
Today, we will discuss the story of converting a motor sequential start/stop circuit into a PLC ladder diagram, suitable for those who want to get started with PLCs. The requirement is that you must first be able to understand the circuit diagram, and then we will proceed. Here is the sequential start/stop circuit diagram:
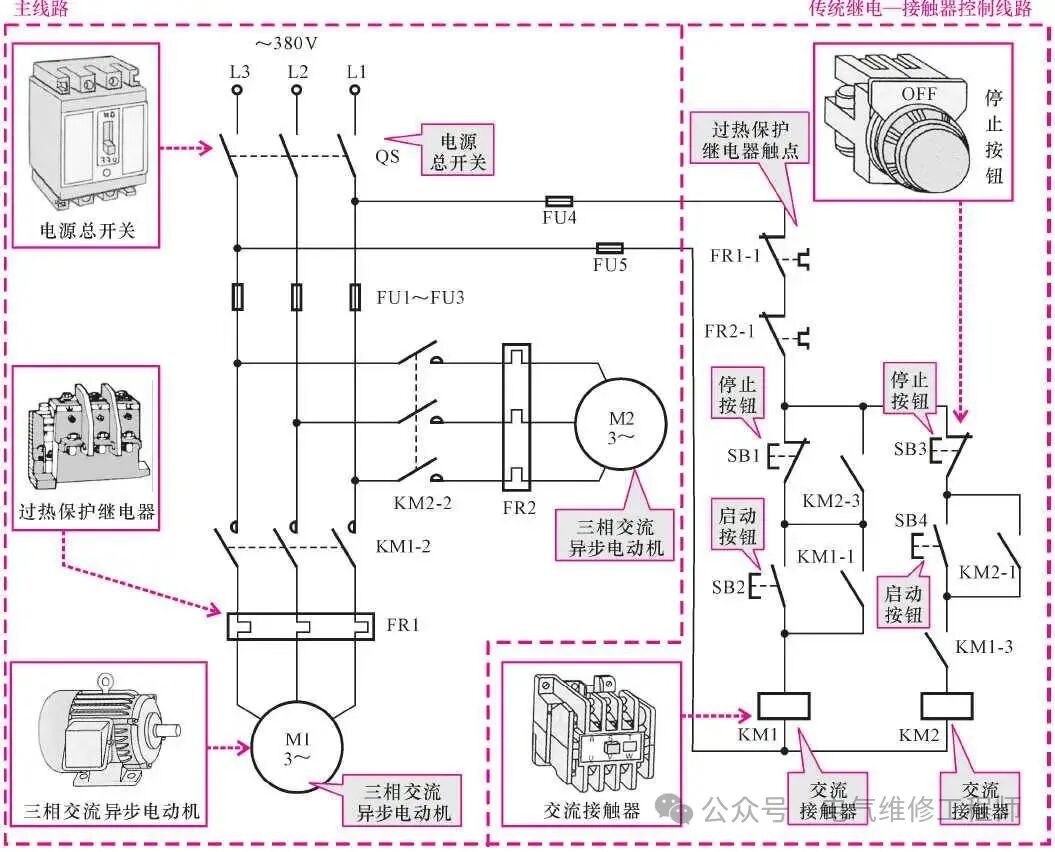
Traditional Motor Sequential Start/Stop Control System
The control requirements are: the motor must start sequentially and stop in reverse order. When starting, the first motor must be operational before the second motor can start. However, during shutdown, the power to the second motor must be disconnected before the first motor can be powered off.
The traditional motor control system consists of electrical components such as relays, contactors, control buttons, and various switches. Each control function or action is implemented by corresponding physical electrical components, and all components are essential.
