-Begin-
Siemens, Mitsubishi, and Omron are the three most commonly used PLC brands in our automation industry. Today, I will share an analysis of the Mitsubishi PLC MC communication protocol.When learning the MC communication protocol, it is recommended to first master the Modbus communication protocol.The MC protocol of Mitsubishi PLC is a data communication protocol used for data transmission between computers and Mitsubishi PLCs. The MC protocol is unique to Mitsubishi and is primarily used for controlling Mitsubishi PLCs.MC protocol is short for Melsec protocol.
1. Communication Frame Types
Many people find it challenging to learn the Mitsubishi PLC communication protocol due to the numerous types of communication frames, each of which has both ASCII and binary encoding formats.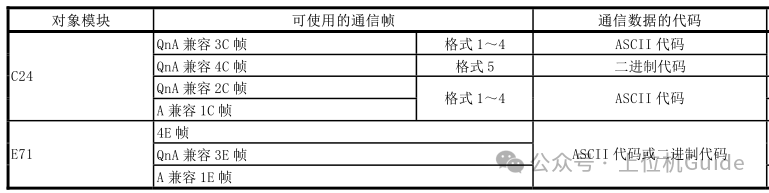 In our actual development, Ethernet communication mainly uses the QnA compatible 3E frame (FX5U series/Q series/Qna series/L series/R series) if it is FX3U, by adding the Fx3U-ENET-ADP, it will use the A compatible 1E frame. For serial devices, QnA compatible 2C frame or QnA compatible 4C frame is generally used.The communication encoding format can be either ASCII or binary. Compared to communication using ASCII encoding, communication using binary encoding has about half the data volume, thus making binary encoding more efficient.
In our actual development, Ethernet communication mainly uses the QnA compatible 3E frame (FX5U series/Q series/Qna series/L series/R series) if it is FX3U, by adding the Fx3U-ENET-ADP, it will use the A compatible 1E frame. For serial devices, QnA compatible 2C frame or QnA compatible 4C frame is generally used.The communication encoding format can be either ASCII or binary. Compared to communication using ASCII encoding, communication using binary encoding has about half the data volume, thus making binary encoding more efficient.
2. PLC Configuration
Mitsubishi PLCs differ from Siemens PLCs.
Siemens PLCs have a fixed port 102, which supports multiple connections.
Mitsubishi PLCs require manual port addition, with each port supporting only one connection.
Therefore, Mitsubishi PLCs need to be manually configured. Here, we take the Mitsubishi R series as an example:
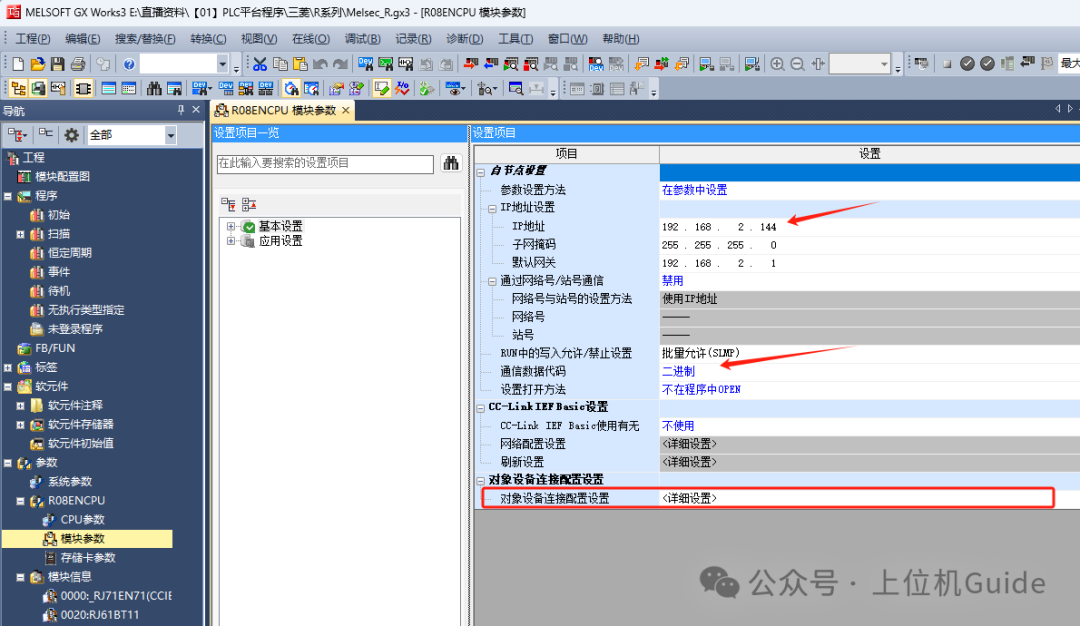
1. In the navigation, through the parameter>>R08ENCPU>> Module Parameters, double-click to set theIP address information of the PLC in the opened interface, change the communication data code to binary, and then find the [Object Device Connection Configuration Settings]:
2. Click settings, you can drag in multiple SLMP connected devices, set the port number according to your needs, then apply the settings and close to finish. After completing the settings, re-download the PLC program and power cycle the PLC.
