Introduction
With the rapid development of information technology, embedded real-time scenarios are undergoing a profound transformation, especially in the automotive industry. Cars are no longer just a combination of mechanics and hardware; they are gradually becoming a platform that integrates hardware, software, and data. Software, as the key to automotive intelligence, directly affects the safety, comfort, and user experience of vehicles. However, with the increasing diversity and personalization of consumer demands for automotive functions, as well as continuous innovations and advancements in automotive technology, traditional software upgrade methods can no longer meet the changing market demands. Rolling upgrades of microservices, as a flexible and efficient software update method, can continuously enhance the performance and functionality of automotive software to meet the ever-changing needs of consumers.
Microservices in Embedded Real-Time Scenarios
Microservices are an architectural pattern that breaks down applications into multiple small, autonomous service units. These service units can be independently deployed, scaled, and maintained, and they communicate with each other through lightweight communication mechanisms. This architectural pattern brings the following core advantages:
- Independent Deployment and Scaling: Each microservice can be independently deployed and scaled, meaning that an upgrade or failure of one service does not affect other services, improving the system’s availability and stability.
- Technological Diversity: Since each microservice can independently choose a more suitable technology stack, this provides teams with greater space for technological innovation.
- Ease of Maintenance and Management: Microservices make each service more modular and clearly defined in responsibilities, reducing maintenance complexity.
Yihui Information, combining the characteristics of mission-critical domains with years of industry technical accumulation, has launched the VSOA (Vehicle Service Oriented Architecture) distributed microservices architecture. This architecture supports implementation across multiple languages, environments, and operating systems, enabling developers to easily build large distributed loosely-coupled applications and support parallel development of applications. With the VSOA distributed microservices framework and a containerized DevSecOps management platform, we provide cloud-native architecture support for embedded real-time scenarios.
In 2023, the Yihui VSOA microservices architecture received five standard certification certificates from the internationally renowned certification body TÜV SÜD Group, including IEC 61508 (SIL3), EN 50128 (SIL4), ISO 26262 (ASIL D), EN 50159, and IEC 61784. This certification verified that the communication residual error rate of Yihui VSOA fully meets the communication functional safety requirements (≤10(−9)), fully confirming that Yihui’s mission-critical cloud-native solutions meet the high safety and high reliability requirements of application scenarios.

Advantages of Rolling Upgrades for Microservices in Embedded Real-Time Scenarios
In embedded real-time scenarios, the continuous operation of systems is crucial. Traditional downtime upgrade methods can cause service interruptions, affecting user experience. In contrast, rolling upgrades can gradually replace old versions of services with new ones without interrupting service, ensuring the system runs continuously and stably.
The value of rolling upgrades is primarily reflected in the following aspects:
-
Zero Downtime: Rolling upgrades allow for smooth version updates without affecting users, enhancing the user experience.
-
Risk Reduction: New versions of services can gradually replace old versions, and if issues arise, a quick rollback can be performed, reducing upgrade risks.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: Rolling upgrades can be combined with automation tools to achieve automated version releases, rollbacks, and other operations, improving system flexibility and scalability.
In embedded real-time scenarios, the practice of microservices rolling upgrades is particularly important. For example, in smart home systems, each device may require frequent software updates to fix defects or add new features. Through a microservices architecture and rolling upgrade approach, these updates can be completed gradually without affecting normal user operations.Similarly, in the field of autonomous driving, the real-time performance and stability of the system directly relate to passenger safety. The rolling upgrade method of microservices can optimize and upgrade the system without interrupting service, ensuring that the system is always in its best state.
As the application of embedded real-time scenarios becomes increasingly widespread, the importance of microservices rolling upgrades is also becoming more prominent. It not only provides continuous and stable services but also offers teams greater space for technological innovation.
Rolling Upgrade Strategies for Microservices in Embedded Real-Time Scenarios
Key technologies for mission-critical cloud-native environments can provide more suitable rolling upgrade solutions for such upgrade scenarios. Developers can configure the service load balancing strategy of the ECSM container management platform to “polling” to ensure that the system can achieve instant business switching during microservices upgrades, thereby minimizing user impact.
