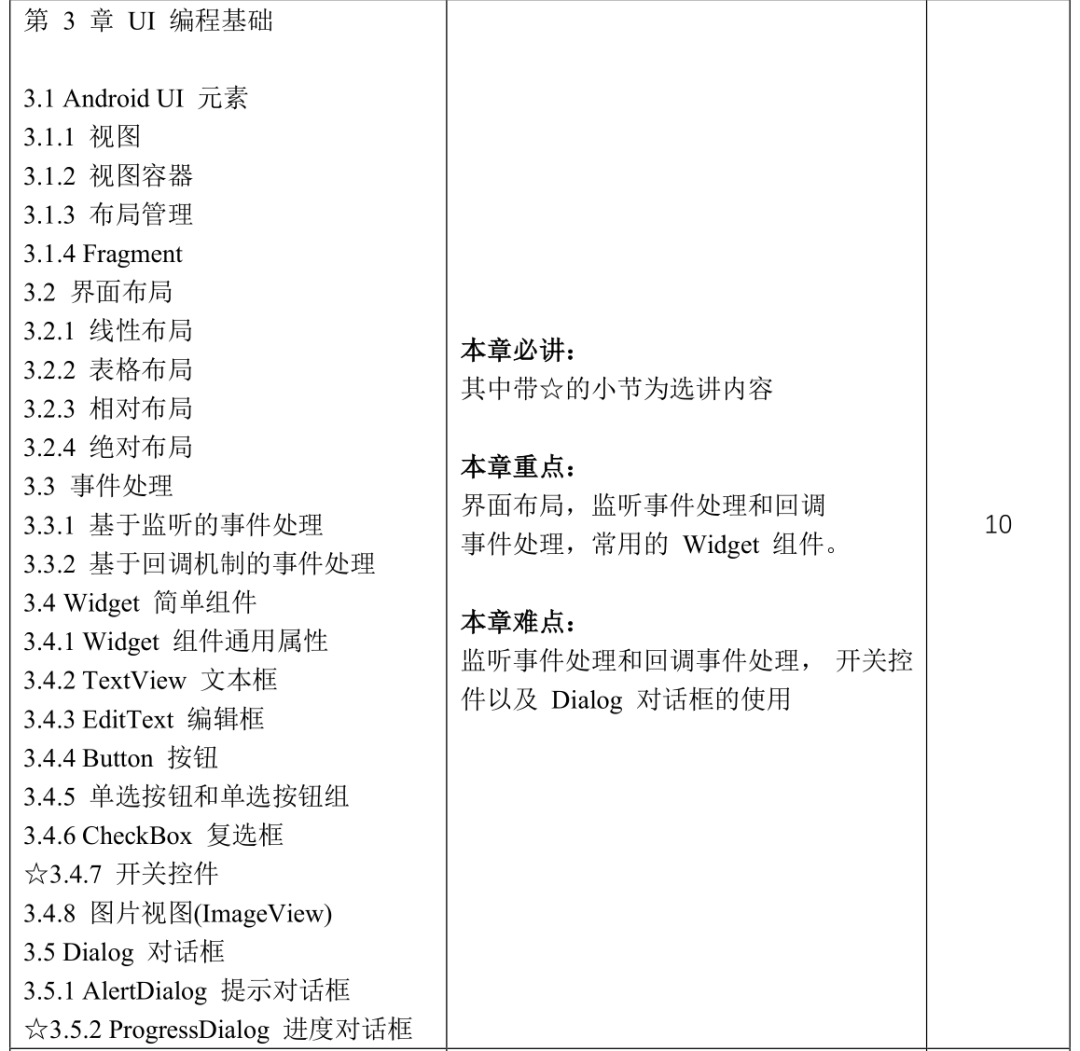
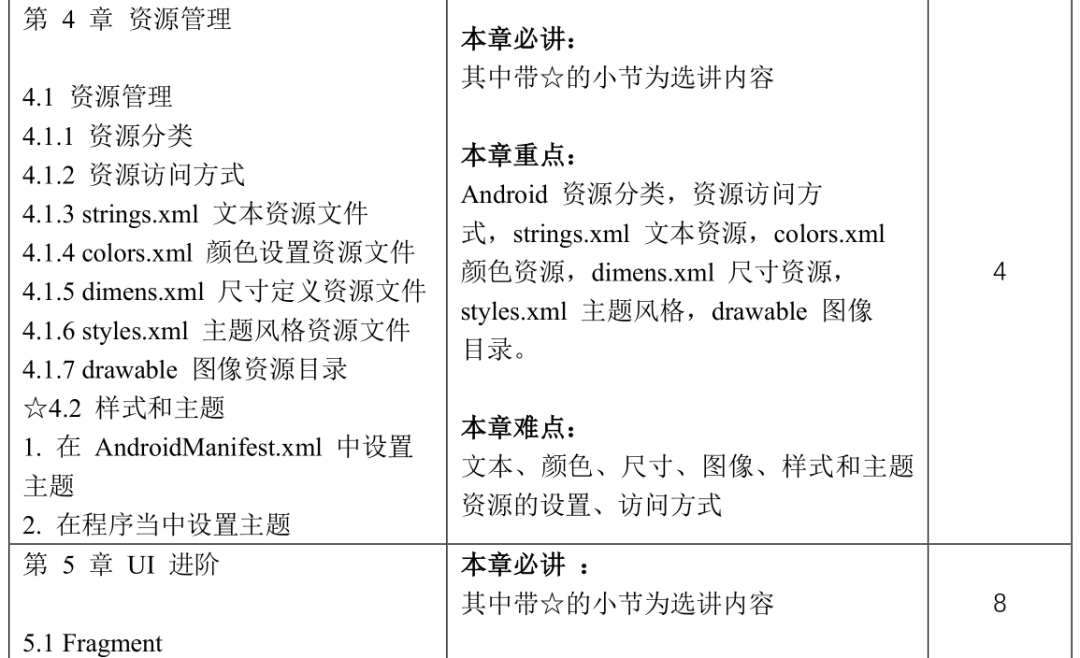
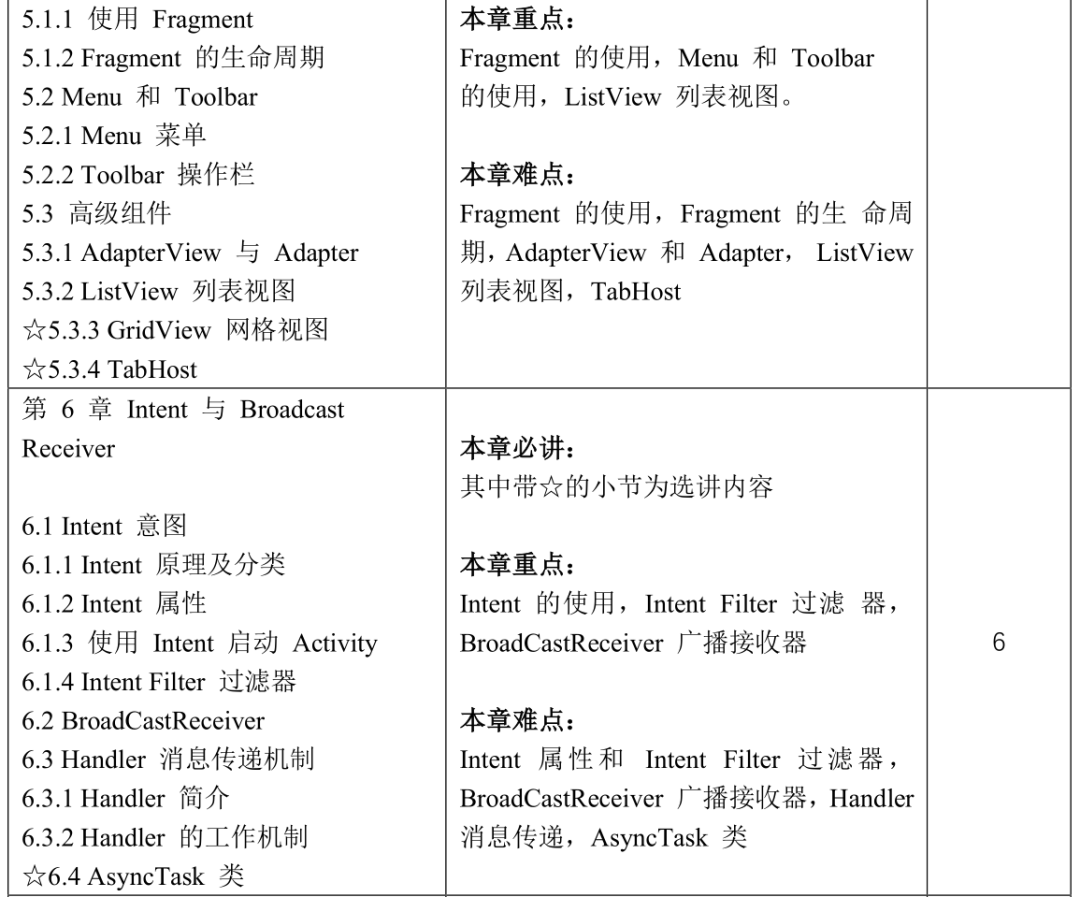
Course Content and Reference Class Hour Distribution
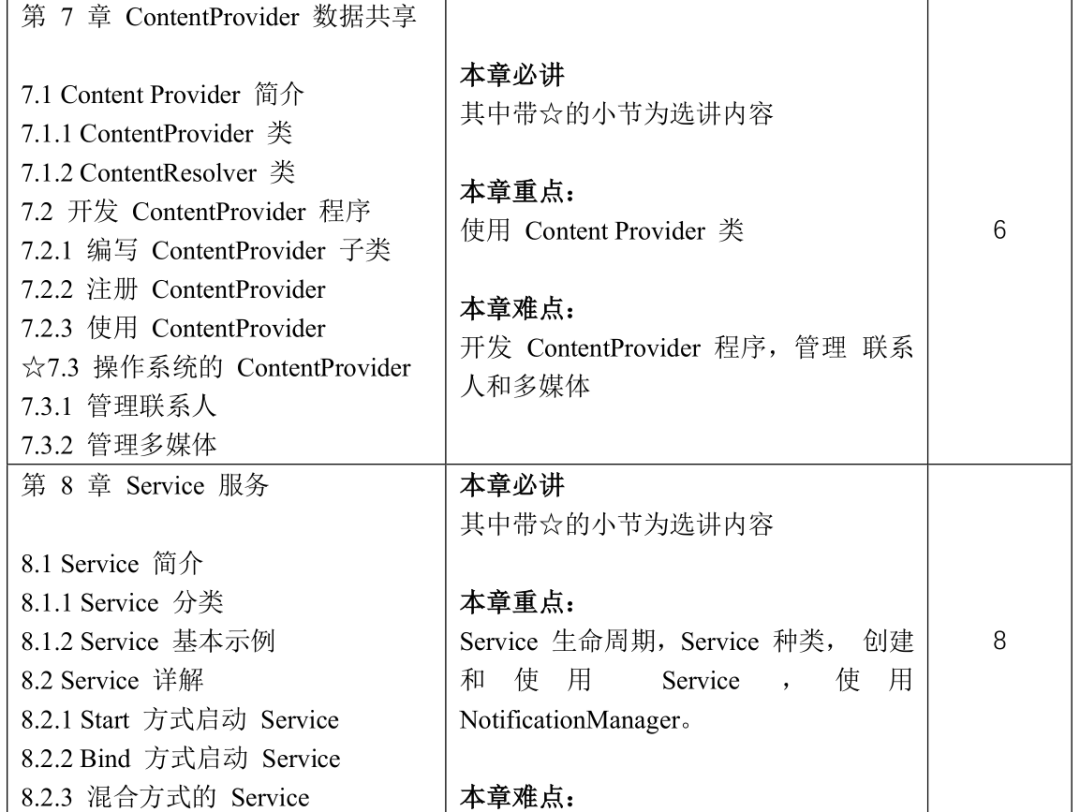
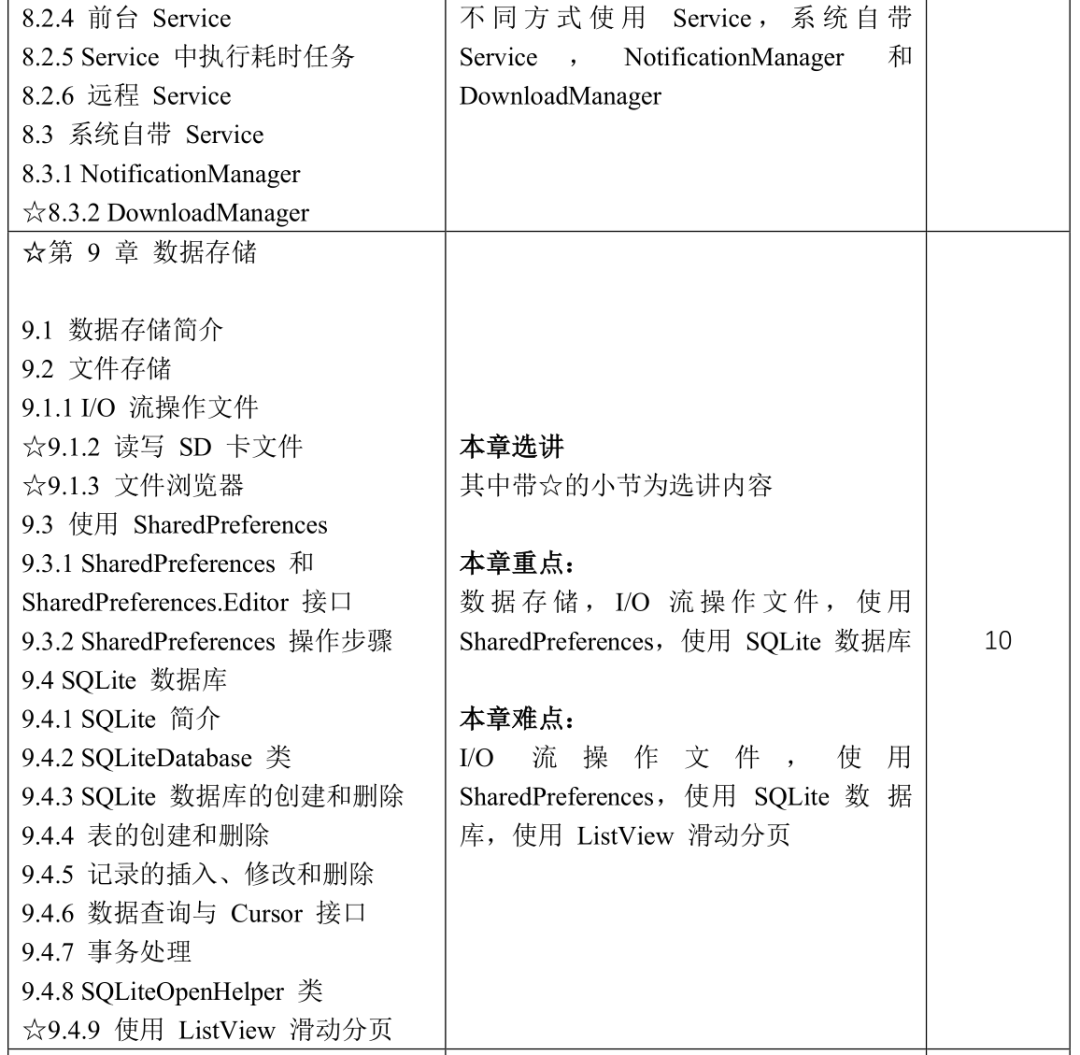
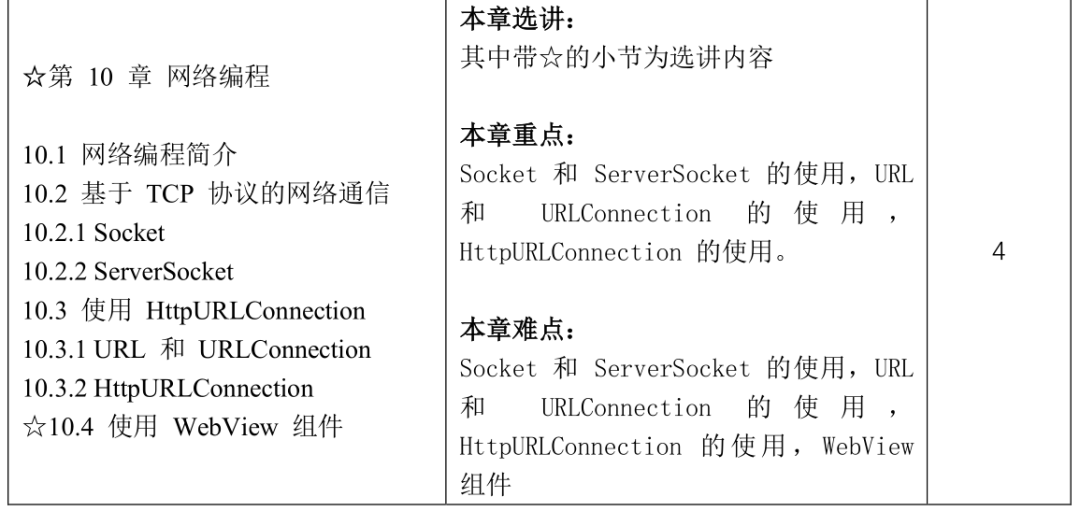
5
Reference Textbooks
1. Main Textbook
Zhao Keling. Android Studio Programming Case Tutorial – Micro Course Edition (2nd Edition). Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2023. ISBN 9787302627449.
2. Reference Books
[1] (UK) Reto Meier. Android 2 Advanced Programming (2nd Edition). Wang Chao, Trans. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2010.
[2] Guo Hongzhi. Android Application Development Details. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2010.
[3] Yang Fengsheng. Android Application Development Revealed. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2011.
[4] Shi Weiming. Android APP Development Introduction: Using Android Studio Environment. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2016.
[5] Zhao Keling. Android Studio Programming Case Tutorial. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018.
6
