The Discovery of Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystals were first discovered by Austrian botanist Friedrich Reinitzer in 1888. While determining the melting point of organic substances, he found that certain organic compounds (cholesterol benzoate and acetate) would melt into an opaque, white, cloudy liquid state, emitting a colorful and beautiful pearlescent sheen, and only became a transparent, clear liquid when heated to a certain temperature.

The following year, German physicist Otto Lehmann used a polarizing microscope with a heating device that he personally designed to observe these fatty compounds. He discovered that although this white, cloudy liquid appeared to be a liquid, it exhibited the unique birefringence of anisotropic crystals. Thus, Lehmann named it “liquid crystal,” which is the origin of the term “liquid crystal.”
The Structure of Liquid Crystals
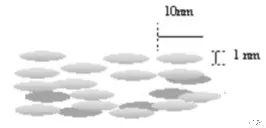
Liquid crystals are organic compounds that exist between solid and liquid states, characterized by a regular molecular arrangement. The most commonly used type of liquid crystal is nematic liquid crystal, where the molecules are elongated rod-shaped, measuring about 1nm to 10nm in length and width. Under different electric fields, the liquid crystal molecules can rotate and rearrange in a regular 90-degree pattern, resulting in differences in light transmission. This principle controls each pixel, allowing for the formation of the desired image when the power is ON/OFF.
Introduction to LCD
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, a digital display technology that uses liquid crystals and color filters to modulate light and produce images on flat panels. Compared to traditional cathode ray tubes (CRT), LCDs take up less space, consume less power, emit less radiation, and reduce flicker, thereby decreasing visual fatigue. However, they are generally more expensive than CRTs of the same size.
After years of leading the notebook market, smooth screens based on liquid crystal display technology are gradually entering the desktop system market.
LCDs offer many advantages over traditional CRT display technologies, providing clearer text display and flicker-free screens, effectively reducing visual fatigue from prolonged screen time.

LCD monitors generally do not exceed 10 inches in thickness, which means that adopting LCD technology for desktop systems will save even more space.
While LCD monitors have their unique advantages, it is undeniable that compared to their main competitor, CRT monitors, LCDs still have shortcomings in high-quality color display. Additionally, the significant price difference means that LCDs remain a luxury product enjoyed by only a few.
Introduction to LCM
LCM stands for Liquid Crystal Display Module, which refers to a component that integrates the liquid crystal display device, connection components, control and drive circuits, PCB circuit board, backlight source, structural components, etc.
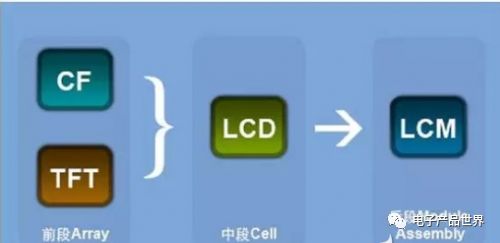
Differences Between LCD and LCM
LCD is short for Liquid Crystal Display, which simply refers to a display. It mainly refers to the liquid crystal panel, including polarizers, color filters, and liquid crystal glass (glass sandwiching liquid crystal), and the TFT control components.
LCD refers to the display screen (LCD liquid crystal screen), while LCM includes the LCD as well as the chips, circuit boards, and other components that control the LCD display modes and content. In other words, LCD is the frontend that displays content, while LCM encompasses the entire operational system including the frontend. However, generally speaking, both are often considered synonymous.
1. LCM includes a character library, while LCD generally does not.
2. LCD is a liquid crystal display, typically referring to a standalone screen; LCM is a liquid crystal display module, which includes the corresponding driving and control circuitry that can connect directly to a microcontroller.
In simple terms, a liquid crystal module consists of an LCD screen + LED backlight + PCB board + metal frame. The module is mainly divided into the screen and backlight components. The two parts are assembled together but operate independently (i.e., the circuits are not related).
The principle of liquid crystal display is that the backlight component emits uniform surface light, which passes through the liquid crystal screen to reach our eyes. The role of the screen is to process this light by pixels to display images.
