The market demand for MCUs has gradually revealed new characteristics and trends in 2024 after experiencing fluctuations in the previous two years. Although international MCU giants are generally under pressure in their 2024 financial reports, Chinese MCU companies are seizing opportunities to increase their market share amid the global industrial chain restructuring…According to the “2024 Global Semiconductor Market Review and 2025 Outlook Report” released by the World Semiconductor Council (WICA), the global semiconductor market size in 2024 is projected to be $635.1 billion, a year-on-year increase of 19.8%. It is expected that the global semiconductor market size will rise to $718.9 billion in 2025, with a year-on-year growth of 13.2%. Market research firm IDC also estimates that the broad Foundry 2.0 market (including wafer foundry, non-memory IDM, OSAT, and photomask manufacturing) will reach $298 billion in 2025, a year-on-year increase of 11%.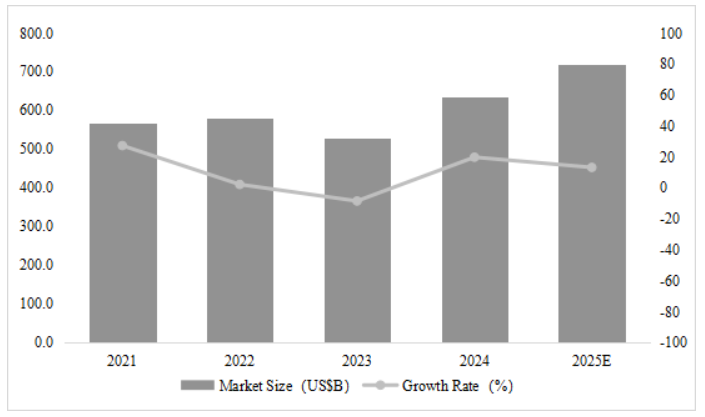 Multiple factors indicate that after a partial recovery of the global semiconductor market in 2024, steady growth is expected to continue in 2025, driven primarily by the sustained growth in AI demand and the gradual recovery of non-AI demand.Domestically, since 2025, the A-share semiconductor sector has shown a dual-driven pattern of “self-controllable” and “demand recovery.” According to a report by Cinda Securities, the institutional holding market value ratio of the semiconductor sector in the first quarter of 2025 was 11.01%, an increase of 1.67 percentage points from the previous quarter. From a fundamental perspective, the semiconductor downstream prosperity is gradually warming, with inventory levels in multiple fields dropping to low positions; from an external environment perspective, in January, the U.S. BIS released a temporary final rule regarding the diffusion of artificial intelligence, while imposing sanctions on chips with a process of 16nm and below, reinforcing the market’s recognition of self-controllable logic; from a technological development perspective, domestic AI chips are continuously breaking through, while ASIC demand elasticity is becoming apparent.From the perspective of institutional position allocation, companies such as SMIC, Chipone, Lattice Semiconductor, Weir Shares, and GigaDevice have received significant institutional increases, reflecting strong market expectations for domestic substitution.
Multiple factors indicate that after a partial recovery of the global semiconductor market in 2024, steady growth is expected to continue in 2025, driven primarily by the sustained growth in AI demand and the gradual recovery of non-AI demand.Domestically, since 2025, the A-share semiconductor sector has shown a dual-driven pattern of “self-controllable” and “demand recovery.” According to a report by Cinda Securities, the institutional holding market value ratio of the semiconductor sector in the first quarter of 2025 was 11.01%, an increase of 1.67 percentage points from the previous quarter. From a fundamental perspective, the semiconductor downstream prosperity is gradually warming, with inventory levels in multiple fields dropping to low positions; from an external environment perspective, in January, the U.S. BIS released a temporary final rule regarding the diffusion of artificial intelligence, while imposing sanctions on chips with a process of 16nm and below, reinforcing the market’s recognition of self-controllable logic; from a technological development perspective, domestic AI chips are continuously breaking through, while ASIC demand elasticity is becoming apparent.From the perspective of institutional position allocation, companies such as SMIC, Chipone, Lattice Semiconductor, Weir Shares, and GigaDevice have received significant institutional increases, reflecting strong market expectations for domestic substitution.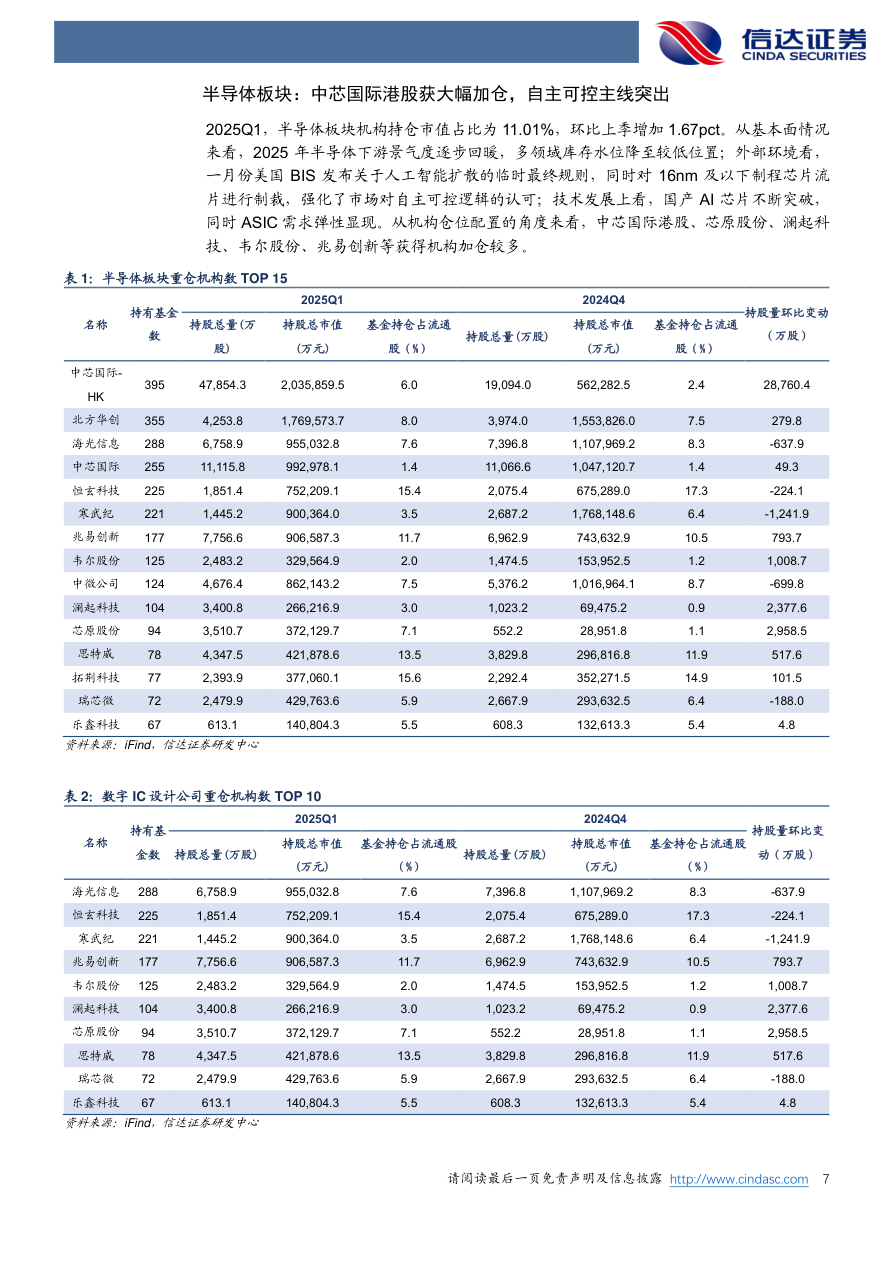 The market demand for MCUs has gradually revealed new characteristics and trends in 2024 after experiencing fluctuations in the previous two years. Although international MCU giants such as ST and NXP are generally under pressure in their 2024 financial reports, Chinese MCU companies are seizing opportunities to increase their market share amid the global industrial chain restructuring. With the support of domestic policies and industrial collaboration, they are actively responding to market changes, striving to enhance their competitiveness, and aiming to occupy a more favorable position in the global MCU market.This article organizes and analyzes the 2024 annual financial report data of 20 local listed semiconductor companies, combined with key news from some companies over the past year, to help readers understand the current state of the local MCU market and corporate layouts. Since most companies do not only have MCU products, this list does not rank them and does not include unlisted companies or listed companies that have not disclosed 2024 data (as of April 27).Overall Industry Situation: Recovery as the Main Line, Significant DifferentiationFrom the 2024 financial report data, the domestic MCU industry shows a differentiation characteristic of “head warming, tail pressure.”Among the 19 companies that have disclosed financial reports (as of April 27, Broadcom Integration has not yet released its financial report), 18 companies achieved positive revenue growth, with only Jiuquan Technology (-1.853%) experiencing negative growth. Guoxin Technology, although increasing by 27.78% year-on-year, saw a quarter-on-quarter decline of 49.75%, while Fudan Microelectronics (1.506%) and Neusoft Carrier (4.534%) had year-on-year growth rates below 5%.In terms of net profit, 6 companies are in a loss state, but leading companies show significant profit elasticity — GigaDevice, Silan Micro, Zhongwei Semiconductor, Puran Shares, and Shanghai Beiling all achieved a year-on-year net profit increase of over 500%, sweeping away the gloom of 2023. Meanwhile, companies such as Four-Dimensional Map, Guomin Technology, Guoxin Technology, Jingfeng Mingyuan, Chipsea Technology, and Hengshuo Shares are showing losses due to high R&D investments and delays in mass production of automotive-grade products. These 6 companies have been in losses for two consecutive years, with 4 companies reducing their losses and 2 companies increasing their losses.
