 Special Topic Summary, Lock in Every ThursdayPERSONAL WORK SUMMARYThisIssueSpecialTopicEdge AI
Special Topic Summary, Lock in Every ThursdayPERSONAL WORK SUMMARYThisIssueSpecialTopicEdge AI

With the development of the industry, companies increasingly require efficient, flexible, and scalable computing resources, leading to a gradual increase in the demand for low-latency and low-cost computing services across various scenarios.Edge computing can address issues such as long response times and high bandwidth costs associated with centralized data centers, not only solving industry challenges related to data privacy, power efficiency, and low latency but also promoting technological innovation and the development of business models.So, what exactly is Edge AI, and how can it solve these industry pain points?
01 Related Concepts
Before understanding Edge AI, let us familiarize ourselves with a few concepts.
Moore’s Law
Moore’s Law, proposed by Gordon Moore in 1965, predicts that the number of transistors on an integrated circuit will double approximately every 18 to 24 months, implying that processor performance will roughly double every two years.
This trend provides a theoretical basis for the exponential growth of computing power, supporting the rapid technological advancements of the past few decades. However, with the rise and popularization of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, the demand for computing resources has exploded, surpassing the speed that traditional hardware upgrades can provide.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) originated in the media field and refers to the connection of any object to the network through information sensing devices, according to agreed protocols, allowing objects to exchange and communicate information through information dissemination media to achieve intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, and supervision functions.

Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, also known as grid computing, is a form of distributed computing that refers to breaking down large data processing programs into countless smaller programs via the “cloud” network, and then processing and analyzing these small programs through a system composed of multiple servers to return results to users. In simple terms, cloud computing can process tens of thousands of data in a very short time (seconds), achieving powerful network services.
Over the past decade, cloud computing has successfully alleviated issues related to storage and management brought about by the growing amount of data. However, the growth rate of network bandwidth currently lags far behind the growth rate of data. Additionally, cloud computing faces bandwidth insufficiency issues. Transmitting all the massive data generated by edge devices to the cloud computing center would place tremendous pressure on network bandwidth.

