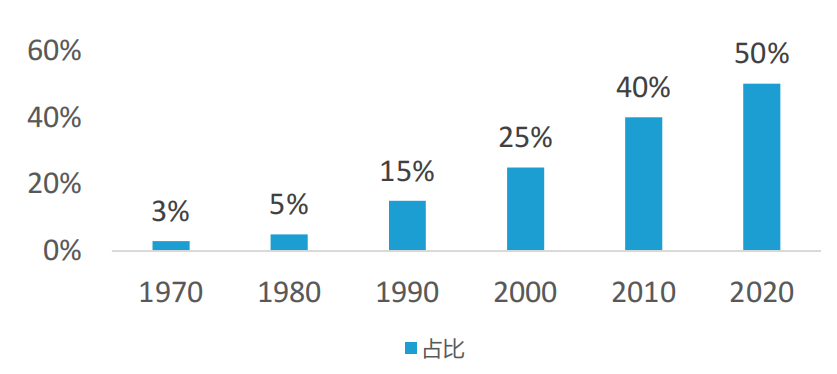The Internet of Vehicles is the necessary path to achieve smart cars, the most important application scenario of 5G, and one of the hottest industries in the current Internet of Things sector.
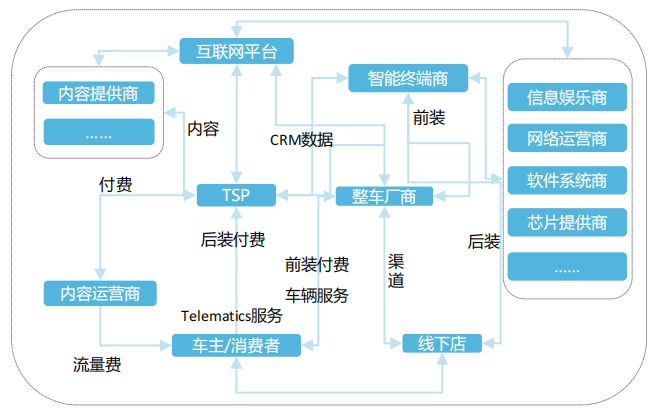
The participants in the Internet of Vehicles industry chain roughly include TSPs, complete vehicle manufacturers, telecom operators, hardware terminals, platforms, and other participants, each having different dominant capabilities and business models in the main areas of the Internet of Vehicles.
The Basic Value Chain of the Internet of Vehicles
In the “big cake” of the Internet of Vehicles industry, where exactly is the business model?
Today, we will analyze the business models of the Internet of Vehicles from three perspectives: software services, hardware support, and overall solutions.
The Business Models of the Internet of Vehicles
In the Internet of Vehicles industry chain, software suppliers account for over 60%, making “software-defined vehicles” an industry consensus.
The software supply in the Internet of Vehicles is relatively flexible, with the business model mainly based on customization and service fees. I will analyze it from three aspects: in-vehicle operating systems, OTA, and network information security + OTA.
1. In-Vehicle Operating Systems
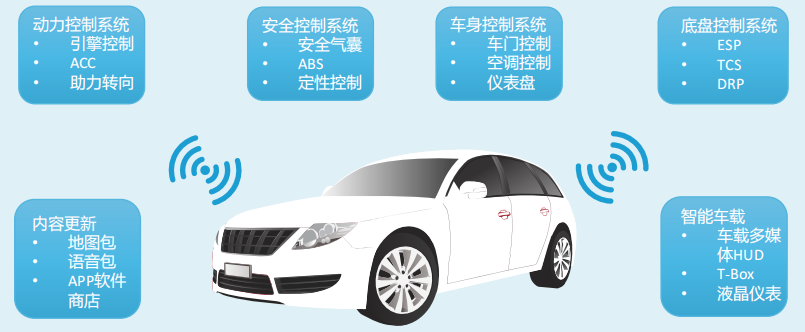
The in-vehicle operating system has become the core software of smart connected vehicles. The operating system, as a standard configuration for vehicles, is functionally divided into entertainment vehicle systems and automotive electronic control devices.
