 Tip:Click the above↑ to quickly follow this account
Tip:Click the above↑ to quickly follow this account
For a long time, the logic analyzer has been shrouded in mystery. While most R&D personnel are very familiar with oscilloscopes, they may still be somewhat unfamiliar with logic analyzers. You might guess that it is an expensive, large instrument with a bulky chassis. Right or wrong, at least that is what I thought back in college until I graduated and started working, when I truly understood what a logic analyzer is. Let’s take a look at what a logic analyzer is, its origin, and its functions.
The Birth of the Logic Analyzer
In 1973, the first instrument for testing the logical relationships between multiple signals in digital systems—the logic analyzer—was born. Initially, this was just a project in collaboration between HP and IBM. Later, HP recognized its commercial value and promoted it as a general-purpose instrument, gaining wide recognition among engineers, thus making its mark in the domain of data testing instruments. With the rapid development of digital circuits, the demand for logic analyzers has increased, and it has gradually become the ultimate tool for debugging digital circuits.

Figure 2 The predecessor of modern logic analyzers
The Development of Logic Analyzers
In the first few years after the logic analyzer was introduced, it was quite expensive, and few people had heard of it. The companies that could afford it were well-known brands, and the number of companies capable of developing such instruments was very limited (mainly HP and Tektronix). During this period, almost all logic analyzers sold were desktop models. In 1994, many international semiconductor and computer companies jointly launched USB communication technology. Around the year 2000, a number of virtual instrument manufacturers rapidly emerged both domestically and internationally, and virtual logic analyzers based on PCs were introduced at this time, gradually becoming mainstream. They commonly use USB communication, and compared to traditional desktop logic analyzers, they are compact, portable, feature-rich, and cost-effective.

Figure 3 Various virtual logic analyzers
Currently, virtual logic analyzers have taken over the main market for logic analyzers. Although their performance is slightly weaker than that of desktop logic analyzers, high-end logic analyzers are still mainly desktop models. However, the performance gap between the two is narrowing, and in most cases, users can solve problems with just a virtual logic analyzer, which has lower procurement costs and more flexible applications, making its advantages very apparent.

Figure 4 Virtual logic analyzers becoming mainstream
Although virtual logic analyzers are already very mature, there are still shortcomings, such as the inability to display waveforms in real-time under high-speed sampling conditions. This situation is unlikely to last long, as technological advancements have significantly increased the bandwidth of serial communication (USB 3.0), and virtual logic analyzers are expected to quickly enter the era of real-time waveform display. Additionally, adding analog input channels to logic analyzers is becoming a trend.
The Role of Logic Analyzers
From the literal understanding, a logic analyzer is an instrument for analyzing the logical timing of digital signals. In digital circuits, signals are transmitted through ordered binary codes of 0s and 1s. When the “order” becomes chaotic or there is a deviation in timing, the communication error rate can be very high, leading to abnormal operation of the electronic system.
In terms of working mechanism, the virtual logic analyzer mainly performs high-speed data acquisition and then uses a USB interface to upload the data to a computer. Relying on the powerful data processing capabilities of modern computers, the accompanying specialized logic analysis software can quickly complete the complex analysis and display of large amounts of waveform data, while providing a user-friendly and convenient human-computer interaction experience.

Figure 5 The role of logic analyzers
Logic analyzers have an extremely high sampling rate, capable of accurately capturing and displaying multiple digital signals, and providing complete testing and measurement methods, quickly identifying timing issues with signals. This is the most commonly used function and also the basic function.
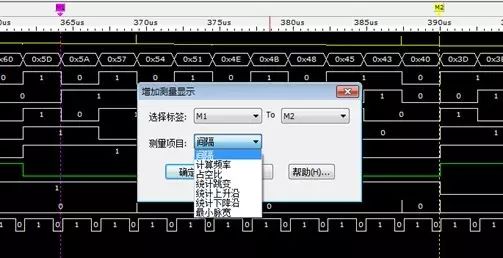
Figure 6 Timing analysis and measurement
Of course, in addition to analyzing signal timing, logic analyzers also have many advanced functions, such as executing disassembly, protocol decoding, and protocol analysis based on waveforms, achieving joint analysis of waveforms with code and data to quickly locate circuit issues.

Figure 7 Protocol analysis and decoding

