
Click the above Computer Enthusiasts to follow us
Windows 11 is currently a focal point of interest for many users, and one of its hardware requirements includes a somewhat unfamiliar yet seemingly recognized item—TMP 2.0. What exactly is this hardware? Will it affect our upgrade? What about the rumors regarding compliance issues in China? Let’s discuss it today.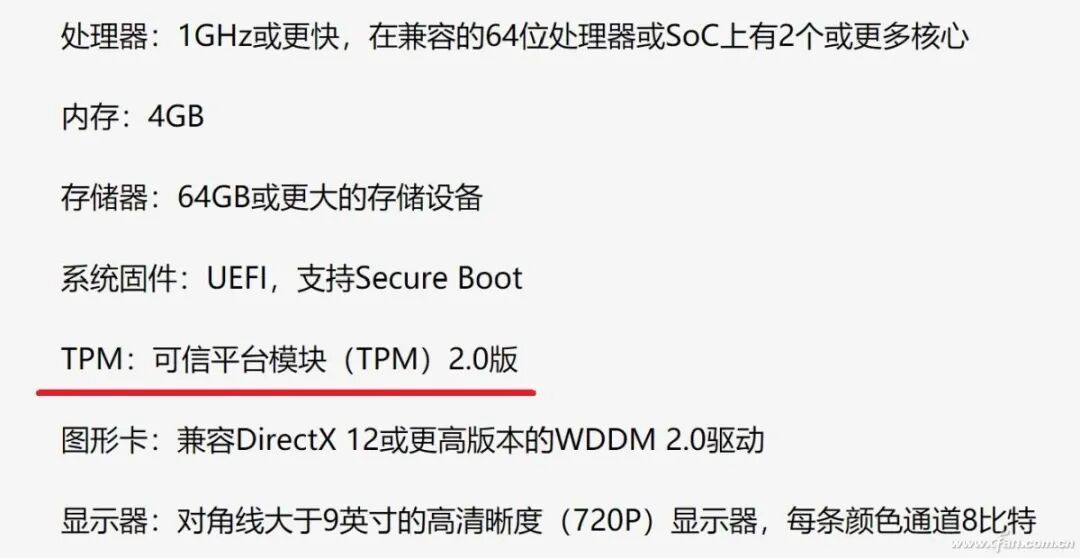 The Chinese name for TPM is 可信平台模块, and its full English name is Trusted Platform Module. It is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor that requires a chip for related processing. Windows 10 already supports this feature for device encryption, advanced BitLocker encryption, and other security features, but in Windows 10, it was only a recommended configuration. With Windows 11, security has been further enhanced, making it a basic configuration requirement.
The Chinese name for TPM is 可信平台模块, and its full English name is Trusted Platform Module. It is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor that requires a chip for related processing. Windows 10 already supports this feature for device encryption, advanced BitLocker encryption, and other security features, but in Windows 10, it was only a recommended configuration. With Windows 11, security has been further enhanced, making it a basic configuration requirement.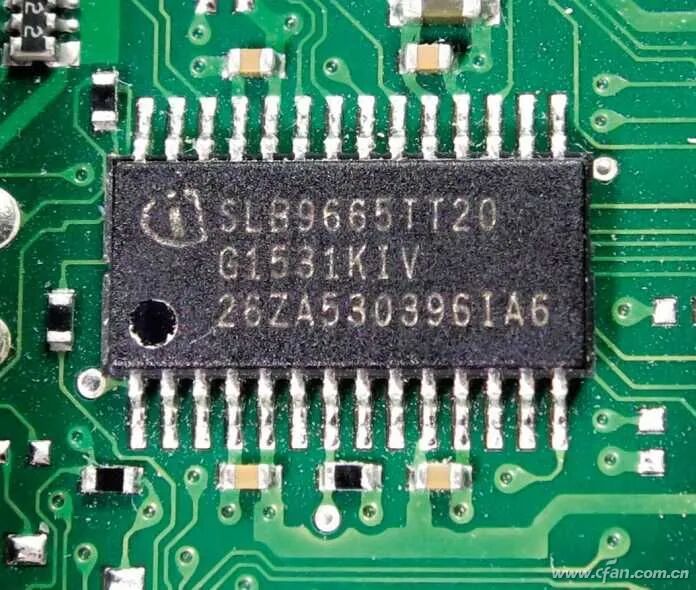 The good news about TPM is that it has long been a necessary module on mainstream motherboards, with most newer motherboards having it installed by default, supporting corresponding technologies from Intel or AMD, and this technology also complies with our national regulations. The so-called compliance issue actually refers to independent TPM modules that need to meet our regulatory approvals, which are relatively few and hard to purchase.