Main In-Vehicle Operating Systems in the Chinese Market (Partial)
Alibaba’s AliOS, Baidu’s DuerOS, Huawei’s HarmonyOS, etc., belong to the entertainment vehicle systems.
It is worth mentioning Tesla, which is the world’s first car company to achieve full vehicle OTA. Utilizing OTA upgrade technology, Tesla has introduced an app store where Tesla owners can purchase various software updates, transforming Tesla into not just a means of transportation but also an intelligent revenue-generating platform.
3. Network Information Security + OTA
In Internet of Vehicles services, new service models have emerged for information security through OTA technology. If the relevant software of smart vehicles fails, it can be resolved via OTA. Compared to traditional offline recall upgrade models, full vehicle OTA not only reduces maintenance costs but also enhances user experience.
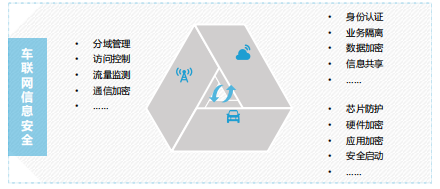
Ensuring the security and privacy of information in the Internet of Vehicles environment is a significant challenge that must be overcome to prevent virus attacks and malicious destruction, and to avoid loss or theft of personal, business, and property information.
Currently, ensuring information security and privacy in the Internet of Vehicles environment is one of the major challenges that need to be addressed.
In the Internet of Vehicles industry chain, the hardware sales model is relatively traditional, with an increasing demand for Internet of Vehicles hardware products, and profit points mainly concentrated in core components and communication module industries.
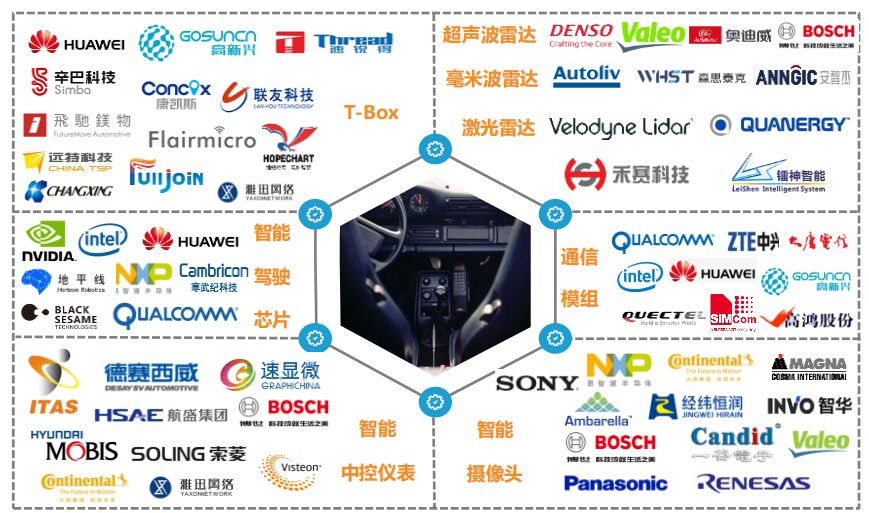
The relevant smart hardware involved in the Internet of Vehicles includes communication modules, T-Boxes, RSUs, smart central control instruments, radars, smart cameras, etc. The relevant companies are as follows:
It can be seen that single hardware can no longer meet the needs of the Internet of Vehicles, and integration of software capabilities is necessary. I will analyze it from four aspects: automotive electronics, T-Box, C-V2X, and smart chips.
1. Automotive Electronics
The scale of the automotive electronics market in China continues to grow rapidly, becoming a giant driving the development of smart connected vehicles.
Source: CCID Consulting “2020 China Automotive Electronics Industry Development Outlook”
The T-Box, as one of the important basic hardware in smart connected vehicles, is key to the commercialization of the Internet of Vehicles. Currently, leading manufacturers in the Chinese passenger car T-Box market include Huawei, High-Technology, Changxing, and Huifanwei.