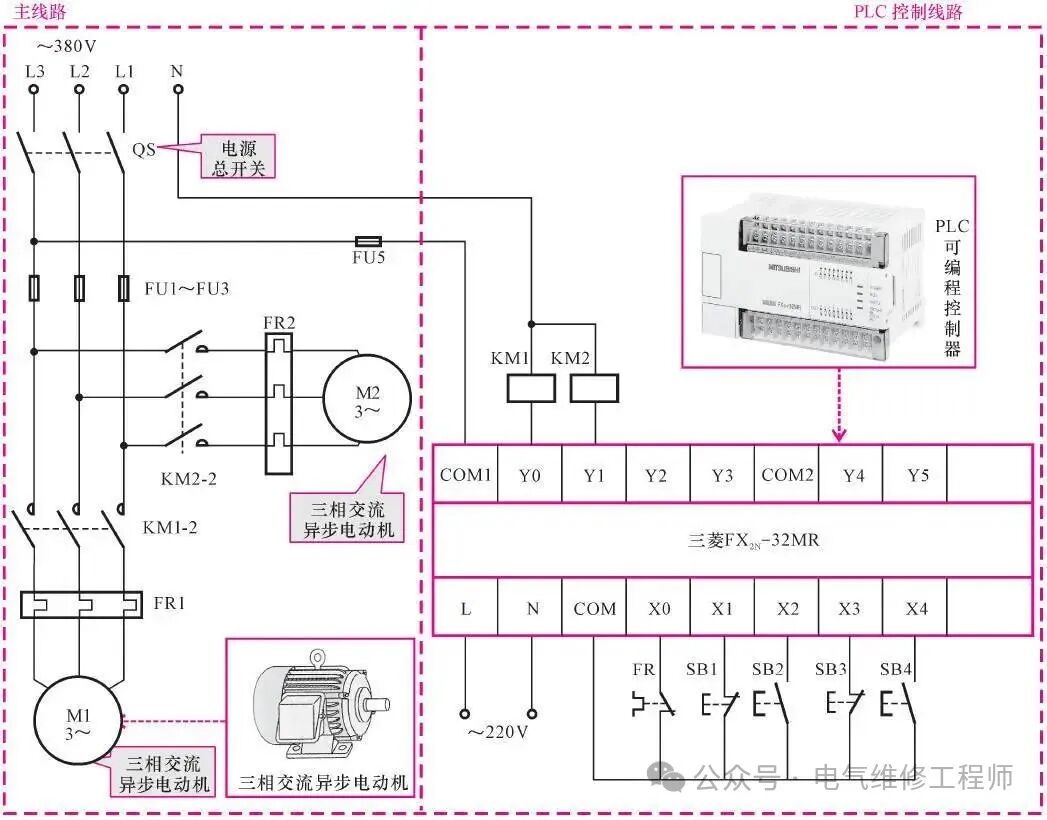
However, after using PLC control, the entire motor control system is greatly simplified. As the core control component, the actions in the motor control system are controlled by the PLC’s internal program. During operation, the entire motor control system can be automatically controlled through the PLC’s internal program.
Next, we will analyze the control process of the motor sequential start/stop control system controlled by the PLC, in conjunction with the PLC’s internal ladder diagram program.
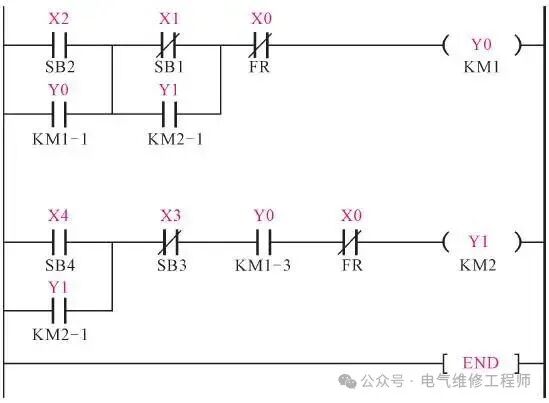
Ladder Diagram of the Motor Sequential Start/Stop Control System
To facilitate understanding, the programming elements in the ladder diagram are labeled with their corresponding buttons, AC contactor contacts, coils, etc., from the traditional control system below. 1. Working process of two motors starting sequentially under PLC control
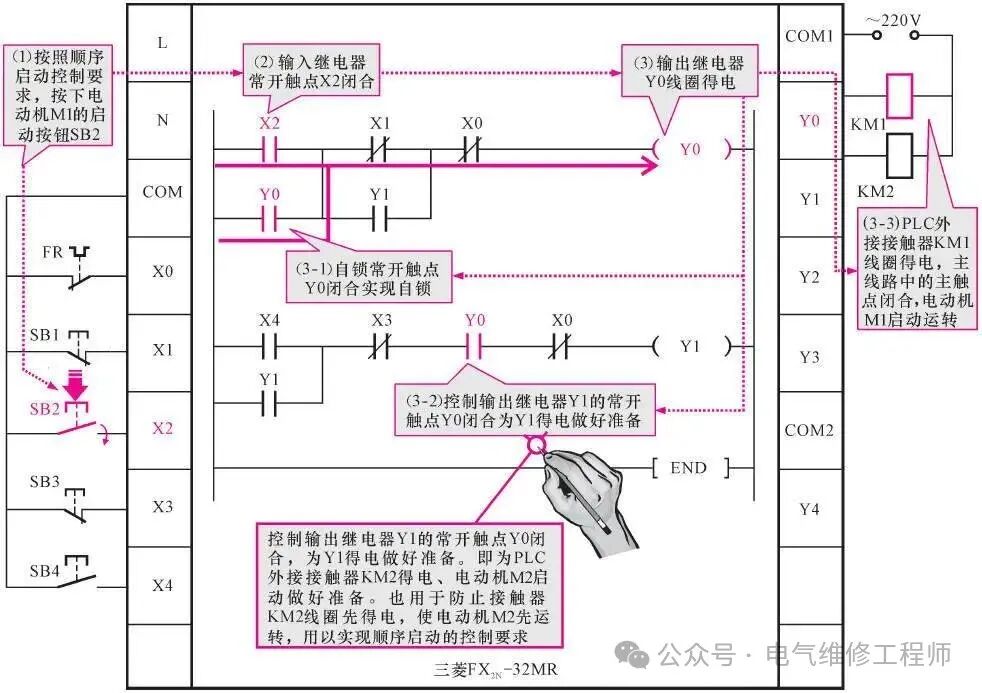
Working process when pressing the start button SB2
(1) Press the start button SB2 for motor M1.