The market demand for MCUs has gradually revealed new characteristics and trends in 2024 after experiencing fluctuations in the previous two years. Although international MCU giants such as ST and NXP are generally under pressure in their 2024 financial reports, Chinese MCU companies are seizing opportunities to increase their market share amid the global industrial chain restructuring. With the support of domestic policies and industrial collaboration, they are actively responding to market changes, striving to enhance their competitiveness, and aiming to occupy a more favorable position in the global MCU market.This article organizes and analyzes the 2024 annual financial report data of 20 local listed semiconductor companies, combined with key news from some companies over the past year, to help readers understand the current state of the local MCU market and corporate layouts. Since most companies do not only have MCU products, this list does not rank them and does not include unlisted companies or listed companies that have not disclosed 2024 data (as of April 27).Overall Industry Situation: Recovery as the Main Line, Significant DifferentiationFrom the 2024 financial report data, the domestic MCU industry shows a differentiation characteristic of “head warming, tail pressure.”Among the 19 companies that have disclosed financial reports (as of April 27, Broadcom Integration has not yet released its financial report), 18 companies achieved positive revenue growth, with only Jiuquan Technology (-1.853%) experiencing negative growth. Guoxin Technology, although increasing by 27.78% year-on-year, saw a quarter-on-quarter decline of 49.75%, while Fudan Microelectronics (1.506%) and Neusoft Carrier (4.534%) had year-on-year growth rates below 5%.In terms of net profit, 6 companies are in a loss state, but leading companies show significant profit elasticity — GigaDevice, Silan Micro, Zhongwei Semiconductor, Puran Shares, and Shanghai Beiling all achieved a year-on-year net profit increase of over 500%, sweeping away the gloom of 2023. Meanwhile, companies such as Four-Dimensional Map, Guomin Technology, Guoxin Technology, Jingfeng Mingyuan, Chipsea Technology, and Hengshuo Shares are showing losses due to high R&D investments and delays in mass production of automotive-grade products. These 6 companies have been in losses for two consecutive years, with 4 companies reducing their losses and 2 companies increasing their losses.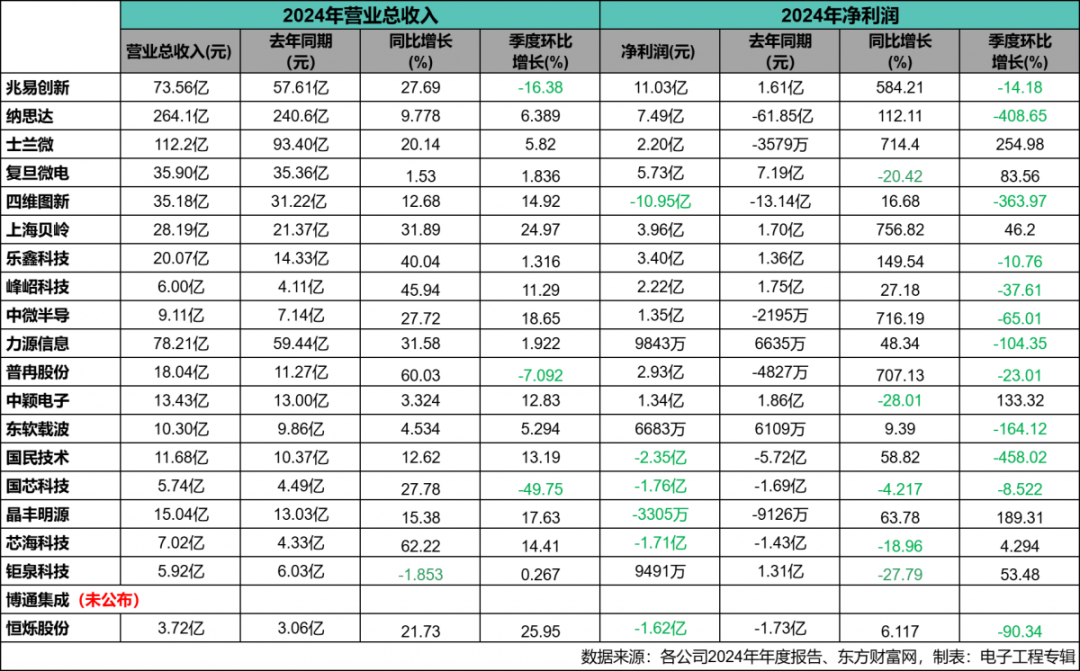 Overall, the recovery of consumer electronics, the increase in industrial control demand, and the deepening of domestic substitution are driving the core indicators of the industry to warm up, but the technical barriers and market cycle differences in subdivided fields lead to differentiated performance among companies.Ranking of Profit and LossIn terms of revenue performance, the top three total operating revenues are: Nasda (26.41 billion yuan), Silan Micro (11.22 billion yuan), and GigaDevice (7.356 billion yuan).The top three companies in year-on-year revenue growthare: Chipsea Technology (62.22%), Puran Shares (60.03%), and Peak Technology (45.94%). The only declining company is Jiuquan Technology (-1.853%).The top three companies in quarter-on-quarter revenue growthare: Hengshuo Shares (25.95%), Shanghai Beiling (24.97%), and Zhongwei Semiconductor (18.65%). The top three declining companies are: Guoxin Technology (-49.75%), GigaDevice (-16.38%), and Puran Shares (-7.092%).In terms of net profit performance, the top three profitable companies are: GigaDevice (1.103 billion yuan), Nasda (749 million yuan), and Fudan Micro (573 million yuan). The top three loss-making companies are: Four-Dimensional Map (-1.095 billion yuan), Guomin Technology (-235 million yuan), and Guoxin Technology (-176 million yuan).The top three companies in year-on-year net profit growthare: Shanghai Beiling (756.82%), Zhongwei Semiconductor (716.19%), and Silan Micro (714.4%). The top three companies in year-on-year decline are: Zhongying Electronics (-28.01%), Jiuquan Technology (-28.79%), and Fudan Microelectronics (-20.42%).The top three companies in quarter-on-quarter net profit growthare: Silan Micro (254.98%), Jingfeng Mingyuan (189.31%), and Zhongying Electronics (133.32%). The top three companies in quarter-on-quarter decline are: Guomin Technology (-458.02%), Nasda (-408.65%), and Four-Dimensional Map (-363.97%).Reasons for Decline/Loss: Multiple Pressures from Technology, Cycles, and CostsJiuquan Technologyexperienced a revenue decline of 1.85% and a year-on-year net profit decline of 28.79%. As a leading smart meter chip company (with a market share of over 60%), the slight revenue decline in 2024 is mainly due to weak demand in the traditional meter market — the adjustment of the power grid bidding cycle led to a 5% decline in smart meter chip sales, compounded by low-price competition from domestic competitors (average selling price down 8%), resulting in a “decline in both volume and price.” The cost side is affected by rising wafer foundry prices and increased R&D investment (R&D expenses in 2024 are 181 million, +18.02%), dragging the gross profit margin down from 47.2% to 44.1%. The newly expanded BMS chip business has not yet scaled (revenue from the new energy sector accounts for < 5%), making it difficult to offset the pressure on the main business in the short term. Additionally, the sale of subsidiaries in 2023 brought a one-time gain of 120 million, and there are no such non-recurring gains in 2024, leading to a year-on-year drop of 42% in net profit after deducting non-recurring items, putting real profits under pressure.Guoxin Technologyexperienced a quarter-on-quarter revenue decline of 49.75% and a net profit loss of 176 million. The company focused on automotive-grade MCU certification in 2024 (such as the CCFC2002MC series), but due to the AEC-Q100 certification cycle lasting 2-3 years, and customer validation iterations leading to more wafer runs than expected (3 wafer runs throughout the year, with an additional expenditure of 80 million), the mass production scale of automotive products in Q4 did not meet expectations. Coupled with seasonal weakness in demand in the industrial control sector, the single revenue structure (industrial + security chips account for 80%) has become prominent. At the same time, government subsidies decreased by 15% year-on-year (to 110 million), and the decline in non-recurring gains exacerbated losses. The annual R&D expense ratio reached 35.2%, but automotive-grade MCUs have not yet contributed to revenue, leading to significant quarterly fluctuations due to mismatches in “input-output.”GigaDeviceexperienced a quarter-on-quarter revenue decline of 16.38%. As a dual leader in storage and MCUs, the revenue decline in Q4 is mainly due to cyclical fluctuations in the storage business: NOR Flash was affected by inventory adjustments in consumer electronics, with a quarter-on-quarter shipment decline of 12%, and SLC NAND Flash prices experiencing a short-term correction, leading to a 20% quarter-on-quarter revenue decline in the storage business. Although the MCU business shipped 4.362 billion units (+39.72%) throughout the year, the demand for consumer MCUs (accounting for 35%) weakened seasonally with the end of the Christmas purchasing cycle, and industrial orders were concentrated in the first half of the year, resulting in an overall revenue rhythm that was high in the front and low in the back. However, the company achieved a year-on-year net profit growth of 584.21% through product structure optimization (the proportion of 32-bit MCUs increased to 70%) and supply chain autonomy, indicating that short-term fluctuations do not affect long-term resilience.Puran Sharesexperienced a quarter-on-quarter revenue decline of 7.092%. Relying on small-capacity NOR Flash and MCUs for TWS headsets and wearable devices (accounting for 70% of revenue), Q4 2024 was significantly affected by the off-season in consumer electronics — the order volume from end customers decreased by 15% quarter-on-quarter, compounded by long customer certification cycles (expanding into industrial sectors such as Huichuan Technology, but with limited incremental growth in