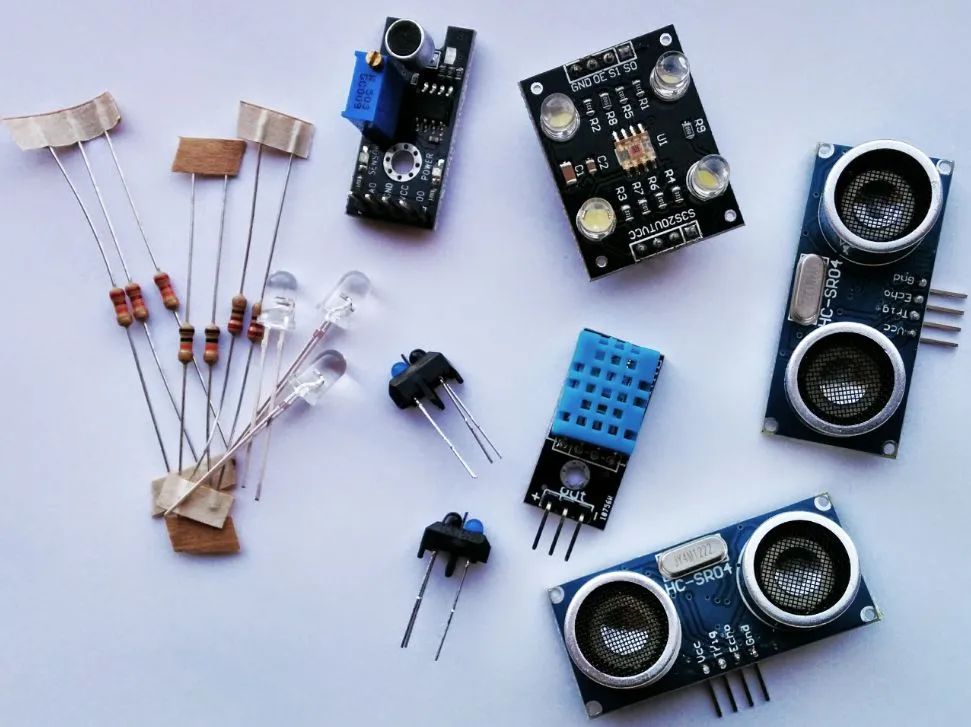
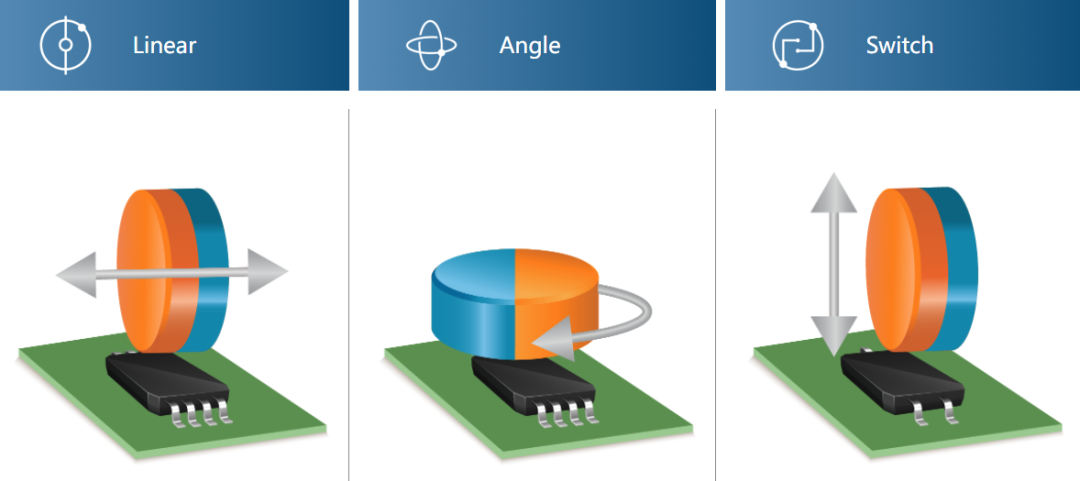
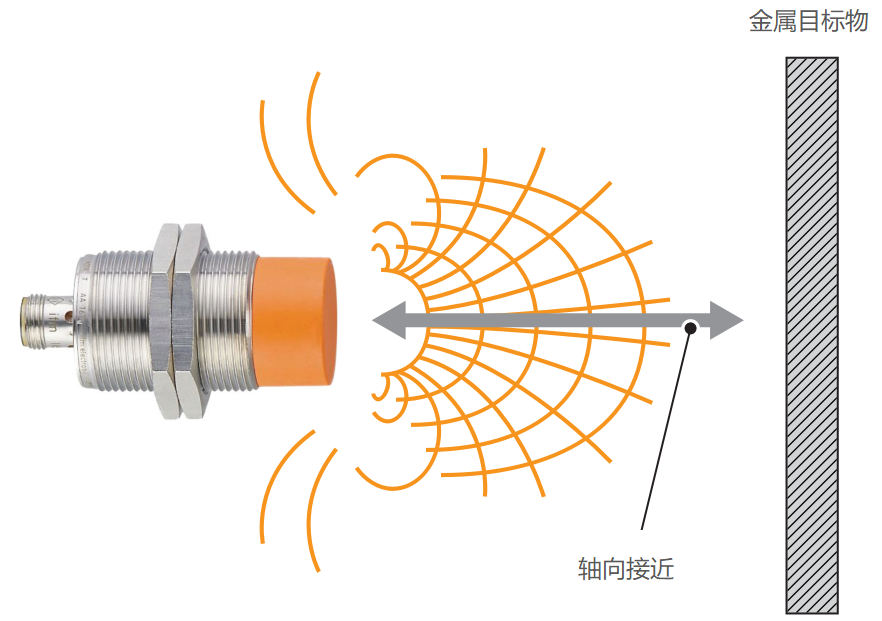
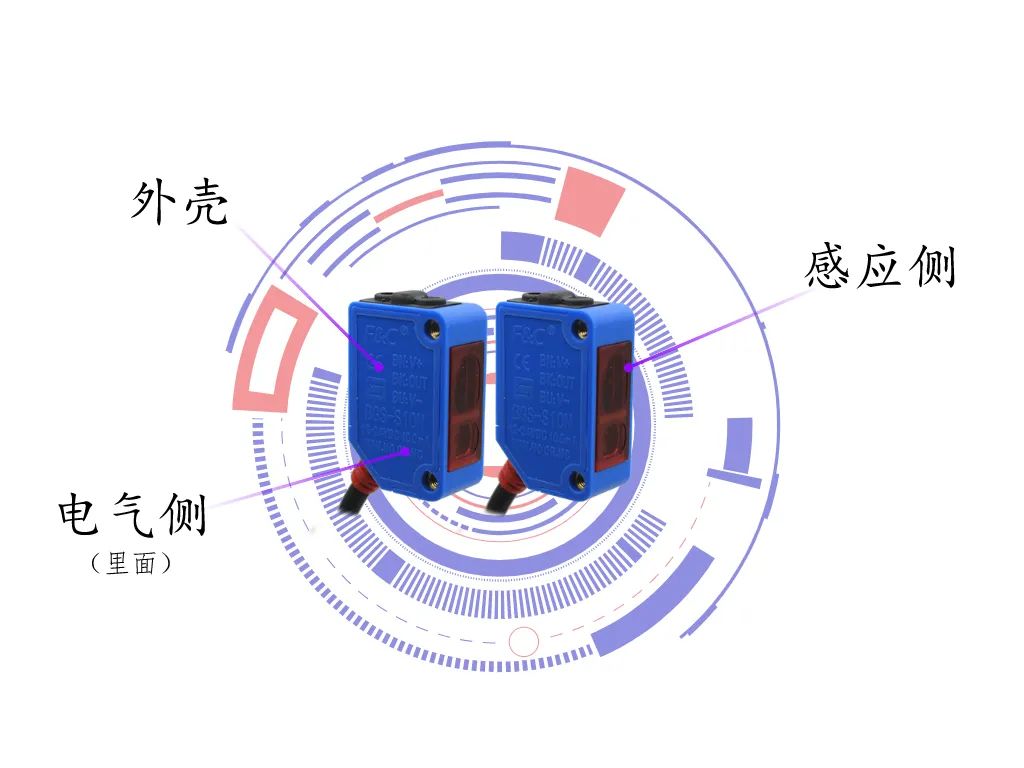
According to the decision made at the fifteenth meeting of the Technical Committee for Commodity Classification under the Coordination System, the classification principles for sensors are as follows:
1. Product Name: Sensor (English Name: transducer/sensor) is a type of detection device that can sense the information being measured and convert the sensed information into electrical signals or other required forms of information output according to certain rules, to meet the requirements for information transmission, processing, storage, display, recording, and control.