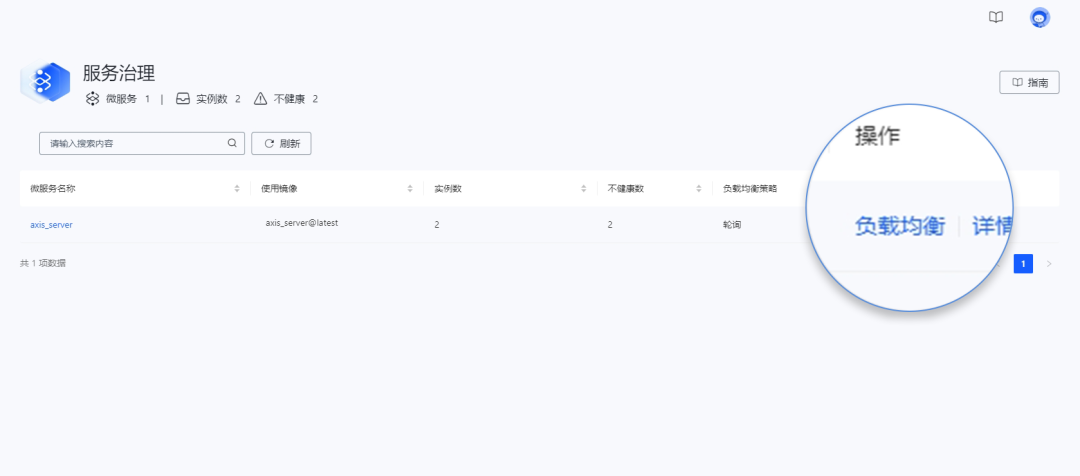
During the microservices upgrade process, if a business request occurs, the container management platform will automatically switch to the pre-configured load-balanced microservice, ensuring that the business remains stable online with zero interruptions, allowing users to experience seamless business changes.
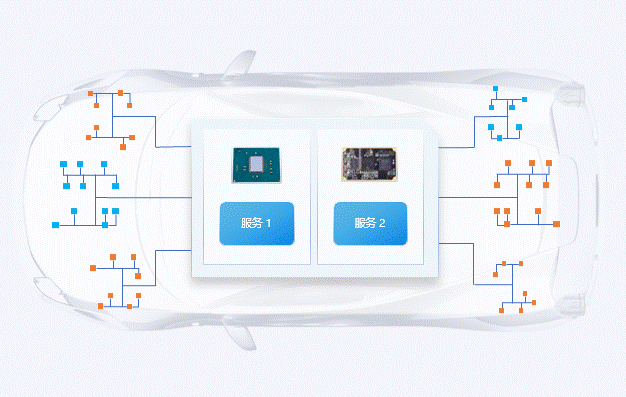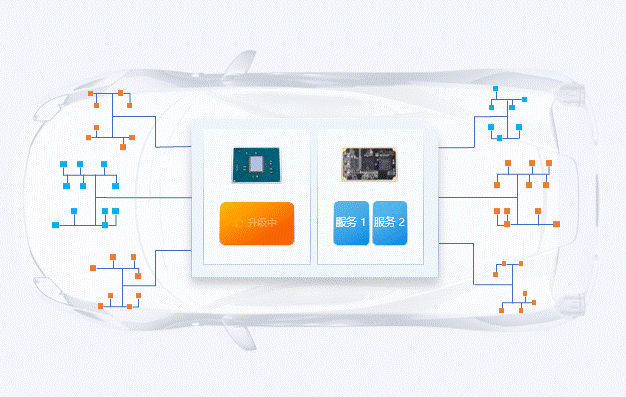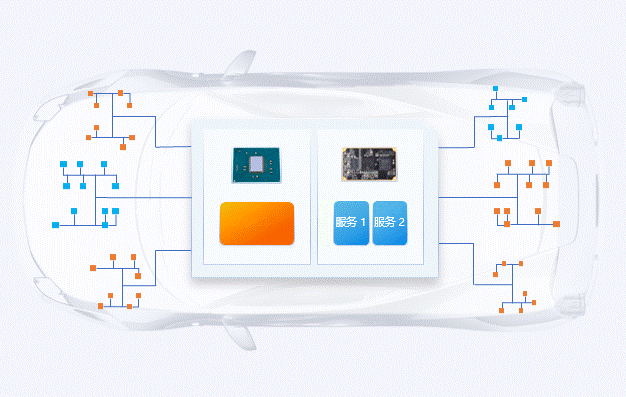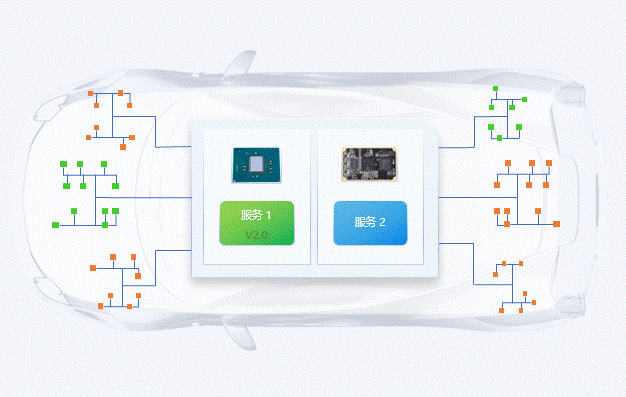
Conclusion
The technology of rolling upgrades for microservices in embedded real-time scenarios brings numerous advantages and value to enterprises. It not only enhances the flexibility and stability of systems but also reduces costs and empowers enterprises with the ability to innovate continuously. Therefore, by continuously optimizing and upgrading their embedded systems through this technology, enterprises can meet market challenges, enhance competitiveness, and achieve sustainable development.