The good news about TPM is that it has long been a necessary module on mainstream motherboards, with most newer motherboards having it installed by default, supporting corresponding technologies from Intel or AMD, and this technology also complies with our national regulations. The so-called compliance issue actually refers to independent TPM modules that need to meet our regulatory approvals, which are relatively few and hard to purchase.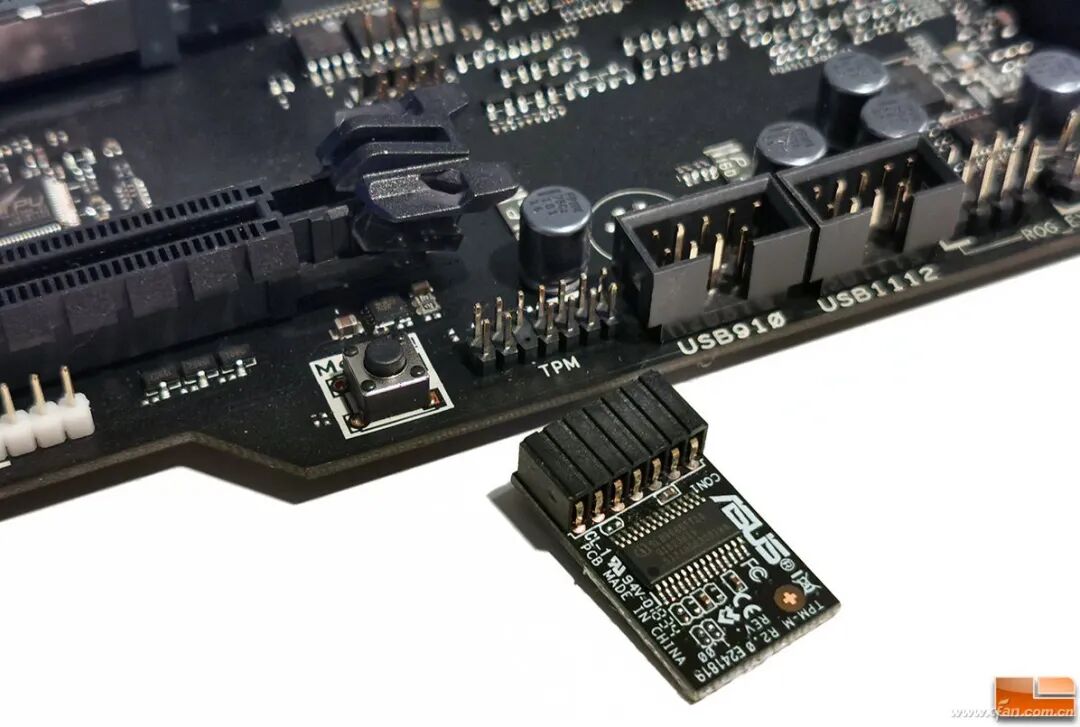 So, why do many users trying out Windows 11 often encounter TMP issues? It’s quite simple; previously, motherboards considered user needs, and this feature is set to be disabled by default. The way to enable it is straightforward: enter the motherboard BIOS (UEFI) settings interface, and you can generally find the security options under “Advanced” or “Settings” pages, where the item related to TMP can be found and set to enabled.
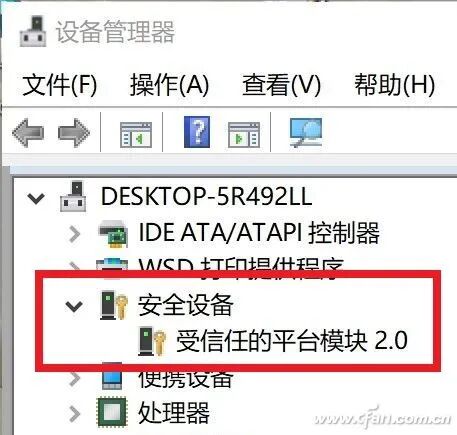
So, why do many users trying out Windows 11 often encounter TMP issues? It’s quite simple; previously, motherboards considered user needs, and this feature is set to be disabled by default. The way to enable it is straightforward: enter the motherboard BIOS (UEFI) settings interface, and you can generally find the security options under “Advanced” or “Settings” pages, where the item related to TMP can be found and set to enabled.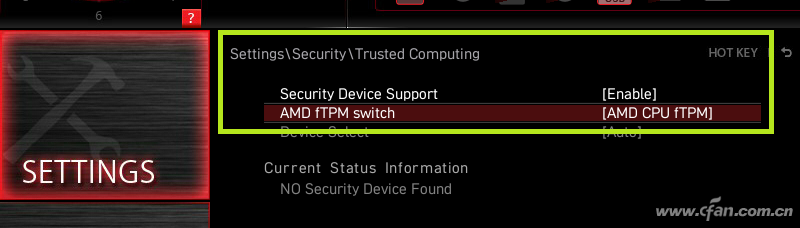 To confirm whether TMP is enabled, simply right-click the Start button in Windows 10, select “Device Manager,” and look for “Security Devices” – “Trusted Platform Module 2.0” to ensure it is present. Lastly, enabling this chip is actually beneficial for some security features in Windows 10, so even if you are not considering trying out Windows 11, it is worth enabling it since it is free; why not give it a try?
To confirm whether TMP is enabled, simply right-click the Start button in Windows 10, select “Device Manager,” and look for “Security Devices” – “Trusted Platform Module 2.0” to ensure it is present. Lastly, enabling this chip is actually beneficial for some security features in Windows 10, so even if you are not considering trying out Windows 11, it is worth enabling it since it is free; why not give it a try?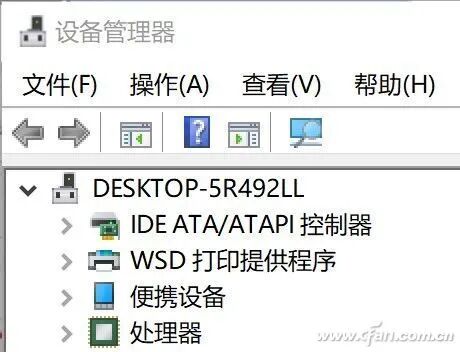
 After reading this article, you might also click:
After reading this article, you might also click:

Click “Read the original text” for more exciting content