(1)→(2) Set the input relay normally open contact X2 in the PLC program to “1”, meaning the normally open contact X2 is closed.
(2)→(3) The output relay Y0 coil is energized.
(3-1) The self-locking normally open contact Y0 closes to achieve self-locking function;
(3-2) The normally open contact Y0 of the output relay Y1 closes, preparing for Y1 to be energized;
(3-3) The coil of the external AC contactor KM1 connected to the PLC is energized, the main contact KM1-2 in the main circuit closes, connecting the power supply to motor M1, and motor M1 starts running.
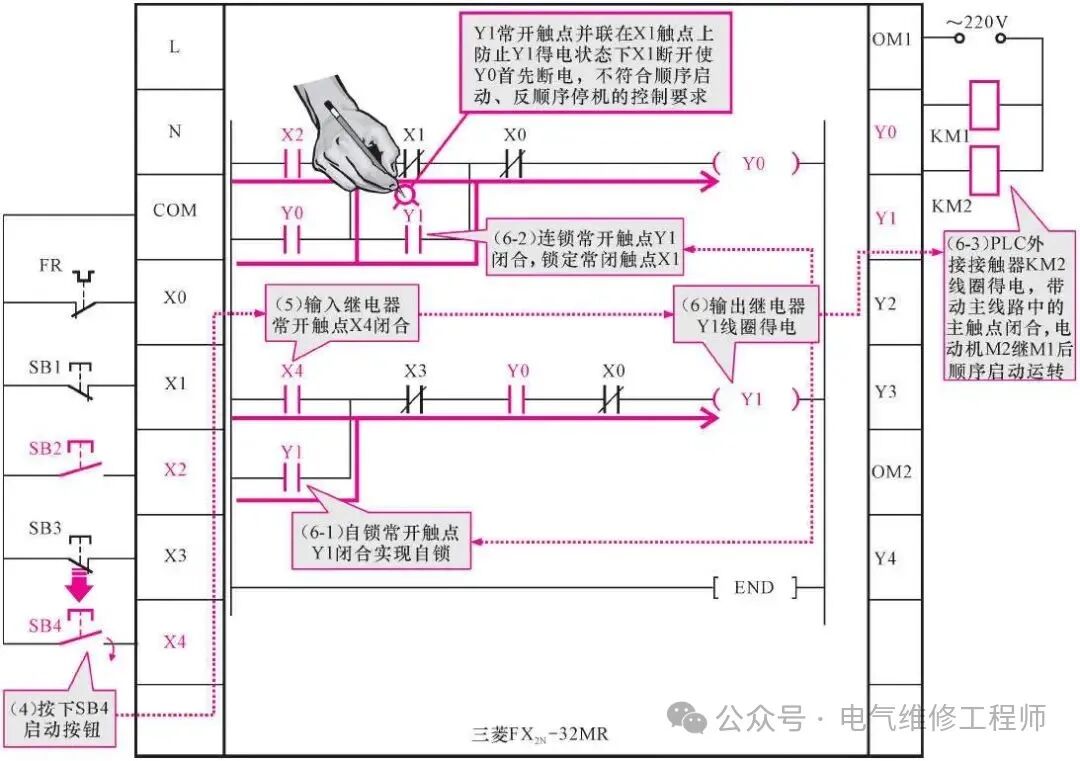
Working process of the second motor when pressing the start button SB4
(4) Press the start button SB4.
(4)→(5) Set the input relay normally open contact X4 in the PLC program to “1”, meaning the normally open contact X4 is closed.
(5)→(6) The output relay Y1 coil is energized.
(6-1) The self-locking normally open contact Y1 closes to achieve self-locking function;
(6-2) The normally open contact Y1 of the output relay Y0 closes, locking the normally closed contact X1, which locks the stop button SB1 to prevent accidental pressing of the stop button SB1 for motor M1 while starting motor M2, which would violate the reverse order stop control requirement;
(6-3) The coil of the external AC contactor KM2 connected to the PLC is energized, the main contact KM2-2 in the main circuit closes, connecting the power supply to motor M2, and motor M2 starts running after M1.