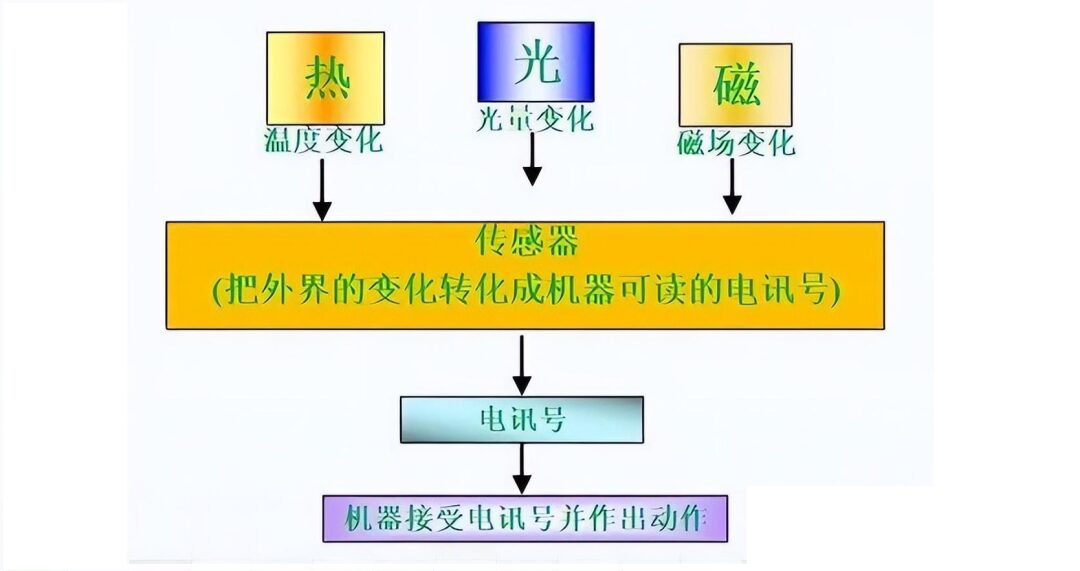
GB/T7665-2005 “General Terms for Sensors” defines
Sensor transducer/sensor: is a device or apparatus that can sense the measured object and convert it into usable output signals according to certain rules, usually composed of sensitive elements and transducing elements.
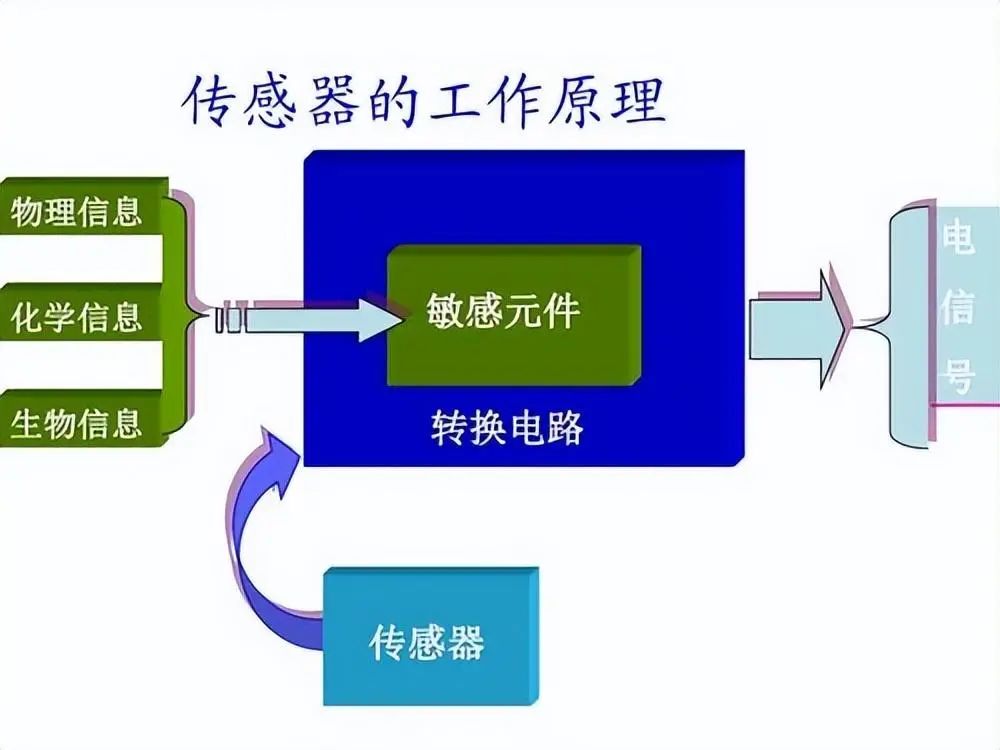
Note 1: Sensitive element (sensing element) refers to the part of the sensor that can directly sense or respond to the measured object.
Note 2: Transducing element refers to the part of the sensor that can convert the response of the sensitive element into electrical signals suitable for transmission or measurement.
Note 3: When the output is a specified standard signal, it is called a transmitter.