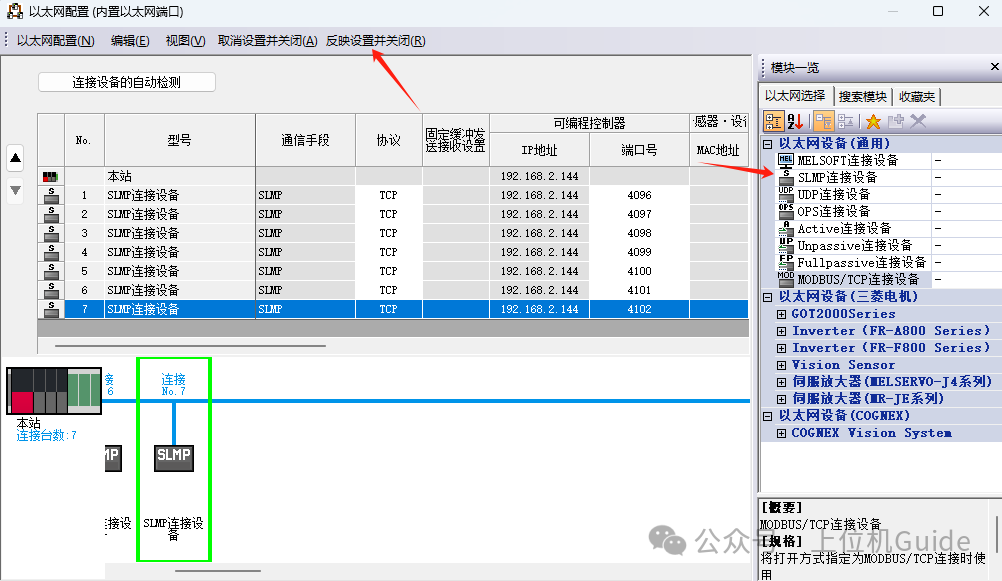 SLMP (Seamless Message Protocol) is a protocol used in Ethernet.The MC protocol includes both serial and Ethernet communication protocols, covering a wider range.
SLMP (Seamless Message Protocol) is a protocol used in Ethernet.The MC protocol includes both serial and Ethernet communication protocols, covering a wider range.
3. Reading Protocol Frames
Next, we will analyze the Mitsubishi communication message, taking the QnA compatible 3E frame as an example; other communication frames are similar.
Protocol frames are generally divided into request frames, response frames, and exception frames.
Request Frame: Represents the message for sending a request.
Response Frame: If the request is correct, the PLC will return with a response frame.
Exception Frame: If the request is incorrect, the CPU will return with an exception frame.