The BAIC New Energy ARCFOX α-T is equipped with Huawei’s next-generation 5G chip MH5000 T-BOX. High-Technology collaborates with major domestic vehicle manufacturers such as Geely, Changan, and BYD to provide 4G/5G vehicle-grade modules and T-Box terminals.
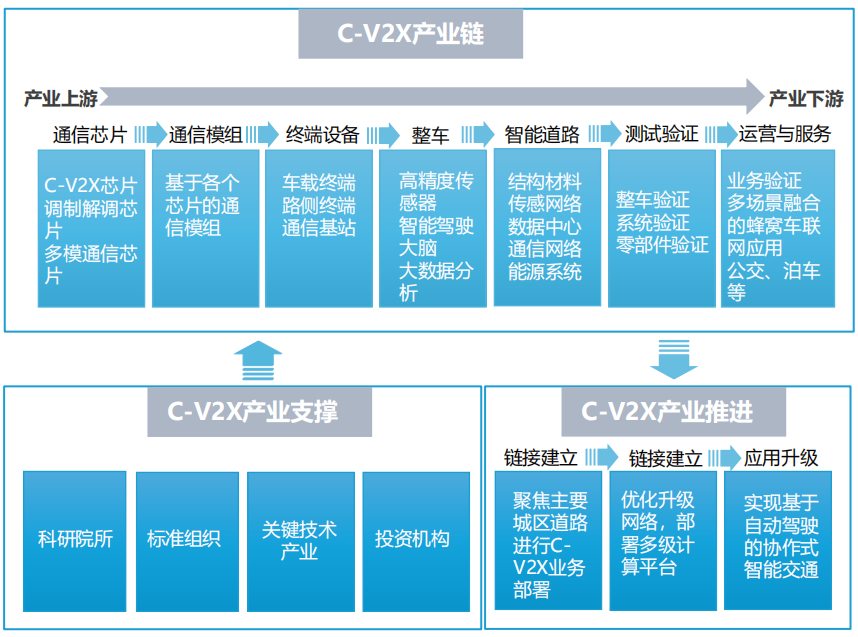
The C-V2X industry chain mainly includes communication chips, communication modules, terminal devices, complete vehicles, smart roads, testing and verification, as well as operation and service segments, with participants including chip manufacturers, equipment manufacturers, OEMs, solution providers, telecom operators, traffic operation departments, and traffic management departments.
Therefore, the upstream and downstream of the Internet of Vehicles industry chain need cross-domain cooperation to ultimately achieve win-win results through technological integration and complementary industrial advantages.
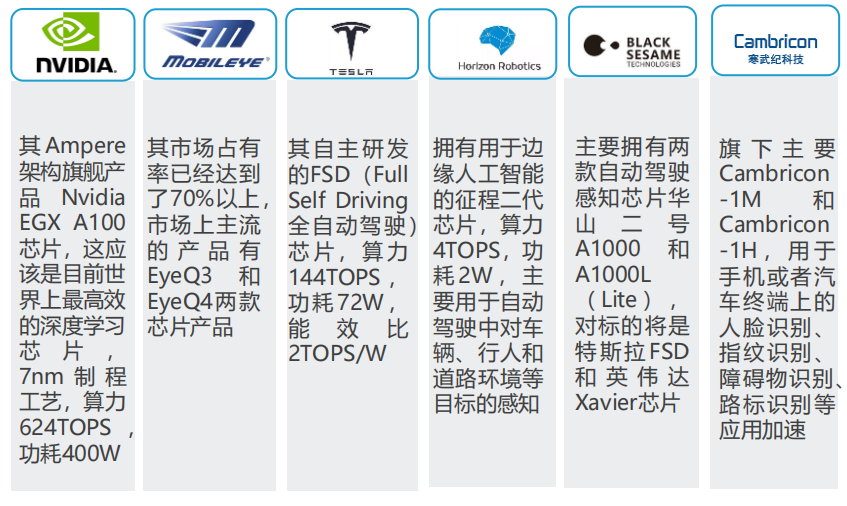
Main Players in Domestic and International Autonomous Driving Chips
After the “ZTE Incident”, a batch of innovative enterprises such as Cambricon, Horizon Robotics, and Black Sesame Intelligence emerged. We deeply realize that the dominance of smart driving chips must be firmly grasped in our own hands.