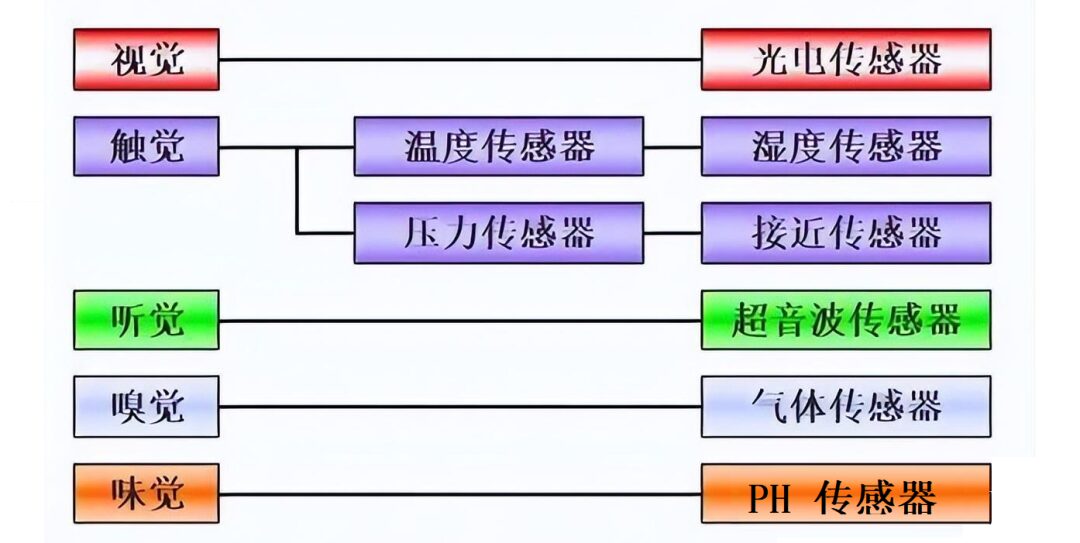
The characteristics of sensors include: miniaturization, digitization, intelligence, multifunctionality, systematization, and networking. They are the primary link for achieving automatic detection and automatic control. The existence and development of sensors give objects tactile, taste, and olfactory senses, making them gradually come to life. Generally, sensors are classified into ten categories based on their basic sensing functions: thermal sensitive elements, optical sensitive elements, gas sensitive elements, force sensitive elements, magnetic sensitive elements, humidity sensitive elements, sound sensitive elements, radiation sensitive elements, color sensitive elements, and taste sensitive elements.
Common Sensor Product Names and Explanations:
The proximity sensor can detect whether an object exists in the nearby area without physical contact. The presence sensor is a discrete output device. Typically, magnetic proximity sensors detect whether the actuator has reached a specific position by sensing the magnet located in the actuator.
It is generally not a good idea to purchase an actuator from one company and a magnetic proximity sensor from another company. Although sensor manufacturers may claim that their sensors are compatible with X, Y, and Z actuators, the reality is that variations in magnets and installation positions may lead to sensing problems. For example, when the magnet is not in the correct position, the sensor may be excited or may not excite at all. If the actuator manufacturer provides proximity sensors that match the actuator, that should be the preferred sensor.
Transistor-based proximity sensors have no moving parts and long lifespans. Reed-based proximity sensors use mechanical contacts, have shorter lifespans, but are cheaper than transistor types. Reed sensors are best suited for applications requiring AC power and high-temperature applications.
Position sensors have analog output and indicate the position of the actuator based on the position of the magnet on the actuator. From a control perspective, position sensors provide great flexibility. Control engineers can determine a range of setpoint values that match component variations.
Since these position sensors are based on magnets (like proximity sensors), it is best to buy sensors and actuators from the same manufacturer (if possible). With IO-Link functionality, data from the position sensor can be obtained, which can also simplify control and achieve parameterization.
Inductive proximity sensors use Faraday’s law of induction to measure the presence of an object or simulate output position. The most critical factor when selecting an inductive sensor is determining the type of metal the sensor detects, which determines the sensing distance. The sensing range for colored metals is reduced by more than 50% compared to black metals. The product manual from the sensor manufacturer should provide the information needed for sample selection.
4. Pressure and Vacuum Sensors
Ensure that pressure or vacuum sensors can meet measurement pressure ranges in imperial (pounds per square inch) and metric (bar). Specify the dimensions that best fit the allocated space. When installing the equipment, consider whether the sensor should be configured with indicator lights or a display screen for ease of use by operators. If quick setpoint changes are needed, consider using pressure and vacuum sensors equipped with IO-Link.
Like pressure and vacuum sensors, flow sensors can be selected based on flow range, size, and variability of setpoints. When ordering sensors, display options can be specified. Flow sensors with relatively low flow rates can be selected for a specific area of the equipment and the entire device.
The most common optical sensors are photoelectric scattering, reflection, and through-beam. Laser sensors and fiber optic sensing devices also belong to the optical sensor category.
Photoelectric sensors are mostly presence sensors that detect objects by reflecting light or blocking light beams. Due to their low cost, versatility, and high reliability, these sensors are among the most widely used sensors in manufacturing. Diffuse photoelectric sensors do not require reflectors. They are cost-effective sensors used to detect the presence of nearby objects.
Through-beam photoelectric sensors can provide the longest sensing range, with the transmitter and receiver units installed at two points. Garage door safety sensors are beam sensors. When the beam is interrupted, it indicates the presence of a target.
Slot-type photoelectric sensors are an interesting variant of through-beam sensors; they integrate a transmitter and receiver in one compact unit. Slot-type optical sensors are used to detect the presence or absence of small parts.