Supporting Resources
Micro-course videos, PPT courseware, teaching outlines, exam outlines, exam papers, 200+ case source codes, exercise answers.
✦
Reference Books
✦

《Android Studio Programming Case Tutorial – Micro Course Edition (2nd Edition)》
ISBN:9787302627449
Author: Zhao Keling, Lü Huailian
Price: 69 yuan
This book comes with practical operation videos, PPT, teaching outlines, exam outlines, papers, source codes, and exercise answers.
Content Introduction
Starting from applications, this book deeply analyzes and comprehensively explains Android technology, covering Android overview, Activity and Application, UI programming basics, resource management, advanced UI, Intent and BroadcastReceiver, ContentProvider data sharing, Service, data storage, and network programming. All code in the book is based on Android version 12.0 and has been debugged and run in the new Android Studio development environment. The content involves the new features of Android versions 10.0, 11.0, and 12.0, as well as commonly used Android Studio environment configurations, shortcuts, and program signatures, making it easier for beginners to learn and refer to.
Catalog
Swipe up to view
Chapter 1 Android Overview
1.1 History of Android
1.2 Android System
1.2.1 Android System Architecture
1.2.2 Android Application Components
1.3 Setting Up Android Development Environment
1.3.1 Downloading and Installing Android Studio
1.3.2 Android SDK Manager
1.3.3 Android Emulator
1.4 Hello Android Program
1.4.1 First Android Project
1.4.2 Android Program Structure
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 2 Activity and Application
2.1 Activity
2.1.1 Introduction to Activity
2.1.2 Creating Activity
2.1.3 Activity Lifecycle
2.1.4 Logcat Debugging
2.2 AndroidManifest.xml Manifest File
2.3 Android Application Lifecycle
2.4 Application Class
2.4.1 Application Lifecycle Events
2.4.2 Implementing Application
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 3 UI Programming Basics
3.1 Android UI Elements
3.1.1 Views
3.1.2 View Containers
3.1.3 Layout Management
3.1.4 Fragments
3.2 Interface Layout
3.2.1 Linear Layout
3.2.2 Table Layout
3.2.3 Relative Layout
3.2.4 Absolute Layout
3.3 Event Handling
3.3.1 Event Handling Based on Listeners
3.3.2 Event Handling Based on Callback Mechanism
3.4 Widget Simple Components
3.4.1 Common Properties of Widget Components