In the Internet of Vehicles solutions, most are based on enterprise customization, with operation platforms, Internet of Vehicles monitoring, and future-oriented mobile travel solutions being popular in the current market.
I will analyze it from three aspects: smart cockpit, Internet of Vehicles platform, and “Internet of Vehicles + car insurance”.
The participants in the smart cockpit include traditional system integrators, emerging Internet companies, and traditional vehicle and parts manufacturers working together to launch comprehensive smart cockpit solutions. Although vehicle manufacturers have diverse needs, this presents huge business opportunities for technology companies in the Internet of Vehicles.
2. Internet of Vehicles Platform
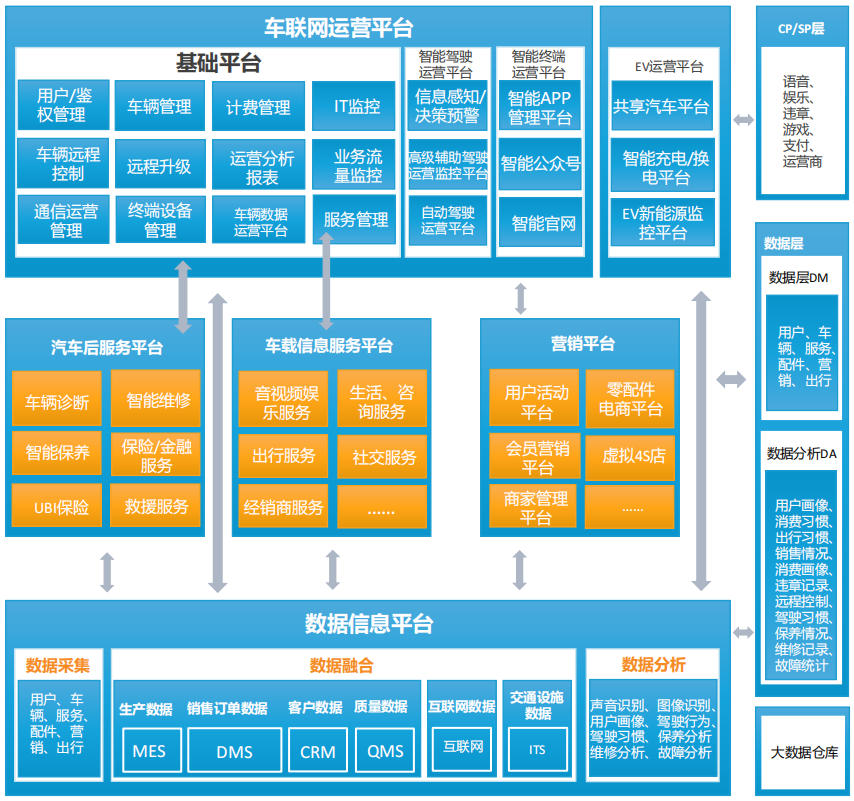
Architecture of the Internet of Vehicles Operation Platform
The Internet of Vehicles operation platform enables interconnectivity between vehicles, roads, people, and cloud platforms, enhancing traffic management levels and promoting urban traffic intelligence, which is also the necessary path to achieving autonomous driving.