Format of the Read Request Frame:
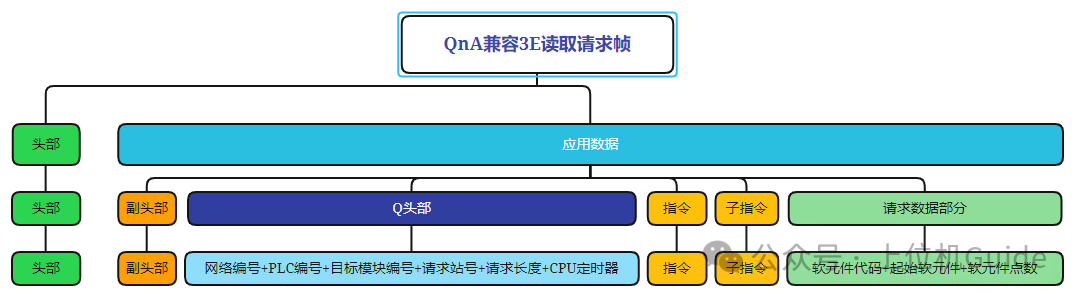
Format of the Read Response Frame:
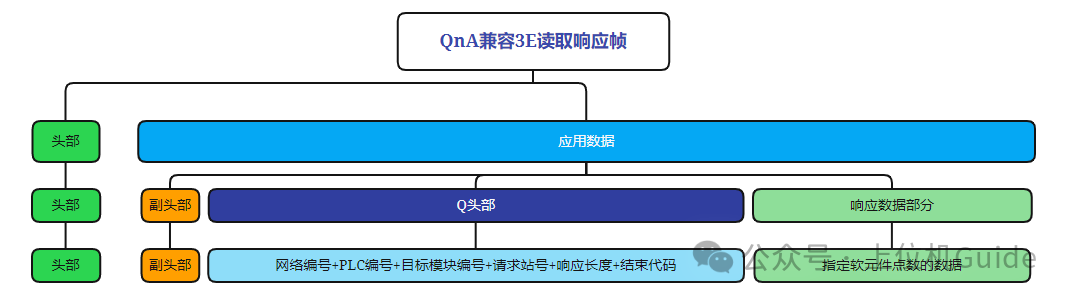
Format of the Read Exception Frame:
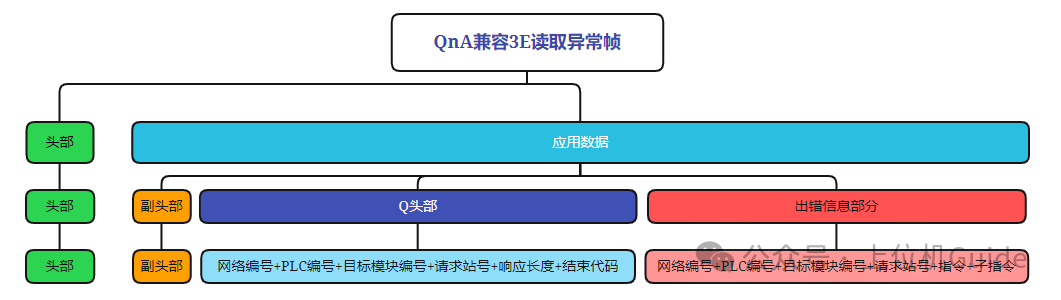
Note: The above three types of protocol frames are summarized based on Mitsubishi’s official documentation, where the header refers to the TCP header, which we can ignore.
4. Writing Protocol Frames
Format of the Write Request Frame: 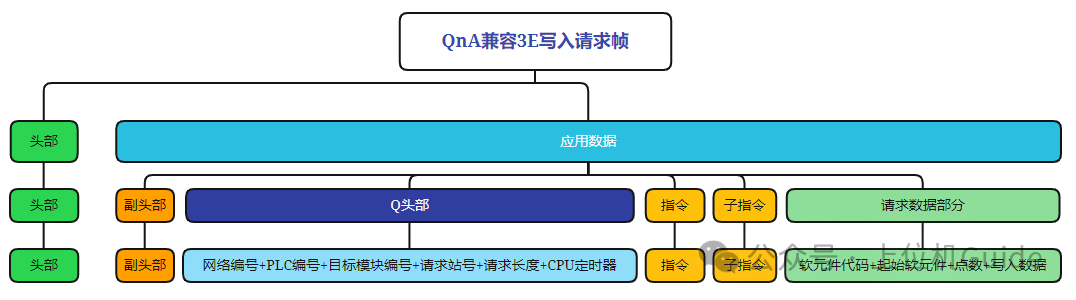
Format of the Write Response Frame:
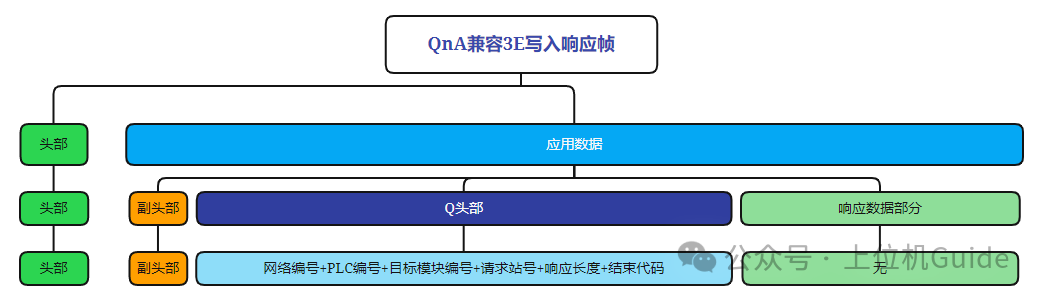
Format of the Write Exception Frame:
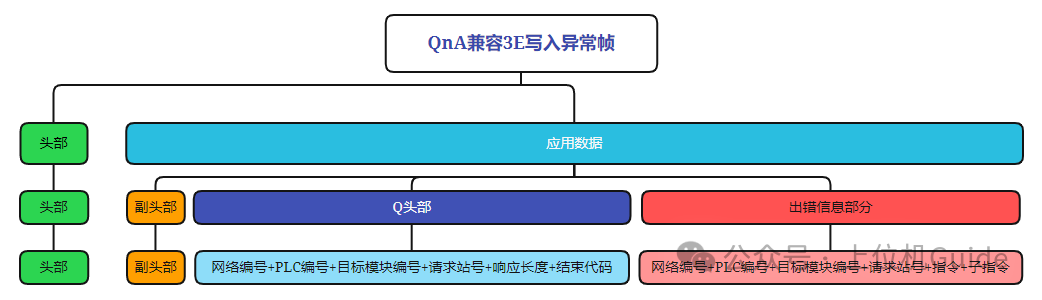
Note: If we have learned Modbus, we can see that the protocols are interconnected; MC is just more complex than the Modbus message structure.
5. Communication Testing
We will take reading the first 5 registers starting from D0 as an example, combining the protocol documentation to splice the message.
The sent message is as follows:
Sub-header: 0x50 0x00