3.4.2 TextView
3.4.3 EditText
3.4.4 Button
3.4.5 Radio Button and Radio Button Group
3.4.6 CheckBox
3.4.7 Switch Control
3.4.8 ImageView
3.5 Dialogs
3.5.1 AlertDialog
3.5.2 ProgressDialog
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 4 Resource Management
4.1 Overview of Resource Management
4.1.1 Resource Classification
4.1.2 Resource Access Methods
4.1.3 strings.xml Text Resource File
4.1.4 colors.xml Color Setting Resource File
4.1.5 dimens.xml Size Definition Resource File
4.1.6 styles.xml Theme Style Resource File
4.1.7 drawable Image Resource Directory
4.2 Styles and Themes
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 5 Advanced UI
5.1 Fragments
5.1.1 Using Fragments
5.1.2 Fragment Lifecycle
5.2 Menu and Toolbar
5.2.1 Menu
5.2.2 Toolbar
5.3 Advanced Components
5.3.1 AdapterView and Adapter
5.3.2 ListView
5.3.3 GridView
5.3.4 TabHost
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 6 Intent and BroadcastReceiver
6.1 Intent
6.1.1 Intent Principles and Classification
6.1.2 Intent Properties
6.1.3 Starting Activity with Intent
6.1.4 Intent Filter
6.2 BroadcastReceiver
6.3 Handler Messaging Mechanism
6.3.1 Introduction to Handler
