

According to the definition of the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), robots are divided into Industrial Robots and Service Robots. Currently, industrial robots account for 80% of the global robot market share, far exceeding that of service robots.
From a mechanical structure perspective, industrial robots can be categorized into single-axis robots, Cartesian robots, horizontal multi-joint robots (SCARA), vertical multi-joint robots, and parallel robots (DELTA). Below, we will sequentially explain these five types.

1. Single-Axis Robots
Single-axis robots are generally divided into two types of drive methods: one is ball screw drive, and the other is synchronous belt drive (commonly referred to as synchronous belt). Both types use linear guides for guidance and are paired with servo motors or stepper motors to achieve positioning, transfer, and handling in various application fields. Through different combinations, two-axis, three-axis, and gantry-style combinations can also be realized.
The application fields of single-axis robots includesemiconductors, home appliances, medical, automotive, packaging, dispensing machines, welding, cutting, inspection, and other automation application fields. Taiwan’s Hiwin Technologies ranks among the top three in the global single-axis robot market.

2. Cartesian Robots
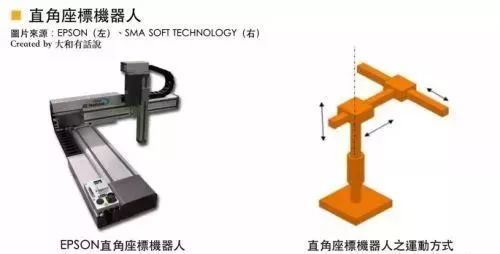
Cartesian robots operate based on X, Y, and Z coordinates, working or moving within the length range of each coordinate. They are suitable for tasks such as handling and placing items. Application fields include robotic arms for injection molding machines, mobile and positioning, stacking, screw locking, cutting, clamping, pressing, insertion, assembly, and automatic pharmacies.
There are approximately 80 robotic related businesses in Taiwan, with over 40 companies engaged in the design and development of Cartesian robot related equipment, with a high degree of localization for key components used. In the field of robotic arms for injection molding machines, Tianxing Automation (Alfa) and Taiwan Apex are leading players with a significant market share in mainland China.
3. Horizontal Multi-Joint (SCARA) Robots
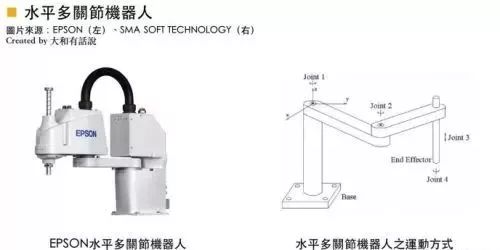
Horizontal multi-joint robots (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm; abbreviated SCARA) are a special type of industrial robot based on cylindrical coordinates. They generally have four degrees of freedom, including translation along the X, Y, Z directions and rotation around the Z-axis.
The characteristics of SCARA robots include small load and high speed, making them mainly applied in fast sorting and precision assembly in the 3C industry or food industry. For example, in the IC industry, SCARA robots can be seen in wafer, panel handling, circuit board transport, and electronic component insertion assembly. Foreign manufacturers include EPSON, IAI, DENSO, and others. Domestic manufacturers include Delta Electronics, Dongyoud, and Hiwin.
4. Vertical Multi-Joint Robots
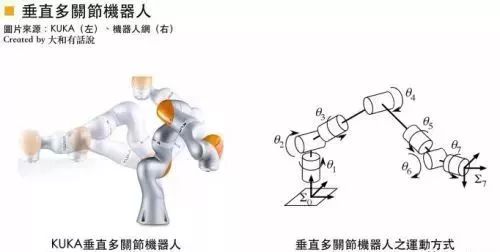
Vertical multi-joint robots possess a high degree of freedom and can work at any trajectory or angle. They feature three-dimensional motion characteristics and can achieve high-order nonlinear motion, making them the most widely used automated mechanical devices, commonly found in automotive manufacturers, automotive components, and electronics-related industries.
Hiwin Technologies, Hezhuang Technology, and Foxconn have all launched their own branded six-axis multi-joint robots at international robotics exhibitions. However, the key component, the harmonic drive, still needs to be imported, making them less competitive in terms of price.
5. Parallel (DELTA) Robots
Parallel robots, also known as DELTA robots, use three sets of drive structures on the upper platform to drive the active and passive arms to displace the end platform. A fourth axis can be mounted at the end or connected to the fourth axis as a rotating axis from the upper platform.
Due to their simple structure, they can achieve the shortest distance in movement, and the mechanism is easy to miniaturize, allowing for high-speed, high-precision control. Thus, they are mainly used in high-speed pick-and-place and sorting operations, primarily in the food industry, electronic inspection, pharmaceuticals, packaging, etc. Generally, a parallel robot can replace 4-6 manual workers, helping users effectively improve production efficiency and reduce production costs.