Reflective photoelectric sensors have a sensor and reflector for medium-distance presence sensing. In terms of accuracy and cost, this sensor is between diffuse and through-beam sensors.
Fiber optic sensing devices are used for presence and distance sensing. The parameters on these versatile sensors can be adjusted to detect various colors, backgrounds, and distance ranges.
Laser sensors can be used for long-distance presence sensing and are the most accurate for short-distance measurement applications.
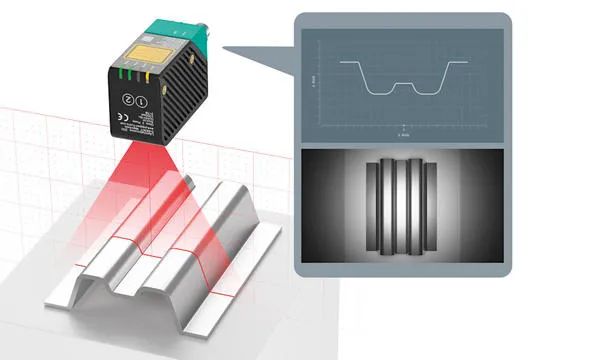 Vision sensors can be used for barcode reading, counting, shape verification, etc. Vision sensors are a cost-effective visual application that can be used in scenarios where camera systems are costly and complex. Vision sensors are used for barcode reading, tracking individual components, and executing process steps that match those components. The sensors can verify the number of functions present on the parts. Vision sensors can determine whether a specified curve or other shape has been reached. Since these sensors need to process light, it is crucial to test the sensors in environments that closely match the operational conditions in terms of ambient light and background reflectivity. In most applications, it is recommended to place vision sensors in enclosures to isolate them from external light sources. Seeking assistance from the vision sensor manufacturer during sensor testing is a good idea. Additionally, do not forget to ensure the selection of the appropriate fieldbus.
Vision sensors can be used for barcode reading, counting, shape verification, etc. Vision sensors are a cost-effective visual application that can be used in scenarios where camera systems are costly and complex. Vision sensors are used for barcode reading, tracking individual components, and executing process steps that match those components. The sensors can verify the number of functions present on the parts. Vision sensors can determine whether a specified curve or other shape has been reached. Since these sensors need to process light, it is crucial to test the sensors in environments that closely match the operational conditions in terms of ambient light and background reflectivity. In most applications, it is recommended to place vision sensors in enclosures to isolate them from external light sources. Seeking assistance from the vision sensor manufacturer during sensor testing is a good idea. Additionally, do not forget to ensure the selection of the appropriate fieldbus.
 Signal converters convert the analog output signal from the sensor into switching signals on the signal converter, with another option to convert to IO-Link process data.
7. Magnetic Switch: This is a specific term for sensors used in cylinders, mainly applied to detect the position of cylinder pistons. Typically, they are provided by cylinder suppliers based on customer usage.
8. Proximity Switch: Proximity switches are also designed and manufactured based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, so they can only detect metal targets, and different metals have slightly different sensing distances. Commonly used proximity switches have detection distances of about: 1mm, 2mm, 4mm, 8mm, 12mm, etc. Proximity switches generally come in two types: embedded and non-embedded. The embedded type means that the sensing head of the proximity switch does not detect metal targets in its circumferential direction but only detects metal targets in front of it, meaning that the sensor’s sensing head can be concealed by the metal mounting bracket; the non-embedded type means that the sensing head of the proximity switch can detect both metal targets in front of it and those in its circumferential direction, meaning that the sensor’s sensing head must protrude a certain distance from the metal mounting bracket, and there must not be metal targets within a certain circumferential range to avoid false judgments. Proximity switches have higher detection accuracy than magnetic switches. Proximity switches are commonly used to determine whether a product is present or whether a tooling fixture is in place, in situations where position accuracy requirements are relatively low.
9. Photoelectric Switch: The photoelectric detection method has advantages such as high precision, fast response, and non-contact, and can measure multiple parameters. The structure of the sensor is simple, and its form is flexible and varied, thus photoelectric sensors are widely used in detection and control. The commonly referred to photoelectric switches generally fall into three categories: one type is reflective photoelectric sensors, one type is through-beam photoelectric sensors, and one type uses a reflector to reflect the light beam. The latter two types achieve detection by blocking light from the target, while the former achieves detection by reflecting light from the target. Therefore, the latter two types usually have longer detection distances and higher precision. Due to the relatively high detection precision of photoelectric sensors, they are typically used to detect the precise positions of products or mechanical arms, as well as feedback devices in stepper and servo systems.
10. Fiber Optic Sensor: Fiber optic sensors are also a type of detection element that utilizes photoelectric signal conversion. Compared to photoelectric switches, they can usually detect smaller targets, have longer detection distances, and higher precision. Therefore, fiber optic sensors are typically used in more precise detection scenarios and as positioning feedback devices in stepper and servo systems.