Q4), leading to a short-term gap due to the contraction of traditional consumer customer orders. Although the annual revenue achieved a high growth of 60.03% due to demand rebound in the first half of the year, Q4 still experienced a slight decline due to seasonal factors. The company is accelerating its layout in industrial-grade MCUs (with a target revenue share of 30% in 2025) to reduce dependence on consumer electronics cycles.Four-Dimensional Mapreported a net profit loss of 1.095 billion, with a quarter-on-quarter decline of 363.97%. As a smart automotive solution provider (with MCU business accounting for less than 10%), the core of the loss stems from high long-term R&D investments — R&D expenses in 2024 are 1.012 billion (expense ratio 28.7%), focusing on projects such as autonomous driving chips (automotive-grade MCUs have not yet been mass-produced) and high-precision maps, with no short-term profit contribution. The smart automotive business is under pressure from customer price reductions (Tesla, Xiaopeng, etc., with gross margins dropping to 22.3%, -3.5 percentage points), compounded by no government subsidies in Q4 (receiving 150 million in the first three quarters), leading to a single-quarter loss of 1.314 billion (annual loss of 1.095 billion). Additionally, the overseas navigation business accounts for 35%, and the depreciation of the RMB in Q4 led to an exchange loss of 70 million, further amplifying the loss.Guomin Technologyreported a net profit loss of 235 million, with a quarter-on-quarter decline of 458.02%. The company fell into a dual dilemma of “traditional business shrinkage + new business burning cash” in 2024: in the traditional consumer electronics sector, revenue from mobile phone security chips dropped by 25%, and the gross margin of 8-bit MCUs in the white goods market fell to 28.7% (-4.2 percentage points), resulting in a loss of 120 million; in terms of new business, R&D investment in automotive-grade MCUs reached 350 million (expense ratio 32.6%), with the first N32G45x series only in small-batch trial production, with no scale revenue. In Q4, single-quarter R&D expenses reached 180 million (accounting for 51% of the annual total), compounded by delayed payments from industrial customers, leading to an increase in financial expenses of 50 million, resulting in a single-quarter loss of 120 million, with a quarter-on-quarter increase of 458.02%.Zhongying Electronicsreported a year-on-year net profit decline of 28.01%. The company relies on AMOLED panel driver MCUs for 30% of its revenue, and in 2024, it faced price pressure from customers such as BOE and TCL, causing the gross margin of this business to drop from 35.2% to 29.8%, dragging down overall profits. The newly laid out industrial control MCUs (32-bit motor control chips) saw an increase in R&D expenses of 90 million (+22%), but in 2024, the revenue share was only 15%, and it has not yet formed a scale effect. Although quarterly profits increased by 133.32% due to concentrated deliveries in Q4, the annual net profit still declined by 28.01% due to the decline in the panel business and slow returns from new business investments, necessitating accelerated customer expansion in the industrial sector to improve profit structure.Fudan Microelectronicsreported a year-on-year net profit decline of 20.42%. Both FPGA and MCU businesses are under pressure: FPGA revenue growth was only 3% in 2024 due to low-price dumping by Xilinx, with a gross margin drop of 4.5 percentage points; the market share of 32-bit MCUs in the security field dropped from 25% to 20%, with GigaDevice and Shanghai Beiling diverting orders through cost-performance strategies, and the shipment volume of high-end Cortex-M7 core MCUs falling short of expectations. Although automotive-grade MCU shipments exceeded 10 million and obtained ASIL-B certification, the revenue share is < 5%, making it difficult to reverse the decline in the short term. R&D investment remains high at 1.142 billion (accounting for 31.8%), compounded by rising wafer foundry costs, leading to a year-on-year net profit decline of 20.42%, necessitating breakthroughs in high-end product mass production and cost control.Nasdareported a quarter-on-quarter net profit decline of 408.65%. As a leader in printing consumables, the sharp decline in net profit in Q4 2024 is mainly due to cyclical fluctuations in the printing business: global laser printer shipments decreased by 12% quarter-on-quarter, leading to a 20% quarter-on-quarter revenue decline in the main control MCU business, with the gross margin dropping to 28.7% (-3.2 percentage points). Additionally, due to an increase in bankruptcy cases among U.S. customers, a provision for bad debts of 80 million was made in Q4, with credit impairment losses increasing by 150 million quarter-on-quarter. Furthermore, the company’s asset-liability ratio is 72.61%, leading to significant short-term repayment pressure, with financial expenses increasing by 60 million, resulting in a single-quarter net profit turning from a cumulative 1.081 billion in the first three quarters to 749 million for the year, with a single-quarter loss of 332 million, a quarter-on-quarter decline of 408.65%.Reasons for Growth/Profit: Product Structure, Market Expansion, and Technological DividendsNasdaachieved revenue of 26.415 billion in 2024, maintaining the top position, with a year-on-year increase of 9.78% and a net profit of 749 million. The core growth comes from the global expansion of the printer business and the reduction of losses in integrated circuits, where both volume and price of the printing business have risen, with Benyu Electronics achieving revenue of 4.658 billion (+19.87%), and shipments in the Xinchuang market increasing by 50%, with overseas sales up 6%; Lexmark International achieved revenue of $2.243 billion (+7.98%), with printer sales increasing by 31.13%, and A3 printer sales surging by 131.44%, driving revenue growth in both machines and consumables. The integrated circuit business also improved, with the MCU/storage chip sales of its subsidiary Jihai Microelectronics increasing by 26.01%, and non-printing consumable chip sales increasing by 42%, with a net profit of 363 million (+109.97%), achieved through mass production at the Zhuhai 12-inch wafer factory, reducing the cost of printing main control MCUs by 8% and improving the gross margin by 2.3 percentage points. Cost control has also been optimized, with the sales expense ratio dropping to 15.2% (down 1.8 percentage points year-on-year), and management expenses decreasing by 5% due to scale effects, although R&D expenses increased by 42% (with increased R&D investment in Benyu Electronics), the overall net profit margin rose from -25.7% in 2023 to 2.8%.Silan Microachieved revenue of 11.221 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 20.14%, with a net profit of 220 million. This is also the first time this domestic IDM leader has surpassed 10 billion, driven by high-end product structure upgrades and scale effects, with explosive growth in IPM modules, where smart power modules (IPM) revenue reached 2.911 billion (+47%), with over 170 million units used by domestic mainstream white goods manufacturers (+57%), covering high-end appliances such as variable frequency air conditioners and refrigerators, with a gross margin of 32.5% (+5.2 percentage points). The coordinated development of power semiconductors and MCUs has led to revenue of 2.261 billion (+60%) from IGBT/SiC modules, penetrating the new energy vehicle and photovoltaic fields; revenue from 32-bit MCU circuits increased by 36%, with high-performance controllers based on the M0 core covering industrial automation and smart appliances, forming a “chip + solution” synergy with power devices. Silan Micro’s integrated circuit business has significantly increased its share, with revenue of 4.105 billion (+31%), accounting for 36.6%, offsetting the decline in discrete device business (-4%). The IDM model’s design and manufacturing synergy reduced costs by 15%, and although operating profit still recorded a loss of 101 million, net profit turned profitable due to government subsidies and asset disposal gains.GigaDeviceachieved revenue of 7.356 