After understanding the five mechanical structures of industrial robots, let’s discuss the remaining three key components: the reducer, the servo motor, and the controller. These components account for about 60-70% of the total cost of the robot, representing a significant barrier to entering the industrial robot industry.
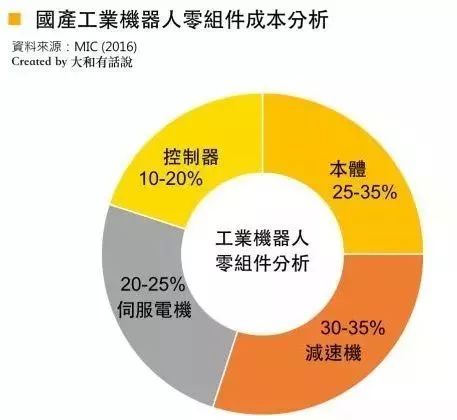
Looking at the four major industrial robot manufacturers globally (Switzerland’s ABB, Japan’s FANUC, Germany’s KUKA, and Japan’s YASKAWA), the controller is the only key component that is self-manufactured by all of them, while servo motors and reducers are partially outsourced. Below, we will sequentially explain these three components:
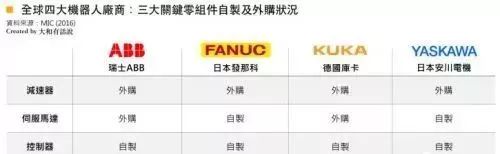
1. Reducer
The reducer is the transmission mechanism connecting the power source and the actuator, capable of reducing the motor’s rotational speed and increasing torque. It engages the power from high-speed operations of electric motors, internal combustion engines, etc., through a small gear on the input shaft, then outputs to a large gear on the shaft to achieve the purpose of deceleration and, in turn, transmit greater torque.
The reducer emphasizes high reliability, high precision, and high rigidity, making it a capital-intensive, high-investment, and slow-return industry. From the perspective of global industrial robot manufacturers, many do not independently develop reducers but primarily rely on two giants, Japan’s Nabtesco and Harmonic Drive, which together account for over 70% of the reducer market share.
According to IFR estimates, industrial robot sales will reach 414,000 units in 2019. If we consider that a multi-joint industrial robot requires 4-6 reducers, the market will have a demand for over two million sets of reducers, indicating that its growth rate will outpace that of industrial robots.
2. Servo Motors
Servo motors are the power system of industrial robots, typically installed at the “joints” of the robot, serving as the heart of robot movement. They can usually be subdivided into two parts: the motor body and the motion control system.
Mainstream suppliers include Japan’s Panasonic, Moog, Yaskawa, Mitsubishi, Sanyo, Fuji, and European and American manufacturers such as Germany’s Lenze and Bosch Rexroth. Currently, Japanese brands alone account for 40% of the global robot market share. In Taiwan, brands like TECO and Delta Electronics also perform well.
3. Controllers
Controllers serve as the “brain” of the robot, comprising both hardware and software components. The hardware is the industrial control board, while the software consists of control algorithms. Generally, more mature robot manufacturers tend to develop controllers independently to ensure product quality stability and maintenance systems, making it a core technology for robot manufacturers.
In addition to the four major industrial robot manufacturers developing their controllers, EPSON, DENSO, and TOSHIBA have also deeply engaged in the controller field, producing their own branded robots. In Taiwan, companies like the Industrial Technology Research Institute, Advantech, and Newland have also achieved good results in the global controller market in recent years.
Source: eefocus
Business Cooperation: 010—88379790 ext. 802, 822
Disclaimer: This article is a network reprint, and the copyright belongs to the original author. However, due to numerous reprints, it is impossible to confirm the true original author, so only the source of reprint is indicated. If the videos, images, and texts used in this article involve copyright issues, please inform us immediately, and we will confirm copyright based on the proof materials you provide and pay remuneration according to national standards or delete the content immediately! The content of this article represents the author’s views and does not represent the views of this official account or take responsibility for its authenticity.

Reply 4: Join the industrial robot technology exchange group 4 (focusing on industrial robot applications, automated production lines, etc.)
Reply 5: Join the industrial robot technology exchange group 5 (focusing on the composition of industrial robots, including body, drive system, control system, etc.)
Reply 6: Join group 6 (focusing on PLC technology, programming technology, etc.)