Large Models
Large models (also known as foundation models) refer to deep neural network models characterized by large-scale parameters and complex computational structures, trained on massive datasets, resulting in the emergence of intelligence similar to that of humans. These models are typically constructed using deep neural networks and possess billions or even trillions of parameters.
The purpose of large models is to enhance the model’s expressive capability and predictive performance, enabling them to handle more complex tasks and data. AI large models such as Wenxin Yiyan, iFlytek Spark, Doubao AI, and Kimi are currently prominent examples of artificial intelligence technology.
02 The Rise of Edge Computing
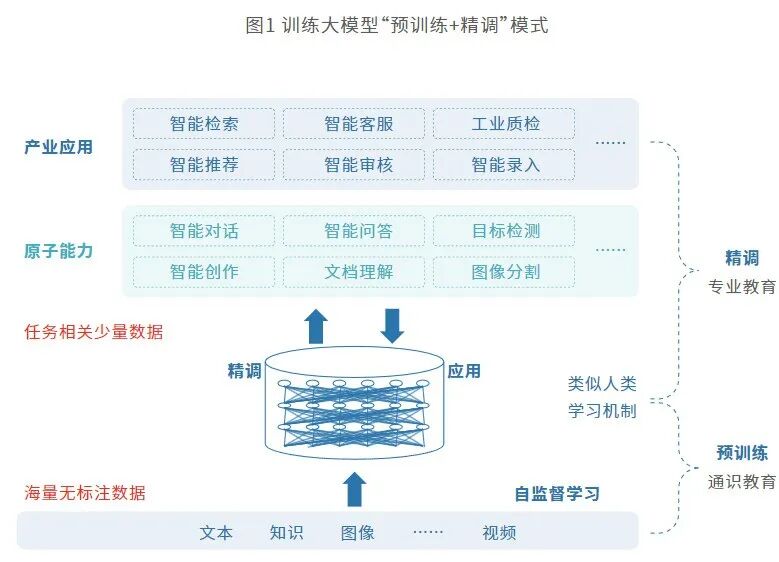
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
-
Cloud computing cannot meet the explosive demand for massive data processing. With the integration of the internet and various industries, especially after the popularization of IoT technology, computing demand has surged, and traditional cloud computing architectures can no longer meet the enormous computing needs.
-
Cloud computing cannot meet the demand for real-time data processing. In traditional cloud computing models, IoT data collected by terminals must first be transmitted to the cloud computing center, then processed through cluster computing before returning results, which inevitably leads to longer response times. However, some emerging application scenarios, such as autonomous driving and smart mining, have extremely high requirements for response times, making reliance on cloud computing unrealistic.
Edge computing is a complement and optimization of cloud computing. If cloud computing is centralized and involves big data processing in the “cloud,” then edge computing can be understood as big data processing at the edge, close to the terminal (such as mobile phones, smart voice devices, etc.).
A vivid analogy is to compare cloud computing and edge computing to the organs of an octopus, which is easy to understand: as the most intelligent invertebrate in nature, the octopus possesses the ability of “conceptual thinking,” which is inseparable from its two powerful memory systems. One is the brain memory system, which has 500 million neurons, and the other is the suckers on its eight arms. In other words, the octopus’s eight legs can think and solve problems. Cloud computing is like the octopus’s brain, while edge computing is akin to the small arms of the octopus, with each arm representing a small data center close to specific physical objects. Edge computing is closer to the device side and the user.
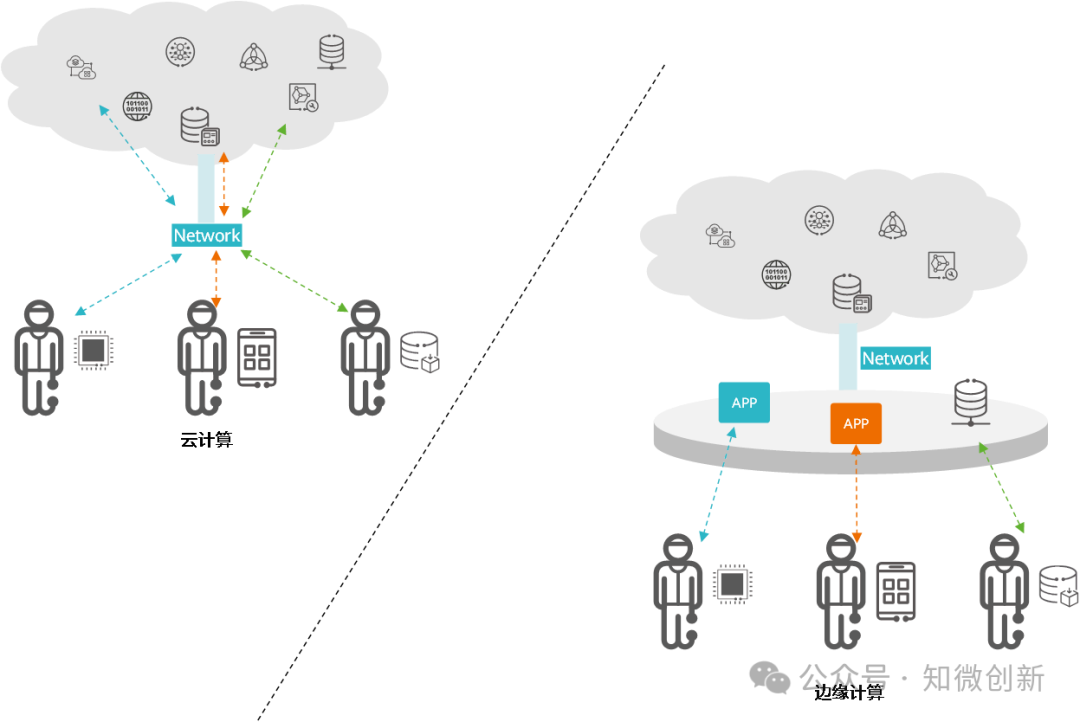
How Does Edge Computing Work?
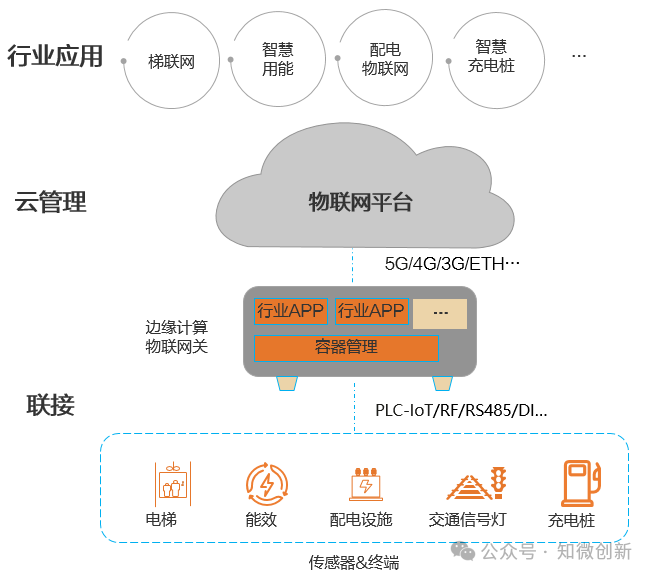
The architecture of edge computing is shown in the figure below, processing data as close to the terminal nodes as possible, moving data, applications, and computing power away from centralized cloud computing centers.
Technical Propositions of Edge Computing
As technology matures, the development concept has become increasingly clear, which is to process data in real-time at the point of generation to extract more data value. This not only aligns with the core concept of edge computing but also fits current technological development trends and application scenarios. Specifically, the current development of edge computing supports three major technical propositions: leveraging AI, simplifying the edge, and protecting the edge.
Edge AI moves the training and inference of AI models closer to users on edge devices (such as smartphones, sensors, routers, surveillance cameras, etc.), performing real-time data processing on these edge devices for quick response and data analysis.
03 Application Scenarios
Edge computing is particularly suitable for application in the IoT field, providing device management and control services through IoT gateways with edge computing capabilities, solving the “last mile” communication problem of IoT, ultimately achieving intelligent connectivity and efficient management of IoT devices, with broad application prospects across various industries.
Smartphones
Siri and Google Assistant are the best examples of edge AI on smartphones, as this technology drives their voice UI. AI on mobile devices allows data processing to occur on the device (edge side), meaning there is no need to send device data to the cloud. This helps protect privacy and reduce traffic.