Network Number: 0x00
PLC Number: 0xFF
Request Target Module I/O Number: 0xFF 0x03
Request Target Module Station Number: 0x00
Request Data Length: 0x0C 0x00
CPU Monitor Timer: 0x0A 0x00
Instruction: 0x01 0x04
Sub-instruction: 0x00 0x00
Starting Soft Element: 0x00 0x00 0x00
Soft Element Code: 0xA8
Soft Element Count: 0x05 0x00
We send this message through the network debugging assistant and observe the returned message:
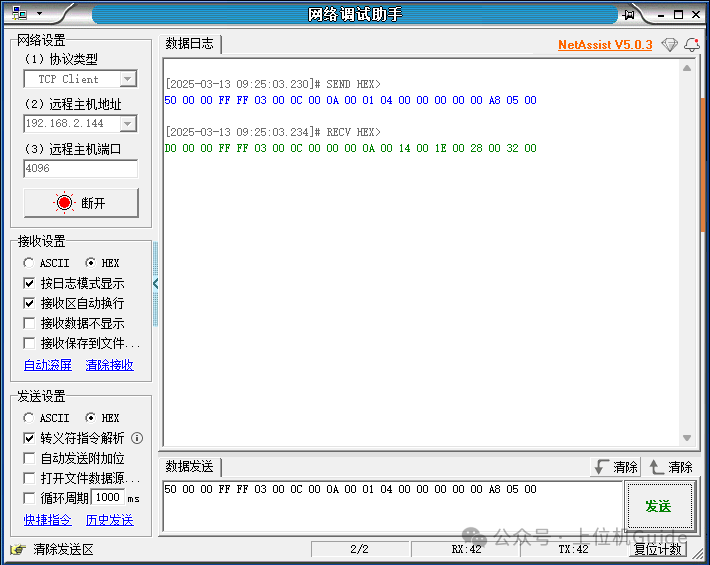
The response message is as follows:
Sub-header: 0xD0 0x00
Network Number: 0x00
PLC Number: 0xFF
Request Target Module I/O Number: 0xFF 0x03
Request Target Module Station Number: 0x00
Response Data Length: 0x0C 0x00
End Code: 0x00 0x00
Soft Element Data: 0x0A 0x00 0x14 0x00 0x1E 0x00 0x28 0x00 0x32 0x00
Where 0x0A 0x00 0x14 0x00 0x1E 0x00 0x28 0x00 0x32 0x00 represents the values of D0-D4, and the processed values after data parsing are 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, which are consistent with the PLC data.