11. Grating: Grating is also a sensor that utilizes photoelectric signals. Grating has a large detection area, so it is often referred to as an area sensor. The main application field of grating is interlocking and safety functions between devices, especially for the protection of people.
12. Thermocouple: Thermocouples are mainly used to detect the surrounding environmental temperature.
13. Laser Measurement Device: The main function of the laser measurement device is to accurately measure the external dimensions of the target.
14. Industrial Camera: Industrial cameras are often referred to as CCD (Charge-coupled Device) in engineering, mainly used to detect the shape and position of target objects. With the improvement of CCD technology, high-resolution industrial cameras can now be applied in precise measurement fields.
15. Encoder: According to their working principles, encoders can be divided into incremental and absolute types. Incremental encoders convert displacement into periodic electrical signals and then convert these electrical signals into counting pulses, with the number of pulses indicating the magnitude of the displacement. Absolute encoders have a specific digital code corresponding to each position, so their readings depend only on the starting and ending positions of the measurement and are independent of the intermediate process. Encoders are typically used in conjunction with stepper motors or servo motors to form closed-loop or semi-closed-loop control systems.
16. Micro Switch: Micro switches are a type of contact sensor, mainly used to detect the connection between devices or the status of safety protection doors of devices.
Signal converters convert the analog output signal from the sensor into switching signals on the signal converter, with another option to convert to IO-Link process data.
7. Magnetic Switch: This is a specific term for sensors used in cylinders, mainly applied to detect the position of cylinder pistons. Typically, they are provided by cylinder suppliers based on customer usage.
8. Proximity Switch: Proximity switches are also designed and manufactured based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, so they can only detect metal targets, and different metals have slightly different sensing distances. Commonly used proximity switches have detection distances of about: 1mm, 2mm, 4mm, 8mm, 12mm, etc. Proximity switches generally come in two types: embedded and non-embedded. The embedded type means that the sensing head of the proximity switch does not detect metal targets in its circumferential direction but only detects metal targets in front of it, meaning that the sensor’s sensing head can be concealed by the metal mounting bracket; the non-embedded type means that the sensing head of the proximity switch can detect both metal targets in front of it and those in its circumferential direction, meaning that the sensor’s sensing head must protrude a certain distance from the metal mounting bracket, and there must not be metal targets within a certain circumferential range to avoid false judgments. Proximity switches have higher detection accuracy than magnetic switches. Proximity switches are commonly used to determine whether a product is present or whether a tooling fixture is in place, in situations where position accuracy requirements are relatively low.
9. Photoelectric Switch: The photoelectric detection method has advantages such as high precision, fast response, and non-contact, and can measure multiple parameters. The structure of the sensor is simple, and its form is flexible and varied, thus photoelectric sensors are widely used in detection and control. The commonly referred to photoelectric switches generally fall into three categories: one type is reflective photoelectric sensors, one type is through-beam photoelectric sensors, and one type uses a reflector to reflect the light beam. The latter two types achieve detection by blocking light from the target, while the former achieves detection by reflecting light from the target. Therefore, the latter two types usually have longer detection distances and higher precision. Due to the relatively high detection precision of photoelectric sensors, they are typically used to detect the precise positions of products or mechanical arms, as well as feedback devices in stepper and servo systems.
10. Fiber Optic Sensor: Fiber optic sensors are also a type of detection element that utilizes photoelectric signal conversion. Compared to photoelectric switches, they can usually detect smaller targets, have longer detection distances, and higher precision. Therefore, fiber optic sensors are typically used in more precise detection scenarios and as positioning feedback devices in stepper and servo systems.
11. Grating: Grating is also a sensor that utilizes photoelectric signals. Grating has a large detection area, so it is often referred to as an area sensor. The main application field of grating is interlocking and safety functions between devices, especially for the protection of people.
12. Thermocouple: Thermocouples are mainly used to detect the surrounding environmental temperature.
13. Laser Measurement Device: The main function of the laser measurement device is to accurately measure the external dimensions of the target.
14. Industrial Camera: Industrial cameras are often referred to as CCD (Charge-coupled Device) in engineering, mainly used to detect the shape and position of target objects. With the improvement of CCD technology, high-resolution industrial cameras can now be applied in precise measurement fields.
15. Encoder: According to their working principles, encoders can be divided into incremental and absolute types. Incremental encoders convert displacement into periodic electrical signals and then convert these electrical signals into counting pulses, with the number of pulses indicating the magnitude of the displacement. Absolute encoders have a specific digital code corresponding to each position, so their readings depend only on the starting and ending positions of the measurement and are independent of the intermediate process. Encoders are typically used in conjunction with stepper motors or servo motors to form closed-loop or semi-closed-loop control systems.
16. Micro Switch: Micro switches are a type of contact sensor, mainly used to detect the connection between devices or the status of safety protection doors of devices.