Smart Homes
With the popularization of IoT, home life will introduce more and more smart applications, such as smart lighting control, smart TVs, smart air conditioning, etc. These applications require the deployment of numerous sensors and controllers in homes. To protect home data privacy, data processing must rely on edge computing, keeping most computing resources confined within the home gateway, preventing sensitive data from leaking. Edge AI optimizes indoor positioning and home intrusion detection, achieving higher accuracy and lower latency than cloud computing.

Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
UAVs can fly to remote and dangerous areas for exploration and capture aerial images in unique ways. The application of UAVs is expanding, including applications in agriculture and mining. However, these devices must be able to “report back to headquarters” to respond to the data they collect. Edge computing enables UAVs to check data and respond in real-time.

Healthcare
Edge AI will have multiple application scenarios in the field of smart healthcare. Firstly, in pre-hospital emergency care, during the transfer of emergency patients to hospitals or between hospitals, current emergency medical services are mostly deployed in the cloud, which can be easily affected and limited by mobile environments and extreme weather. Edge AI can establish a bidirectional real-time communication channel between ambulances and hospitals, enabling real-time natural language and image processing to improve timeliness and efficiency. Secondly, in smart wearable devices, current smart wearables are limited by computing power and only serve data collection purposes.

Manufacturing
In the industrial manufacturing sector, AI and edge applications are expected to play an increasingly important role in the development of smart factories. Driven by the Industry 4.0 model, the next generation of smart factories will apply advanced robotics and machine learning technologies to software services and industrial IoT, enhancing capacity and maximizing production efficiency.

Edge intelligence, as an emerging computing paradigm, is gradually demonstrating its immense potential and value across multiple industries. Although it is still in its early stages of development, it is expected to play a greater role in the future for the communications industry, internet industry, and industrial sectors.
Disclaimer
This article is an observational or commentary piece published by a third-party self-media author, and all text and image copyrights belong to the author. It is shared for informational purposes only; please contact for resolution or deletion in case of copyright issues.
About Us

The “Industrial AI” magazine is published by Yashi International Business News, focusing on the technical applications of AI in the industrial field, aiming to provide Chinese process and manufacturing engineers, managers, and executives with timely access to the latest news and technical information regarding the integration of artificial intelligence into manufacturing. Industrial AI also aims to create a leading comprehensive media and value platform in the industry, providing practical communication opportunities for the implementation of AI in the industrial field.
 Your “shares,” “likes,” and “views” contribute to the advancement of technology in China!
Your “shares,” “likes,” and “views” contribute to the advancement of technology in China!