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 27.69%, with a net profit of 1.103 billion. The core benefit comes from product cycle resonance and supply chain autonomy, where NOR Flash demand has rebounded, with demand in consumer, networking, and automotive sectors rebounding, achieving record high shipment volumes, with SLC NAND Flash revenue/shipment both increasing, and the gross margin of the storage business improving by 5.2 percentage points to 38.7%, with 20nm process products accounting for over 40%. On the other hand, MCU shipments exceeded 4.362 billion units (+39.72%), with 32-bit products accounting for over 70%, and revenue in the industrial control sector increased by 45%, replacing imported brands such as NXP and ST, with a gross margin of 35.2% (+3.8 percentage points), and automotive-grade MCUs entering the sample testing stage, expected to contribute revenue in 2025. Additionally, the supply chain resilience of last year has significantly improved, with SMIC’s 19nm process NOR Flash entering mass production, and inventory turnover days reduced from 120 days to 95 days, significantly enhancing operational resilience.Chipsea Technologyachieved revenue of 702 million in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 62.22%. Although it recorded a net loss of 173 million (an increase of 29.42 million year-on-year), its revenue growth rate is the highest, primarily due to the recovery in consumer electronics and breakthroughs in new products. In particular, traditional businesses have rebounded, with shipments of touch MCUs and heart rate sensors for TWS headsets and smartwatches increasing by 75%, with consumer business revenue reaching 520 million (accounting for 74%), with a gross margin of 23.46% (+5.73 percentage points), and multiple BMS chips entering the supply chain of Yiwei Lithium Energy. Industrial-grade products are also starting to scale, with revenue from pressure sensors in the industrial control sector reaching 182 million (+32%), and 32-bit MCUs entering the trial phase in servo systems, with 28nm high-precision ADC chips entering mass production, with related product revenue increasing by 120%, opening up high-end market space. However, Chipsea’s R&D investment remains high, with R&D expenses of 198 million (+22%), and share-based payment expenses of 73.13 million (accounting for 42% of the loss), while automotive-grade MCUs are still in the certification stage, leading to continued short-term loss pressure.Puran Sharesachieved revenue of 1.804 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 60.03%, with a net profit of 292 million. Focusing on small-capacity storage and MCU synergy, like GD, it has deeply benefited from the rebound in consumer electronics demand and domestic substitution. Among them, the NOR Flash market has seen both volume and price rise, with Puran’s 1-8GB capacity products in TWS headsets and wearable devices increasing by 55%, achieving revenue of 1.28 billion (+68%), with a gross margin of 38.2% (+6.5 percentage points), and automotive-grade 256MB products entering the AEC-Q100 certification stage. Although it is not the most profitable business, the MCU has also rapidly scaled due to its binding with storage chip sales, achieving revenue of 524 million (+48%) in the white goods and small appliances sector, with shipments exceeding 1.5 billion units and a gross margin of 28.7% (+3.2 percentage points). In 2024, the company’s customer structure further optimized, with the concentration of the top five customers decreasing from 45% to 38%, adding strategic customers such as AAC Technologies and Goertek, enhancing risk resistance, with a net operating cash flow of 310 million (+180%).Peak Technologyachieved revenue of 600 million in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 45.94%, with a net profit of 222 million. The high growth of motor drive MCU technology barriers has been built, with the explosive demand for industrial automation driving revenue of 420 million (+58%) for 32-bit MCUs used in inverters and servo systems, binding with leading companies such as Huichuan Technology and Invt, with a market share exceeding 20%, and products with floating-point operation units achieving a gross margin of 52.3% (+4.1 percentage points). The penetration of new energy vehicles is accelerating, with automotive motor controller MCUs entering the supply chain of BYD and NIO, with related revenue of 120 million (+70%), and AEC-Q100 certified products entering mass production, with the proportion of automotive-grade business increasing to 20% in 2024. Notably, Peak Technology’s R&D efficiency is far ahead in the industry, with an R&D expense ratio of 18% (lower than the industry average of 25%), but in 2024, it only completed one wafer run (compared to two in 2023), shortening the new product iteration cycle by 30%, with a net profit margin reaching 37% (high in the industry).Hengshuo Sharesachieved a quarter-on-quarter revenue increase of 25.95% in Q4 2024. We found that all companies with NOR Flash and MCU production lines experienced quarterly business resonance, including Hengshuo — Q4 single-quarter revenue reached 102 million (with a cumulative 270 million in the first three quarters). This was driven by consumer electronics stocking in Q4 2024, with end customers preparing for the Spring Festival, leading to a 20% quarter-on-quarter increase in shipments of 1-4GB NOR Flash and a 15% increase in MCU orders for small appliances, achieving a new high in single-quarter revenue for 2024. The company’s automotive-grade products are entering the preheating stage, with 256MB NOR Flash entering automotive certification, attracting industrial customers to place orders in advance. Although the automotive business has not yet contributed revenue, it has boosted market confidence in its technical capabilities, leading to a 30% quarter-on-quarter increase in industrial revenue.Shanghai Beilingachieved a quarter-on-quarter revenue increase of 24.97% in Q4 2024, with a net profit of 396 million, a year-on-year increase of 756.82%. Driven by both consumer and industrial sectors, the net profit growth rate is the highest, primarily due to product substitution and cost control. Among them, the market share of fast-charging chips has increased, with revenue from mobile phone fast-charging PMIC reaching 820 million (+40%), entering the supply chain of OPPO and vivo, with high-power products above 20W accounting for over 60%, and a gross margin of 42.5% (+8.3 percentage points). Industrial MCUs also achieved breakthroughs, with 32-bit products generating revenue of 350 million (+55%) in industrial instruments and motor control, with prices only 70% of imported brands, replacing similar products from STMicroelectronics, with market share increasing from 15% in 2023 to 22%. Finally, in terms of cost control, Shanghai Beiling’s R&D expense ratio is 16.7% (down 2.3 percentage points year-on-year), with management expenses decreasing by 12%, and the net profit margin rising from 5.2% in 2023 to 14.1%, with a single-quarter net profit of 130 million (with a cumulative 266 million in the first three quarters), a quarter-on-quarter increase of 46.2%.Zhongwei Semiconductorachieved a quarter-on-quarter revenue increase of 18.65% in Q4 2024, with a net profit of 135 million, a year-on-year increase of 716.19%. Like several previous companies, benefiting from the recovery of consumer MCUs and supply chain optimization, it turned losses into profits, with Q4 single-quarter revenue reaching 280 million (annual total of 911 million). In particular, the demand for white goods MCUs has rebounded, with shipments of 8-bit MCUs for air conditioners and refrigerators increasing by 30%, with consumer business revenue reaching 650 million (+35%), and a gross margin of 35.2% (+6.5 percentage points). Additionally, a long-term price agreement was signed with SMIC, reducing wafer costs by 10%. Furthermore, R&D efficiency has improved, with only two wafer runs in 2024 (compared to four in 2023), and R&D expenses decreased by 15%, with the expense ratio dropping from 25% to 20%, with 32-bit industrial MCUs entering the sample testing stage, expected to contribute revenue in 2025. The customer structure has also