Sensors, as components of machines, devices, and instruments, should follow the classification principles of the “Tariff” and the provisions of Notes 2 of Chapter 16, Notes 2 of Chapter 17, and Notes 2 of Chapter 90, and should be classified into the corresponding tariff items of Chapter 84, Chapter 85, and Chapter 90 according to the specific item names;
2. Based on the basic characteristics of sensors, classify them according to the measurement devices or parts corresponding to the sensing objects. For example, temperature sensors are classified under tariff item 90.25;
Flow sensors are classified under tariff item 90.26;
Gas sensors are classified under tariff item 90.27;
Sensors for measuring quantities not listed are classified under tariff item 90.31.
These “sensors” are no longer considered to be applied in automobiles, engines, machine tools, inspection equipment, or automatic control equipment, DCS control systems, etc.
3. In addition to following the above classification principles, query the “Pre-Determination” column of the customs based on the “product name”.
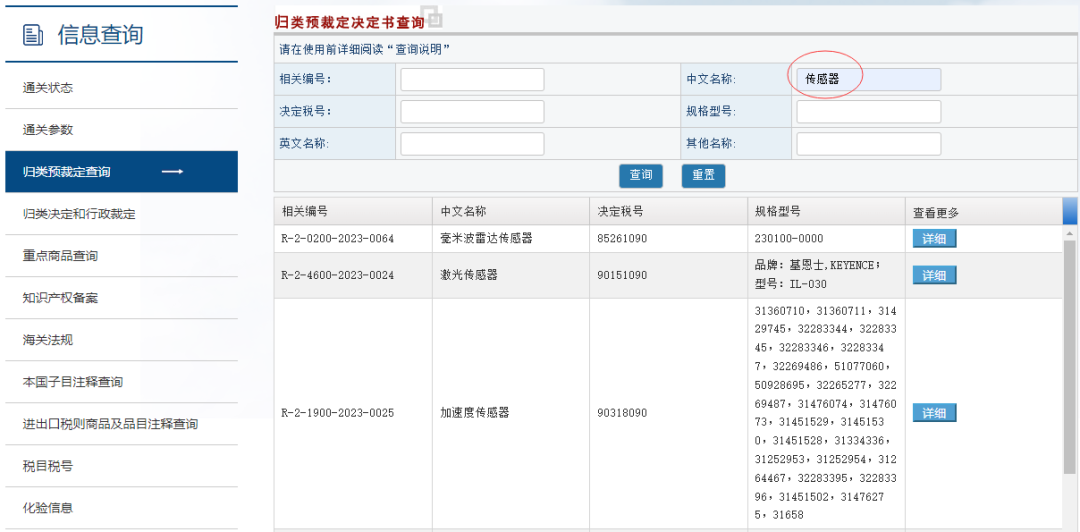
| Related Number |
Chinese Name |
Determined Tariff Number |
Specifications and Models |
| R-2-0200-2023-0064 |
Millimeter Wave Radar Sensor |
85261090 |
230100-0000 |
| R-2-4600-2023-0024 |
Laser Sensor |
90151090 |
Brand: Keyence; Model: IL-030 |
| R-2-1900-2023-0025 |
Acceleration Sensor |
90318090 |
31360710, 31360711, 31429745, 32283344, 32283345, 32283346, 32283347, 32269486, 51077060, 50928695, 32265277, 32269487, 31476074, 31476073, 31451529, 31451530, 31451528, 31334336, 31252953, 31252954, 31264467, 32283395, 32283396, 31451502, 31476275, 31658 |
| R-2-8000-2023-0007 |
Gas Analyzer Sensor |
90278990 |
MIDAS-E-TEO |
| R-2-8000-2023-0006 |
Gas Analyzer Sensor |
90278990 |
MIDAS-E-XHF |
| R-2-8000-2023-0005 |
Gas Analyzer Sensor |
90278990 |
MIDAS-E-HAL |
| R-2-1500-2023-0004 |
Millimeter Wave Radar Sensor |
85261090 |
2Q0 907 561 J, 80A 907 566 C |
| R-2-5300-2023-0007 |
Temperature Sensor |
90251910 |
No Model |
| R-2-0100-2023-0018 |
Focal Plane Photoelectric Conversion Sensor |
85437099 |
CG-IAS-FPA-16K |
| R-2-2200-2022-0265 |
Speed Sensor |
85437099 |
HDD2L32NA/20 |
| R-2-5100-2022-0058 |
Blind Spot Monitoring Radar Sensor |
85261090 |
Model: 881623307000, 881624209100, 881624814100 |
| R-2-5100-2022-0057 |
Flow Sensor |
85437099 |
Model: AB32-S21P012C-11R, Specification: Aperture: 1.2mm, Angle: 0 degrees |
| R-2-2200-2022-0199 |
Hall Sensor |
85437099 |
HALL-S1 |
| R-2-5200-2022-0106 |
Temperature Sensor |
85334000 |
NTSF0482 |
| R-2-2300-2022-0056 |