6.3.2 Handler Working Mechanism
6.4 AsyncTask Class
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 7 ContentProvider Data Sharing
7.1 Introduction to ContentProvider
7.1.1 ContentProvider Class
7.1.2 ContentResolver Class
7.2 Developing ContentProvider Programs
7.2.1 Writing ContentProvider Subclass
7.2.2 Registering ContentProvider
7.2.3 Using ContentProvider
7.3 Operating System’s ContentProvider
7.3.1 Managing Contacts
7.3.2 Managing Multimedia
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 8 Service
8.1 Introduction to Service
8.1.1 Service Classification
8.1.2 Basic Example of Service
8.2 Service Details
8.2.1 Starting Service in Start Mode
8.2.2 Starting Service in Bind Mode
8.2.3 Mixed Mode Service
8.2.4 Foreground Service
8.2.5 Executing Time-consuming Tasks in Service
8.2.6 Remote Service
8.3 System Built-in Services
8.3.1 NotificationManager
8.3.2 DownloadManager
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 9 Data Storage
9.1 Introduction to Data Storage
9.2 File Storage
9.2.1 I/O Stream Operations on Files
9.2.2 Reading and Writing SD Card Files
9.2.3 File Browser
9.3 Using SharedPreferences
9.3.1 SharedPreferences and SharedPreferences.Editor Interface