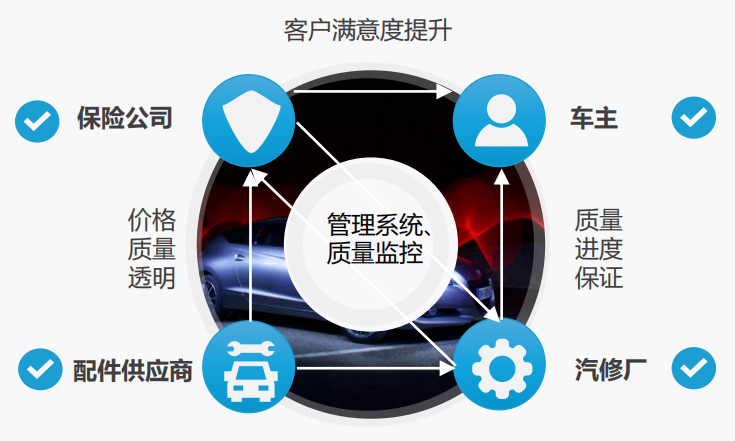
3. “Internet of Vehicles + Car Insurance”
CCCIS China’s Direct Repair Model for Accident Vehicles
In the future, the Internet of Vehicles can be integrated throughout the smart vehicle service end, including active assessment of human injuries, vehicle damage, upstream and downstream integration, proactive service support, and active rescue, which can provide significant value for insurance companies, repair companies, and vehicle manufacturers, and is also a specific scenario for the future implementation of the Internet of Vehicles business model.
Common Issues in the Commercialization of the Internet of Vehicles in China
1. Industry Standards Are Not Yet Unified
There has always been ambiguity between the C-V2X and DSRC protocols in the Internet of Vehicles, with the EU leaning towards the development of DSRC, while China supports the promotion of C-V2X.On April 26, 2020, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology approved seven V2X (Internet of Vehicles) standards, making C-V2X the mainstream in China’s Internet of Vehicles.
2. Information Security Vulnerabilities
Currently, strengthening information security in the Internet of Vehicles is urgent, requiring improvement of the information security protection capabilities at all stages of smart vehicles, strengthening the graded and classified management and access control of Internet of Vehicles data throughout its lifecycle, improving the identity authentication system during the research and development, production, and use of vehicles, and building a multi-party interactive, information-sharing, real-time accurate operational safety service platform.
3. Lagging Infrastructure Construction
The Internet of Vehicles achieves information sharing through interconnectivity between “vehicles and vehicles”, “vehicles and people”, and “vehicles and roads”, collecting information on vehicles, roads, and the environment to provide professional navigation, scenario services, and media entertainment.However, in the entire closed-loop service scenario of the Internet of Vehicles, various infrastructures are involved, including communication, roads, roadside infrastructure, etc. The lack of infrastructure is one of the biggest obstacles to the commercialization of the Internet of Vehicles.
In summary, every link in the Internet of Vehicles industry chain has profitable opportunities, and the key lies in whether companies can provide valuable value-added services.
Currently, the Internet of Vehicles has two operating modes: pre-installed and aftermarket, with significant differences between the two models. The pre-installed model is mainly led by automobile manufacturers. The pre-installed model refers to the Internet of Vehicles terminal suppliers selling products to automobile manufacturers before the vehicles leave the factory, which are then assembled and launched into the market by the automobile manufacturers. In the pre-installed market, automobile manufacturers usually designate a specific brand of Internet of Vehicles products for a specific model, serving the entire lifecycle of the vehicle.
Regarding the business model of the Internet of Vehicles, in the future, it can serve government departments such as transportation and traffic management, ordinary consumers, or automotive companies and certain key industry clients.
In the short term, the development of the Internet of Vehicles industry still requires government guidance. The Internet of Vehicles itself has rich profit models, but what kind of changes will it bring to the industry in the future? The road is still long, and it will take more time for Internet of Vehicles companies to emerge from chaos.
-
Welcome to all angel round and Series A enterprises in the entire automotive industry chain (including the electrification industry chain) to join the group,to connect with 500 automotive investment institutions including top institutions; some quality projects will be selected to present to existing institutions by theme.There are communication groups for technology innovation companies, automotive industry complete vehicles, automotive semiconductors, key components, new energy vehicles, smart connected vehicles, aftermarket, automotive investment, autonomous driving, Internet of Vehicles, and dozens of other groups. Please scan the administrator’s WeChat to join the group (please indicate your company name)
-