What Is Ultrasonic Testing DAC/TCG Curve?
 DAC Curve Concept: DAC=Distance Amplitude Curve
DAC Curve Concept: DAC=Distance Amplitude Curve
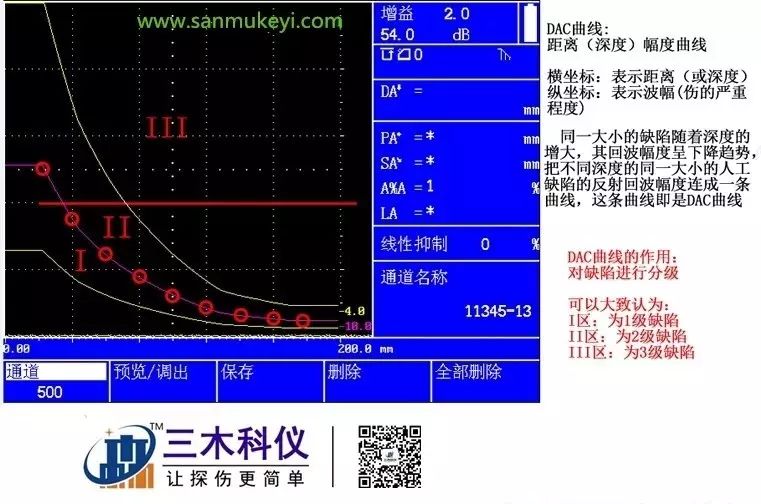
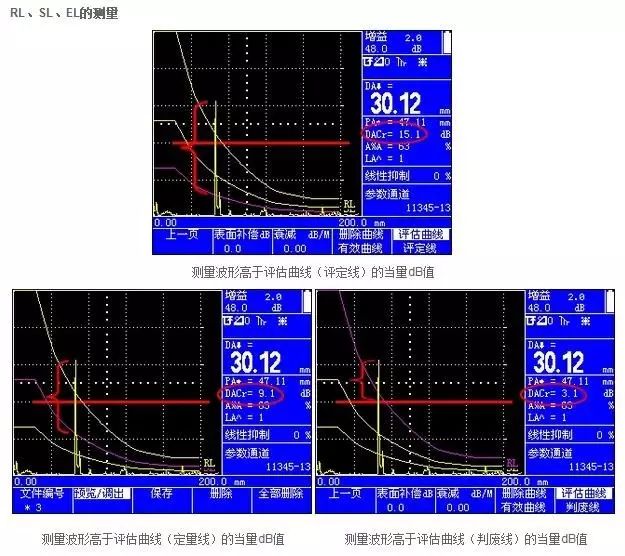
The DAC curve, or “Distance-Amplitude Curve”, represents the relationship between the amplitude of echo signals and the distance of the ultrasonic waves. For defects of the same size, the echo amplitude varies due to different sound path lengths. The horizontal axis represents the sound path length while the vertical axis represents the echo amplitude. By connecting the highest points of different amplitudes corresponding to various sound paths, we create a smooth curve known as the mother line of the DAC curve. Based on this mother line, we input the corresponding defect detection standards to determine the cutoff line, quantitative line, and evaluation line corresponding to the dB values.
DAC/TCG is a distance-amplitude curve. For equivalent defects, as the depth increases, the echo amplitude decreases exponentially due to signal attenuation, beam spreading, and other factors. Therefore, we connect the reflection echo amplitudes of artificial defects of the same equivalence at different depths to form a curve, which is the DAC curve. We then use this DAC curve to compensate for the reflection echo amplitudes at different depths, and the ultrasonic testing instrument operates in TCG mode. By connecting all the compensation values at different depths, we create the TCG curve.
Click the “Read Original” button in the lower left corner to visit the official website of Sanmu Technology for more details!