9.3.2 SharedPreferences Operation Steps
9.4 SQLite Database
9.4.1 Introduction to SQLite
9.4.2 SQLiteDatabase Class
9.4.3 Creating and Deleting SQLite Database
9.4.4 Creating and Deleting Tables
9.4.5 Inserting, Modifying, and Deleting Records
9.4.6 Data Query and Cursor Interface
9.4.7 Transaction Handling
9.4.8 SQLiteOpenHelper Class
9.4.9 Using ListView for Paging
Summary
Exercises
Chapter 10 Network Programming
10.1 Introduction to Network Programming
10.2 TCP-based Network Communication
10.2.1 Socket
10.2.2 ServerSocket
10.3 Using HttpURLConnection
10.3.1 URL and URLConnection
10.3.2 HttpURLConnection
10.4 Using WebView Component
Summary
Exercises
Appendix A New Features of Android Versions
A.1 New Features of Android 10.0
A.2 New Features of Android 11.0
A.3 New Features of Android 12.0
Appendix B Common Android Studio Settings
B.1 Basic Configuration of Android Studio
B.2 Android Studio Shortcuts
Appendix C Android Application Signature
C.1 Completing APK Signature via DOS Command
C.2 Completing APK Signature in Android Studio

Scan the QR code for discounts on books
Click the link below to subscribe to the 【Teaching Outline】 section