improved, with the concentration of the top five customers decreasing from 55% to 48%, adding strategic customers such as Midea and Gree, and accounts receivable turnover days reduced from 120 days to 90 days, improving cash flow.Fudan Microelectronicsreported a net profit of 573 million in 2024, a year-on-year decline of 20.42%, but still ranked third in net profit. Although net profit declined year-on-year, it remains stable due to high-end products and government subsidies. In terms of product lines, FPGA continues to contribute revenue of 1.52 billion (+3%), with a market share of 25% in the security and industrial control fields, benefiting from the domestic substitution background, taking over orders transferred from Xilinx, with a gross margin of 55% for 28nm process products. In terms of MCUs, automotive-grade products are starting to scale, with AEC-Q100 certified products exceeding 10 million units shipped, covering body control modules, generating revenue of 120 million (accounting for 3.3%), with a gross margin of 45% (20 percentage points higher than consumer products), expected to increase the proportion of automotive business to 10% in 2025. Additionally, the company received a special subsidy of 180 million for integrated circuits, accounting for 31.4% of net profit, offsetting some R&D pressure (R&D expenses of 1.142 billion, +15%), although the market share of MCUs in the security field has dropped to 20%, high-end products still maintain high gross margins.Jingfeng Mingyuanreported a quarter-on-quarter net profit increase of 189.31% in Q4 2024, with losses narrowing + product structure adjustments driving quarterly growth, with a single-quarter net profit of -3.3 million (compared to -21 million in Q3). Benefiting from the recovery of the general lighting market, the demand for LED driver chips has rebounded, with Jingfeng Mingyuan’s Q4 revenue increasing by 17.63% quarter-on-quarter, with a gross margin increasing by 3 percentage points to 28.5%, and inventory turnover days reduced from 150 days to 120 days, showing significant destocking effects. Additionally, the company is actively developing its layout in the new energy business, with automotive LED driver chips entering the sample testing stage, obtaining certifications from BYD and CATL, although not yet in mass production, boosting investor confidence, with Q4 operating cash flow turning positive (+12 million).Zhongying Electronicsreported a quarter-on-quarter net profit increase of 133.32% in Q4 2024, with a seasonal rebound in panel driver MCUs and expense deferral driving growth, with a net profit of 134 million in Q4 (compared to 57 million in Q3). Among them, the demand for AMOLED drivers was concentrated, with orders from BOE and Huaxing Optoelectronics rebounding in Q4, with related MCU revenue reaching 120 million (quarter-on-quarter increase of 40%), with gross margins recovering to 31.5% (compared to 27.8% in Q3), and the mass production of 55nm process products reducing costs by 15%. The company has implemented optimizations in expense control, with R&D investments concentrated in the first three quarters (accounting for 70% of the annual total), with Q4 expense ratios decreasing by 5 percentage points, saving 30 million in management costs, coupled with government subsidies of 50 million (received in Q4), driving a surge in net profit.Conclusion: Anchoring Future Growth Points Amid DifferentiationIn summary, we find that the core profit points of the domestic MCU industry in 2024 are concentrated in three major areas:
Overall, the recovery of consumer electronics, the increase in industrial control demand, and the deepening of domestic substitution are driving the core indicators of the industry to warm up, but the technical barriers and market cycle differences in subdivided fields lead to differentiated performance among companies.Ranking of Profit and LossIn terms of revenue performance, the top three total operating revenues are: Nasda (26.41 billion yuan), Silan Micro (11.22 billion yuan), and GigaDevice (7.356 billion yuan).The top three companies in year-on-year revenue growthare: Chipsea Technology (62.22%), Puran Shares (60.03%), and Peak Technology (45.94%). The only declining company is Jiuquan Technology (-1.853%).The top three companies in quarter-on-quarter revenue growthare: Hengshuo Shares (25.95%), Shanghai Beiling (24.97%), and Zhongwei Semiconductor (18.65%). The top three declining companies are: Guoxin Technology (-49.75%), GigaDevice (-16.38%), and Puran Shares (-7.092%).In terms of net profit performance, the top three profitable companies are: GigaDevice (1.103 billion yuan), Nasda (749 million yuan), and Fudan Micro (573 million yuan). The top three loss-making companies are: Four-Dimensional Map (-1.095 billion yuan), Guomin Technology (-235 million yuan), and Guoxin Technology (-176 million yuan).The top three companies in year-on-year net profit growthare: Shanghai Beiling (756.82%), Zhongwei Semiconductor (716.19%), and Silan Micro (714.4%). The top three companies in year-on-year decline are: Zhongying Electronics (-28.01%), Jiuquan Technology (-28.79%), and Fudan Microelectronics (-20.42%).The top three companies in quarter-on-quarter net profit growthare: Silan Micro (254.98%), Jingfeng Mingyuan (189.31%), and Zhongying Electronics (133.32%). The top three companies in quarter-on-quarter decline are: Guomin Technology (-458.02%), Nasda (-408.65%), and Four-Dimensional Map (-363.97%).Reasons for Decline/Loss: Multiple Pressures from Technology, Cycles, and CostsJiuquan Technologyexperienced a revenue decline of 1.85% and a year-on-year net profit decline of 28.79%. As a leading smart meter chip company (with a market share of over 60%), the slight revenue decline in 2024 is mainly due to weak demand in the traditional meter market — the adjustment of the power grid bidding cycle led to a 5% decline in smart meter chip sales, compounded by low-price competition from domestic competitors (average selling price down 8%), resulting in a “decline in both volume and price.” The cost side is affected by rising wafer foundry prices and increased R&D investment (R&D expenses in 2024 are 181 million, +18.02%), dragging the gross profit margin down from 47.2% to 44.1%. The newly expanded BMS chip business has not yet scaled (revenue from the new energy sector accounts for < 5%), making it difficult to offset the pressure on the main business in the short term. Additionally, the sale of subsidiaries in 2023 brought a one-time gain of 120 million, and there are no such non-recurring gains in 2024, leading to a year-on-year drop of 42% in net profit after deducting non-recurring items, putting real profits under pressure.Guoxin Technologyexperienced a quarter-on-quarter revenue decline of 49.75% and a net profit loss of 176 million. The company focused on automotive-grade MCU certification in 2024 (such as the CCFC2002MC series), but due to the AEC-Q100 certification cycle lasting 2-3 years, and customer validation iterations leading to more wafer runs than expected (3 wafer runs throughout the year, with an additional expenditure of 80 million), the mass production scale of automotive products in Q4 did not meet expectations. Coupled with seasonal weakness in demand in the industrial control sector, the single revenue structure (industrial + security chips account for 80%) has become prominent. At the same time, government subsidies decreased by 15% year-on-year (to 110 million), and the decline in non-recurring gains exacerbated losses. The annual R&D expense ratio reached 35.2%, but automotive-grade MCUs have not yet contributed to revenue, leading to significant quarterly fluctuations due to mismatches in “input-output.”GigaDeviceexperienced a quarter-on-quarter revenue decline of 16.38%. As a dual leader in storage and MCUs, the revenue decline in Q4 is mainly due to cyclical fluctuations in the storage business: NOR Flash was affected by inventory adjustments in consumer electronics, with a quarter-on-quarter shipment decline of 12%, and SLC NAND Flash prices experiencing a short-term correction, leading to a 20% quarter-on-quarter revenue decline in the storage business. Although the MCU business shipped 4.362 billion units (+39.72%) throughout the year, the demand for consumer MCUs (accounting for 35%) weakened seasonally with the end of the Christmas purchasing cycle, and industrial orders were concentrated in the first half of the year, resulting in an overall revenue rhythm that was high in the front and low in the back. However, the company achieved a year-on-year net profit growth of 584.21% through product structure optimization (the proportion of 32-bit MCUs increased to 70%) and supply chain autonomy, indicating that short-term fluctuations do not affect long-term resilience.Puran Sharesexperienced a quarter-on-quarter revenue decline of 7.092%. Relying on small-capacity NOR Flash and MCUs for TWS headsets and wearable devices (accounting for 70% of revenue), Q4 2024 was significantly affected by the off-season in consumer electronics — the order volume from end customers decreased by 15% quarter-on-quarter, compounded by long customer certification cycles (expanding into industrial sectors such as Huichuan Technology, but with limited incremental growth in Q4), leading to a short-term gap due to the contraction of traditional consumer customer orders. Although the annual revenue achieved a high growth of 60.03% due to demand rebound in the first half of the year, Q4 still experienced a slight decline due to seasonal factors. The company is accelerating its layout in industrial-grade MCUs (with a target revenue share of 30% in 2025) to reduce dependence on consumer electronics cycles.Four-Dimensional Mapreported a net profit loss of 1.095 billion, with a quarter-on-quarter decline of 363.97%. As a smart automotive solution provider (with MCU business accounting for less than 10%), the core of the loss stems from high long-term R&D investments — R&D expenses in 2024 are 1.012 billion (expense ratio 28.7%), focusing on projects such as autonomous driving chips (automotive-grade MCUs have not yet been mass-produced) and high-precision maps, with no short-term profit contribution. The smart automotive business is under pressure from customer price reductions (Tesla, Xiaopeng, etc., with gross margins dropping to 22.3%, -3.5 percentage points), compounded by no government subsidies in Q4 (receiving 150 million in the first three quarters), leading to a single-quarter loss of 1.314 billion (annual loss of 1.095 billion). Additionally, the overseas navigation business accounts for 35%, and the depreciation of the RMB in Q4 led to an exchange loss of 70 million, further amplifying the loss.Guomin Technologyreported a net profit loss of 235 million, with a quarter-on-quarter decline of 458.02%. The company fell into a dual dilemma of “traditional business shrinkage + new business burning cash” in 2024: in the traditional consumer electronics sector, revenue from mobile phone security chips dropped by 25%, and the gross margin of 8-bit MCUs in the white goods market fell to 28.7% (-4.2 percentage points), resulting in a loss of 120 million; in terms of new business, R&D investment in automotive-grade MCUs reached 350 million (expense ratio 32.6%), with the first N32G45x series only in small-batch trial production, with no scale revenue. In Q4, single-quarter R&D expenses reached 180 million (accounting for 51% of the annual total), compounded by delayed payments from industrial customers, leading to an increase in financial expenses of 50 million, resulting in a single-quarter loss of 120 million, with a quarter-on-quarter increase of 458.02%.Zhongying Electronicsreported a year-on-year net profit decline of 28.01%. The company relies on AMOLED panel driver MCUs for 30% of its revenue, and in 2024, it faced price pressure from customers such as BOE and TCL, causing the gross margin of this business to drop from 35.2% to 29.8%, dragging down overall profits. The newly laid out industrial control MCUs (32-bit motor control chips) saw an increase in R&D expenses of 90 million (+22%), but in 2024, the revenue share was only 15%, and it has not yet formed a scale effect. Although quarterly profits increased by 133.32% due to concentrated deliveries in Q4, the annual net profit still declined by 28.01% due to the decline in the panel business and slow returns from new business investments, necessitating accelerated customer expansion in the industrial sector to improve profit structure.Fudan Microelectronicsreported a year-on-year net profit decline of 20.42%. Both FPGA and MCU businesses are under pressure: FPGA revenue growth was only 3% in 2024 due to low-price dumping by Xilinx, with a gross margin drop of 4.5 percentage points; the market share of 32-bit MCUs in the security field dropped from 25% to 20%, with GigaDevice and Shanghai Beiling diverting orders through cost-performance strategies, and the shipment volume of high-end Cortex-M7 core MCUs falling short of expectations. Although automotive-grade MCU shipments exceeded 10 million and obtained ASIL-B certification, the revenue share is < 5%, making it difficult to reverse the decline in the short term. R&D investment remains high at 1.142 billion (accounting for 31.8%), compounded by rising wafer foundry costs, leading to a year-on-year net profit decline of 20.42%, necessitating breakthroughs in high-end product mass production and cost control.Nasdareported a quarter-on-quarter net profit decline of 408.65%. As a leader in printing consumables, the sharp decline in net profit in Q4 2024 is mainly due to cyclical fluctuations in the printing business: global laser printer shipments decreased by 12% quarter-on-quarter, leading to a 20% quarter-on-quarter revenue decline in the main control MCU business, with the gross margin dropping to 28.7% (-3.2 percentage points). Additionally, due to an increase in bankruptcy cases among U.S. customers, a provision for bad debts of 80 million was made in Q4, with credit impairment losses increasing by 150 million quarter-on-quarter. Furthermore, the company’s asset-liability ratio is 72.61%, leading to significant short-term repayment pressure, with financial expenses increasing by 60 million, resulting in a single-quarter net profit turning from a cumulative 1.081 billion in the first three quarters to 749 million for the year, with a single-quarter loss of 332 million, a quarter-on-quarter decline of 408.65%.Reasons for Growth/Profit: Product Structure, Market Expansion, and Technological DividendsNasdaachieved revenue of 26.415 billion in 2024, maintaining the top position, with a year-on-year increase of 9.78% and a net profit of 749 million. The core growth comes from the global expansion of the printer business and the reduction of losses in integrated circuits, where both volume and price of the printing business have risen, with Benyu Electronics achieving revenue of 4.658 billion (+19.87%), and shipments in the Xinchuang market increasing by 50%, with overseas sales up 6%; Lexmark International achieved revenue of $2.243 billion (+7.98%), with printer sales increasing by 31.13%, and A3 printer sales surging by 131.44%, driving revenue growth in both machines and consumables. The integrated circuit business also improved, with the MCU/storage chip sales of its subsidiary Jihai Microelectronics increasing by 26.01%, and non-printing consumable chip sales increasing by 42%, with a net profit of 363 million (+109.97%), achieved through mass production at the Zhuhai 12-inch wafer factory, reducing the cost of printing main control MCUs by 8% and improving the gross margin by 2.3 percentage points. Cost control has also been optimized, with the sales expense ratio dropping to 15.2% (down 1.8 percentage points year-on-year), and management expenses decreasing by 5% due to scale effects, although R&D expenses increased by 42% (with increased R&D investment in Benyu Electronics), the overall net profit margin rose from -25.7% in 2023 to 2.8%.Silan Microachieved revenue of 11.221 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 20.14%, with a net profit of 220 million. This is also the first time this domestic IDM leader has surpassed 10 billion, driven by high-end product structure upgrades and scale effects, with explosive growth in IPM modules, where smart power modules (IPM) revenue reached 2.911 billion (+47%), with over 170 million units used by domestic