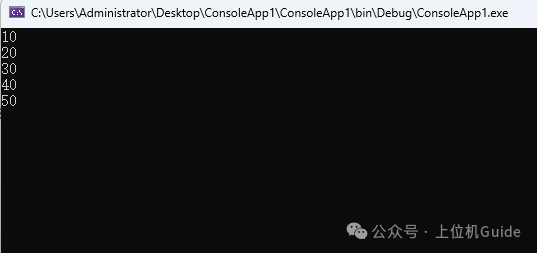
6. Code Implementation
We can also write a C# program to implement the entire process.
Here, the test is the main focus, and the code is relatively simple. In actual applications, it can be further encapsulated. The code is as follows:
static void Main(string[] args){ // Connect Socket socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); socket.Connect("192.168.2.144", 4096);
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 0x50,0x00,//Sub-header, fixed 50 00 0x00,// Network Number 0xFF,//PLC Number 0xFF,0x03,//Target Module I/O Number, fixed FF 03 0x00,// Target Module Station Number 0x0C,0x00, // Byte Length, current byte forward 0x0A,0x00,//PLC response timeout, calculated in 250ms units 0x01,0x04,// Batch read, main command 0x00,0x00,// Word operation, sub-command 0x00,0x00,0x00,// Starting address 0xA8,// Area code 0x05,0x00 //Read length }; socket.Send(bytes); byte[] respBytes = new byte[1024]; int count = socket.Receive(respBytes);
if (count == 21) { for (int i = 11; i < count; i+=2) { // Little-endian processing, every 2 bytes as one data byte[] dataBytes = new byte[2]; dataBytes[0] = respBytes[i]; dataBytes[1] = respBytes[i+1]; Console.WriteLine(BitConverter.ToInt16(dataBytes, 0)); } }}The output result is as follows:
 Finally, if you find this article helpful, please give it a like to support! Your support is my motivation to continue sharing knowledge. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to leave a message. You can also join the WeChat public account[DotNet Technology Craftsman] community to exchange insights with other technology enthusiasts and grow together!
Finally, if you find this article helpful, please give it a like to support! Your support is my motivation to continue sharing knowledge. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to leave a message. You can also join the WeChat public account[DotNet Technology Craftsman] community to exchange insights with other technology enthusiasts and grow together!
Author: Little Code Craftsman
Source: gitee.com/smallcore/DotNetCoreStatement: Online content is for learning purposes only, respecting copyright, infringement will be deleted promptly, apologies and thanks!ENDFacilitating communication, resource sharing, and mutual growthPure technical exchange group, those who want to join please scan the code and note【Join Group】

Recommended ReadingWPF Visual Development Integrated Hikvision Operator for Image Processing.NET Lightweight Key Mouse Recording and Playback Automation Extension LibraryC# Open Source USBCAN Device, Comprehensive Solution from Hardware to Upper ComputerHigh-Performance Industrial Vision Image Display Control Based on C# (Pure Native Without Dependencies).NET 8 Industrial PLC Communication Library: Achieving Functions Comparable to KepServerWPF General SCADA Upper Computer Framework, Zero Deployment Database and Industrial Interface PracticeOpen Source HMI/SCADA System, Powerful Web Configuration Tool with Low-Code Drag-and-Drop Design.NET Industrial All-in-One Tool Library (High-Precision Timing, Reliable Communication, Efficient File and Image Processing)
Do you feel you have gained something? Please share to benefit more people
Follow “DotNet Technology Craftsman“, to enhance technical strength together
 Collect
Collect Like
Like Share
Share Looking
Looking