2. Working process of two motors stopping in reverse order under PLC control
When pressing the stop buttons SB1 and SB3, the working process of controlling the two motors to stop in reverse order occurs.
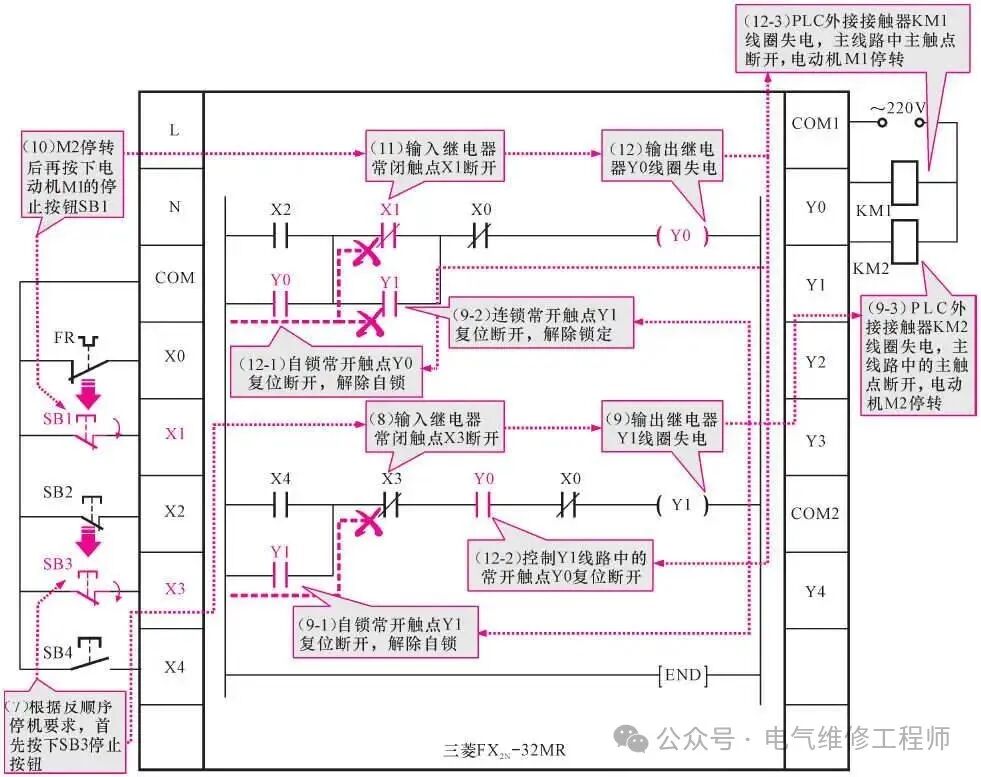 Working process of the two motors stopping in reverse order
Working process of the two motors stopping in reverse order
(7) Press the stop button SB3. (7)→(8) Set the input relay normally closed contact X3 in the PLC program to “0”, meaning the normally closed contact X3 is opened.
(8)→(9) The output relay Y1 coil is de-energized.
(9-1) The self-locking normally open contact Y1 resets and opens, releasing the self-locking function;
(9-2) The interlocking normally open contact Y1 resets and opens, releasing the lock on the normally closed contact X1, thus unlocking the stop button SB1, preparing for the operation of disconnecting the contactor KM1, achieving the reverse order stop control requirement;
(9-3) The coil of the external AC contactor KM2 connected to the PLC is de-energized, the main contact KM2-2 in the main circuit resets and opens, disconnecting the power supply to motor M2, and motor M2 stops running.
(10) Then, according to the reverse order stop control requirement, press the stop button SB1.
(10)→(11) Set the input relay normally closed contact X1 in the PLC program to “0”, meaning the normally closed contact X1 is opened.
(11)→(12) The output relay Y0 coil is de-energized.
(12-1) The self-locking normally open contact Y0 resets and opens, releasing the self-locking function;
(12-2) The normally open contact Y0 of the output relay Y1 resets and opens to prevent Y1 from being energized before Y1 is energized, which would violate the sequential start control requirement;
(12-3) The coil of the external AC contactor KM1 connected to the PLC is de-energized, the main contact KM1-2 in the main circuit resets and opens, disconnecting the power supply to motor M1, and motor M1 stops running after M2.
Through the above circuit analysis, we can summarize the working process of the motor sequential start/stop control system.

So, did you learn it?
———————
Thank you for reading, viewing, and sharing, everyone can send relevant keywords in the public account page to participate in the lottery. Reply with 【666】 in the background to enter the monthly lottery! The prize amount each month is related to the reading volume of the previous month. Participating in the lottery before the draw is valid.
Note: Reply with 【666】 in the background (not in the comment section) to participate in the lottery.