mainstream white goods manufacturers (+57%), covering high-end appliances such as variable frequency air conditioners and refrigerators, with a gross margin of 32.5% (+5.2 percentage points). The coordinated development of power semiconductors and MCUs has led to revenue of 2.261 billion (+60%) from IGBT/SiC modules, penetrating the new energy vehicle and photovoltaic fields; revenue from 32-bit MCU circuits increased by 36%, with high-performance controllers based on the M0 core covering industrial automation and smart appliances, forming a “chip + solution” synergy with power devices. Silan Micro’s integrated circuit business has significantly increased its share, with revenue of 4.105 billion (+31%), accounting for 36.6%, offsetting the decline in discrete device business (-4%). The IDM model’s design and manufacturing synergy reduced costs by 15%, and although operating profit still recorded a loss of 101 million, net profit turned profitable due to government subsidies and asset disposal gains.GigaDeviceachieved revenue of 7.356 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 27.69%, with a net profit of 1.103 billion. The core benefit comes from product cycle resonance and supply chain autonomy, where NOR Flash demand has rebounded, with demand in consumer, networking, and automotive sectors rebounding, achieving record high shipment volumes, with SLC NAND Flash revenue/shipment both increasing, and the gross margin of the storage business improving by 5.2 percentage points to 38.7%, with 20nm process products accounting for over 40%. On the other hand, MCU shipments exceeded 4.362 billion units (+39.72%), with 32-bit products accounting for over 70%, and revenue in the industrial control sector increased by 45%, replacing imported brands such as NXP and ST, with a gross margin of 35.2% (+3.8 percentage points), and automotive-grade MCUs entering the sample testing stage, expected to contribute revenue in 2025. Additionally, the supply chain resilience of last year has significantly improved, with SMIC’s 19nm process NOR Flash entering mass production, and inventory turnover days reduced from 120 days to 95 days, significantly enhancing operational resilience.Chipsea Technologyachieved revenue of 702 million in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 62.22%. Although it recorded a net loss of 173 million (an increase of 29.42 million year-on-year), its revenue growth rate is the highest, primarily due to the recovery in consumer electronics and breakthroughs in new products. In particular, traditional businesses have rebounded, with shipments of touch MCUs and heart rate sensors for TWS headsets and smartwatches increasing by 75%, with consumer business revenue reaching 520 million (accounting for 74%), with a gross margin of 23.46% (+5.73 percentage points), and multiple BMS chips entering the supply chain of Yiwei Lithium Energy. Industrial-grade products are also starting to scale, with revenue from pressure sensors in the industrial control sector reaching 182 million (+32%), and 32-bit MCUs entering the trial phase in servo systems, with 28nm high-precision ADC chips entering mass production, with related product revenue increasing by 120%, opening up high-end market space. However, Chipsea’s R&D investment remains high, with R&D expenses of 198 million (+22%), and share-based payment expenses of 73.13 million (accounting for 42% of the loss), while automotive-grade MCUs are still in the certification stage, leading to continued short-term loss pressure.Puran Sharesachieved revenue of 1.804 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 60.03%, with a net profit of 292 million. Focusing on small-capacity storage and MCU synergy, like GD, it has deeply benefited from the rebound in consumer electronics demand and domestic substitution. Among them, the NOR Flash market has seen both volume and price rise, with Puran’s 1-8GB capacity products in TWS headsets and wearable devices increasing by 55%, achieving revenue of 1.28 billion (+68%), with a gross margin of 38.2% (+6.5 percentage points), and automotive-grade 256MB products entering the AEC-Q100 certification stage. Although it is not the most profitable business, the MCU has also rapidly scaled due to its binding with storage chip sales, achieving revenue of 524 million (+48%) in the white goods and small appliances sector, with shipments exceeding 1.5 billion units and a gross margin of 28.7% (+3.2 percentage points). In 2024, the company’s customer structure further optimized, with the concentration of the top five customers decreasing from 45% to 38%, adding strategic customers such as AAC Technologies and Goertek, enhancing risk resistance, with a net operating cash flow of 310 million (+180%).Peak Technologyachieved revenue of 600 million in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 45.94%, with a net profit of 222 million. The high growth of motor drive MCU technology barriers has been built, with the explosive demand for industrial automation driving revenue of 420 million (+58%) for 32-bit MCUs used in inverters and servo systems, binding with leading companies such as Huichuan Technology and Invt, with a market share exceeding 20%, and products with floating-point operation units achieving a gross margin of 52.3% (+4.1 percentage points). The penetration of new energy vehicles is accelerating, with automotive motor controller MCUs entering the supply chain of BYD and NIO, with related revenue of 120 million (+70%), and AEC-Q100 certified products entering mass production, with the proportion of automotive-grade business increasing to 20% in 2024. Notably, Peak Technology’s R&D efficiency is far ahead in the industry, with an R&D expense ratio of 18% (lower than the industry average of 25%), but in 2024, it only completed one wafer run (compared to two in 2023), shortening the new product iteration cycle by 30%, with a net profit margin reaching 37% (high in the industry).Hengshuo Sharesachieved a quarter-on-quarter revenue increase of 25.95% in Q4 2024. We found that all companies with NOR Flash and MCU production lines experienced quarterly business resonance, including Hengshuo — Q4 single-quarter revenue reached 102 million (with a cumulative 270 million in the first three quarters). This was driven by consumer electronics stocking in Q4 2024, with end customers preparing for the Spring Festival, leading to a 20% quarter-on-quarter increase in shipments of 1-4GB NOR Flash and a 15% increase in MCU orders for small appliances, achieving a new high in single-quarter revenue for 2024. The company’s automotive-grade products are entering the preheating stage, with 256MB NOR Flash entering automotive certification, attracting industrial customers to place orders in advance. Although the automotive business has not yet contributed revenue, it has boosted market confidence in its technical capabilities, leading to a 30% quarter-on-quarter increase in industrial revenue.Shanghai Beilingachieved a quarter-on-quarter revenue increase of 24.97% in Q4 2024, with a net profit of 396 million, a year-on-year increase of 756.82%. Driven by both consumer and industrial sectors, the net profit growth rate is the highest, primarily due to product substitution and cost control. Among them, the market share of fast-charging chips has increased, with revenue from mobile phone fast-charging PMIC reaching 820 million (+40%), entering the supply chain of OPPO and vivo, with high-power products above 20W accounting for over 60%, and a gross margin of 42.5% (+8.3 percentage points). Industrial MCUs also achieved breakthroughs, with 32-bit products generating revenue of 350 million (+55%) in industrial instruments and motor control, with prices only 70% of imported brands, replacing similar products from STMicroelectronics, with market share increasing from 15% in 2023 to 22%. Finally, in terms of cost control, Shanghai Beiling’s R&D expense ratio is 16.7% (down 2.3 percentage points year-on-year), with management expenses decreasing by 12%, and the net profit margin rising from 5.2% in 2023 to 14.1%, with a single-quarter net profit of 130 million (with a cumulative 266 million in the first three quarters), a quarter-on-quarter increase of 46.2%.Zhongwei