Weight Sensor |
90318090 |
K-SFT-III |
| R-2-2200-2022-0144 |
Automotive Millimeter Wave Radar Sensor |
85261090 |
Specification Model: 681981200 |
| R-2-5300-2022-0009 |
Digital Flow Sensor |
90268010 |
SMC Brand; PFMB7201S-C8CWM Model |
| R-2-5200-2022-0003 |
Humidity Sensor |
90258000 |
Specification: 30~90%RH Model: HIS-06KVV-N |
| R-2-2300-2021-0147 |
Particulate Matter Sensor |
90271000 |
Model EGS-PM2-CV |
| R-2-2300-2021-0089 |
Measurement Gear for Steering Angle Sensor |
90319000 |
Model: F005B10728 |
Table 1: 20 Items of Pre-Determination for “Sensors” Classification
The classification decision data retrieved with the keyword “sensor” is empty: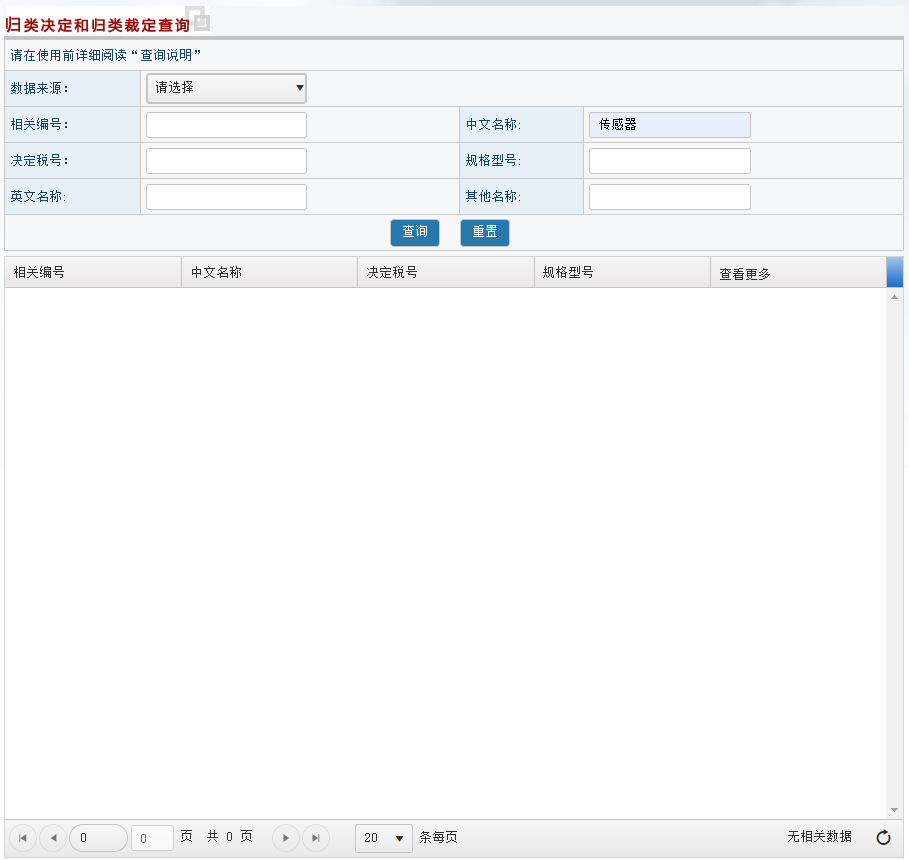
In summary, the import and export of sensors require more specialized and detailed classification customs declaration. Hengjie Supply Chain has served tens of thousands of distributors in Huaqiangbei since its establishment, with a professional customs declaration team and rich historical customs declaration data. We focus on helping customers improve supply chain management efficiency, allowing customers to focus on their core business and enhance their value in the industrial chain. The comprehensive supply chain services provided by Hengjie Supply Chain offer advanced ERP enterprise management software and financial management software, enabling distributors to complete “procurement, warehousing, logistics, customs declaration, inspection, VMI management, automatic settlement” in one stop, and keep track of the status of capital flow, information flow, logistics, and business flow at any time.
— End —
Click below“Hengjie Supply Chain” to follow the official account
1. We respect intellectual property rights. The content of this official account, including text, data, videos, etc., is sourced from the internet or other publicly available materials, and the copyright belongs to the original authors and original publishing sources. If the copyright holder has any objections to the citation of this official account, please leave a message or contact us, and we guarantee prompt handling.
2. The content provided by this official account is for readers’ communication, learning, and reference only and does not involve commercial purposes.
3. The content of this official account only represents the author’s views. We do not guarantee the accuracy, reliability, or completeness of the content, whether express or implied. Any decisions or actions made by readers after reading are based on their own will and independent judgment, and readers should be aware of the relevant results.