

In “Early C, Late A,” the “A” refers to retinol. Research suggests that retinol has beneficial effects on the skin, which is why it is widely included in various skincare products. Advertisements often highlight its effects on whitening, anti-aging, acne treatment, and redness reduction, but the irritative properties of retinol and its potential adverse reactions should not be underestimated.

Summary
1. Retinol can promote skin metabolism and reduce melanin production, thereby aiding in skin repair and regeneration, achieving the effects of spot removal and skin whitening.
2. Retinol has skin irritative properties; excessive use may lead to skin sensitivity, barrier damage, and even toxicity risks. Retinol is contraindicated during pregnancy due to teratogenic risks.
3. When using for the first time or switching products, it is recommended to perform a patch test and gradually build tolerance; it is advisable to use it at night to avoid light exposure; mixing products with different effects is not recommended.
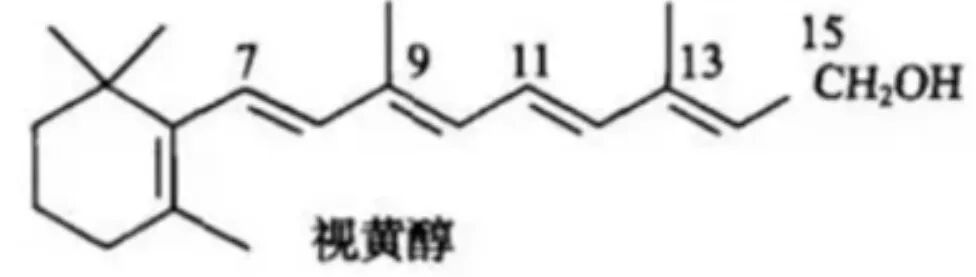
This is what retinol looks like ⬆
Retinol, also known as retinoids, is a derivative of vitamin A. It participates in various biological processes in the human body, including embryonic development, vision production, and the proliferation and damage of tissues and cells. Additionally, it can promote skin metabolism and accelerate the generation of new cells by regulating the mitogenic action of epidermal growth factors, thus aiding in skin repair and regeneration. It can reduce melanin production to achieve an even skin tone and spot removal.
Compared to other skincare ingredients, there are more precautions to consider when using retinol.
Adverse Reactions from Improper Use of Retinol

1. Skin Irritation
Retinol has skin irritative and phototoxic properties, and the higher the concentration in skincare products, the stronger the irritation. Improper use can lead to irritant contact dermatitis, phototoxic dermatitis, and allergic contact dermatitis, with common symptoms including erythema, itching, flushing, dryness, and peeling.
2. Skin Barrier Damage
After using retinol, noticeable effects generally take 2-3 months to appear. If one seeks rapid results by combining it with alpha hydroxy acids, it may lead to skin sensitivity and barrier damage. Studies have found that compared to Western testers, Chinese individuals have a lower tolerance to retinol, with more pronounced irritative reactions, including redness, stinging, and even severe side effects like pigmentation.
3. Toxicity Risks
The maximum daily intake of vitamin A for normal adults is 3000μg/d; exceeding this amount poses toxicity risks. Excessive use of retinol can be absorbed into the body, and if one also consumes vitamin A-rich supplements, health products, or foods, it may lead to vitamin A overdose, resulting in systemic adverse reactions such as nausea, headaches, abdominal pain, liver damage, and osteoporosis.
4. Teratogenic Risks
Retinol is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. Excessive intake during early pregnancy poses teratogenic risks. Some forms of retinol, such as tretinoin and its salts, are prohibited ingredients in cosmetics, with the highest teratogenic risks, and must be used strictly according to medical advice. Although the concentration of retinol in cosmetics is relatively low, for safety reasons, it is recommended that pregnant women, nursing mothers, and those planning to conceive use caution.
Use with Caution and Gradually
1. Patch Test to Build Tolerance
When using for the first time or switching products, it is recommended to perform a patch test to confirm the absence of adverse reactions. When using for the first time, control the dosage and choose products with lower concentrations (e.g., ≤0.15%) to gradually build tolerance. If adverse reactions occur during the test, it is advisable to discontinue use of such products.

2. Use at Night and Ensure Sun Protection
Retinol products are photosensitive; it is recommended to use them at night and ensure sun protection during the day.

3. Don’t Rush, Be Cautious with Combinations
In the initial stages of use, it is advisable not to mix with other functional skincare products to effectively reduce skin irritation.

4. Follow Medical Advice, Don’t Use Blindly
For certain special populations, such as pregnant women, it is essential to consult a doctor before using retinol products.

Given the skincare effects and potential risks of retinol, several international organizations have standardized its concentration in cosmetics.
In October 2022, the European Commission’s Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) stated in its revised assessment SCCS/1576/16 that the safe concentration of this ingredient in body lotions should not exceed 0.05% retinol equivalent; for other leave-on and rinse-off products, the concentration should not exceed 0.3% retinol equivalent.

[Terminology Tip]
Retinol Equivalent refers to the total amount of all vitamin A active substances, including vitamin A and provitamin A, converted into retinol.
References:
[1] See, J. A., Goh, C. L., Hayashi, N., Suh, D. H., & Casintahan, F. A. (2018). Optimizing the use of topical retinoids in Asian acne patients. The Journal of dermatology, 45(5), 522–528.
[2] Chinese Nutrition Society. “Reference Intake of Dietary Nutrients for Chinese Residents (2023 Edition)” [M]. People’s Health Publishing House, 2023, 332-333.
[3] https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/revision-scientific-opinion-sccs157616-vitamin-retinol-retinyl-acetate-retinyl-palmitate_en.
Submitted by: Huan Luo
Edited by: Jie Ji
Reviewed by: Lihong Zhou, Gonghua Tao