Semiconductorachieved a quarter-on-quarter revenue increase of 18.65% in Q4 2024, with a net profit of 135 million, a year-on-year increase of 716.19%. Like several previous companies, benefiting from the recovery of consumer MCUs and supply chain optimization, it turned losses into profits, with Q4 single-quarter revenue reaching 280 million (annual total of 911 million). In particular, the demand for white goods MCUs has rebounded, with shipments of 8-bit MCUs for air conditioners and refrigerators increasing by 30%, with consumer business revenue reaching 650 million (+35%), and a gross margin of 35.2% (+6.5 percentage points). Additionally, a long-term price agreement was signed with SMIC, reducing wafer costs by 10%. Furthermore, R&D efficiency has improved, with only two wafer runs in 2024 (compared to four in 2023), and R&D expenses decreased by 15%, with the expense ratio dropping from 25% to 20%, with 32-bit industrial MCUs entering the sample testing stage, expected to contribute revenue in 2025. The customer structure has also improved, with the concentration of the top five customers decreasing from 55% to 48%, adding strategic customers such as Midea and Gree, and accounts receivable turnover days reduced from 120 days to 90 days, improving cash flow.Fudan Microelectronicsreported a net profit of 573 million in 2024, a year-on-year decline of 20.42%, but still ranked third in net profit. Although net profit declined year-on-year, it remains stable due to high-end products and government subsidies. In terms of product lines, FPGA continues to contribute revenue of 1.52 billion (+3%), with a market share of 25% in the security and industrial control fields, benefiting from the domestic substitution background, taking over orders transferred from Xilinx, with a gross margin of 55% for 28nm process products. In terms of MCUs, automotive-grade products are starting to scale, with AEC-Q100 certified products exceeding 10 million units shipped, covering body control modules, generating revenue of 120 million (accounting for 3.3%), with a gross margin of 45% (20 percentage points higher than consumer products), expected to increase the proportion of automotive business to 10% in 2025. Additionally, the company received a special subsidy of 180 million for integrated circuits, accounting for 31.4% of net profit, offsetting some R&D pressure (R&D expenses of 1.142 billion, +15%), although the market share of MCUs in the security field has dropped to 20%, high-end products still maintain high gross margins.Jingfeng Mingyuanreported a quarter-on-quarter net profit increase of 189.31% in Q4 2024, with losses narrowing + product structure adjustments driving quarterly growth, with a single-quarter net profit of -3.3 million (compared to -21 million in Q3). Benefiting from the recovery of the general lighting market, the demand for LED driver chips has rebounded, with Jingfeng Mingyuan’s Q4 revenue increasing by 17.63% quarter-on-quarter, with a gross margin increasing by 3 percentage points to 28.5%, and inventory turnover days reduced from 150 days to 120 days, showing significant destocking effects. Additionally, the company is actively developing its layout in the new energy business, with automotive LED driver chips entering the sample testing stage, obtaining certifications from BYD and CATL, although not yet in mass production, boosting investor confidence, with Q4 operating cash flow turning positive (+12 million).Zhongying Electronicsreported a quarter-on-quarter net profit increase of 133.32% in Q4 2024, with a seasonal rebound in panel driver MCUs and expense deferral driving growth, with a net profit of 134 million in Q4 (compared to 57 million in Q3). Among them, the demand for AMOLED drivers was concentrated, with orders from BOE and Huaxing Optoelectronics rebounding in Q4, with related MCU revenue reaching 120 million (quarter-on-quarter increase of 40%), with gross margins recovering to 31.5% (compared to 27.8% in Q3), and the mass production of 55nm process products reducing costs by 15%. The company has implemented optimizations in expense control, with R&D investments concentrated in the first three quarters (accounting for 70% of the annual total), with Q4 expense ratios decreasing by 5 percentage points, saving 30 million in management costs, coupled with government subsidies of 50 million (received in Q4), driving a surge in net profit.Conclusion: Anchoring Future Growth Points Amid DifferentiationIn summary, we find that the core profit points of the domestic MCU industry in 2024 are concentrated in three major areas:
- Recovery in Consumer Electronics:Demand for 8-bit / 32-bit MCUs rebounded due to TWS headsets, smartwatches, etc., with companies like GigaDevice and Puran Shares seeing significant increases in shipments;
- Upgrading Industrial Control:Inverters and servo systems are driving demand for high-performance 32-bit MCUs, with Peak Technology and Zhongwei Semiconductor’s revenue in the industrial sector exceeding 50%;
- Deepening Domestic Substitution:The domestic substitution rate in the mid-to-low-end market (such as home appliances and meters) exceeds 60%, with companies like Shanghai Beiling and Zhongying Electronics squeezing overseas brand shares through cost-performance advantages.
The main reasons for lossesinclude high R&D investments and pressures from inventory and costs. The R&D cycles for automotive-grade and safety MCUs are long (certification takes 2-3 years), making it difficult for companies to achieve short-term profitability; companies relying on the Foundry model have weaker cost control capabilities amid capacity fluctuations, compounded by prolonged inventory destocking cycles in consumer electronics. Additionally, market competition leading to product price declines, fluctuations in raw material prices, and excessive dependence on specific markets or products can also lead to declines in gross margins due to price adjustments.Looking ahead to 2025, the MCU market will present three major trends:
- Technological Upgrades:MCU products will develop towards higher performance, lower power consumption, stronger security, and smaller sizes. 32-bit MCUs will accelerate the replacement of 16-bit / 8-bit products, with automotive-grade AEC-Q100 certified products entering mass production;
- Market Differentiation:Demand for MCUs in fields such as IoT, automotive electronics, and industrial control will continue to grow, while the traditional consumer MCU market may maintain relatively stable or low-speed growth;
- Ecological Construction:Leading companies like GigaDevice and Silan Micro are creating integrated ecosystems through “MCU + storage/power devices” collaborative solutions, while small and medium-sized manufacturers focus on niche markets (such as display drivers and motor drivers) to form differentiated competition. The MCU industry will strengthen cooperation with upstream and downstream enterprises to form a closer industrial ecosystem.
As mentioned by AspenCore analysts at the MCU and Embedded Systems Application Forum held concurrently in Shanghai in March, after the semiconductor downturn in 2023 and 2024, there is reason to expect a wave of improvement in the MCU market this year. The strategic contraction of international giants has freed up market space for domestic manufacturers, and the domestic MCU industry is expected to transition from “increased quantity” to “improved quality,” with companies possessing automotive-grade certifications, AI integration capabilities, and ecological stickiness standing out. The process of domestic substitution is accelerating, and with policy support and the driving force of the industry’s own development, the market share of domestic MCUs is expected to further increase.Editor: LuffyRelated Articles: “What Are Domestic MCU Manufacturers Doing in 2025?”
Hot Articles
Dissecting OPPO’s “Brandless” Fast Charger: Can It Be Used?
2025-04-19

Huaqiangbei Merchants “Hiding” Goods Awaiting Price Increase: Suspended Quotation!
2025-04-15

Dissecting a New Design Panasonic Tape Recorder: A Glimpse of Japan’s Semiconductor Industry Prosperity~
2025-04-20

The World’s First Humanoid Robot Half Marathon Concludes: Tiangong Ultra Wins
2025-04-19
