China MobileEmbodied Intelligence Industry Innovation CenterIntroduction
The China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center relies on the China Mobile Smart Home Operation Center, focusing on the innovation and research and development of embodied intelligence technologies and products, aiming to create a leading domestic and world-class robot industry innovation center. The center leverages China Mobile’s resource advantages in computing power, networks, data, scenarios, and channels, focusing on diverse scenarios such as homes, communities, and shops, driving industrial upgrades through technological innovation, reshaping a new ecosystem of intelligent services, and striving to become the world’s largest robot operator.
The center positions itself as a technology innovator, product provider, industry promoter, and service operator in the field of robotics, achieving collaborative development through technological breakthroughs, industrial co-construction, investment empowerment, and ecological operation.
At this year’s 2025 Digital Summit, the China Mobile Love Home exhibition area resembled a bustling future town, with scenes that were simply amazing! The robotic dog, Xiao Li, was busy delivering supplies among the crowd; the bionic robot, Xiao Si, showcased its singing talent, attracting many onlookers with its star-like voice; and the robotic arm, Xiao Zhi, was quick and efficient, cleaning up table scraps in just a few minutes. Behind these futuristic scenes are the breakthroughs in the “four autonomies” technologies of the China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center: autonomous interaction, autonomous operation, autonomous movement, and autonomous learning. This transforms robots from “clumsy mechanical tools” into incredibly thoughtful “intelligent partners”. Let’s explore the secrets together!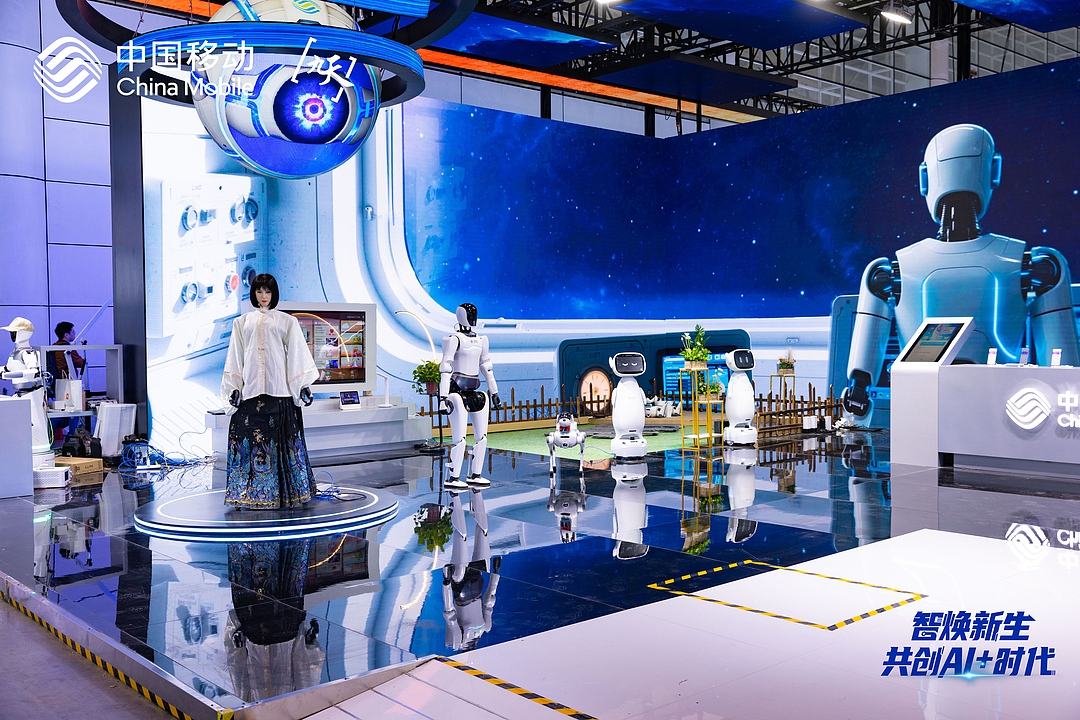
Autonomous Interaction: The “Evolution of Robot Conversation”
Can you imagine a robot chatting? Autonomous interaction gives robots this magical skill, and it comes in different “levels”! At the beginner stage (L0 – L2), robots are like toddlers just learning to talk, only understanding simple commands like “turn on the light” or “play music”; for them, this is a piece of cake. Their responses are also simple, either through voice replies or displaying a few words on a screen, making them obedient little companions.At the intermediate (L3) level, robots seem to have a breakthrough! If you ask, “Where did the package from yesterday go?”, they can quickly find the answer by combining previous conversations. Even more impressively, they learn to “read the room” by recognizing your tone and facial expressions to gauge emotions. If you sound anxious, they will comfort you with soft lighting and gentle movements. Isn’t that heartwarming?At the advanced (L4 – L5) level, robots become “chatting masters”. In the future, they will proactively engage in conversations and work seamlessly with other robots.Currently, most household robots are still striving to upgrade from L2 to L3.The robots from the China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center can not only understand complex commands but also recognize gestures, although there is still room for improvement in the naturalness of their “conversations” and adaptability to different scenarios. Internationally, Figure robots can sort items based on verbal commands, while domestic companies like Yushu and Weilan Technology are also working hard to catch up in autonomous interaction.
Autonomous Operation: The “Workplace Transformation of Robots”
Autonomous operation refers to a robot’s ability to independently perceive, understand, and complete tasks without direct human control. In its initial development stages (L0 – L1, program control), robots are like “wooden men” programmed to follow fixed steps, becoming confused when the environment changes. Assembly line robotic arms and basic cleaning robots operate this way, repeating the same actions daily.As technology advances, robots reaching L2 – L3 (intelligent perception) can “understand” their surroundings, adapt to changes in the positions of different objects, and possess preliminary learning abilities. In home scenarios, these robots can autonomously complete tasks like pouring milk, organizing toys, and sorting items.At the L4 (general autonomy) stage, robots are considered “all-rounders”! In open environments, they can tackle complex tasks and unfamiliar objects and scenes with ease! Imagine a robot skillfully cooking and cleaning in the kitchen, acting like a dedicated smart “butler”.Currently, leading embodied intelligence companies have achieved L2 levels. Internationally, Physical Intelligence robots are nearing L3 levels, capable of completing kitchen cleaning tasks, but they still require human assistance when encountering obstacles or uncommon items.The household service robots from the China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center have achieved intelligent planning for common household tasks, with the ability to recognize and grasp common items and perform precise operations on small targets (1cm). They have implemented end-to-end dexterous operations like “pouring milk” based on imitation learning, currently reaching L2.8 levels. The team is fully committed to tackling the embodied intelligence large model, aiming to reach L3.3 levels by 2025 and challenge more difficult tasks!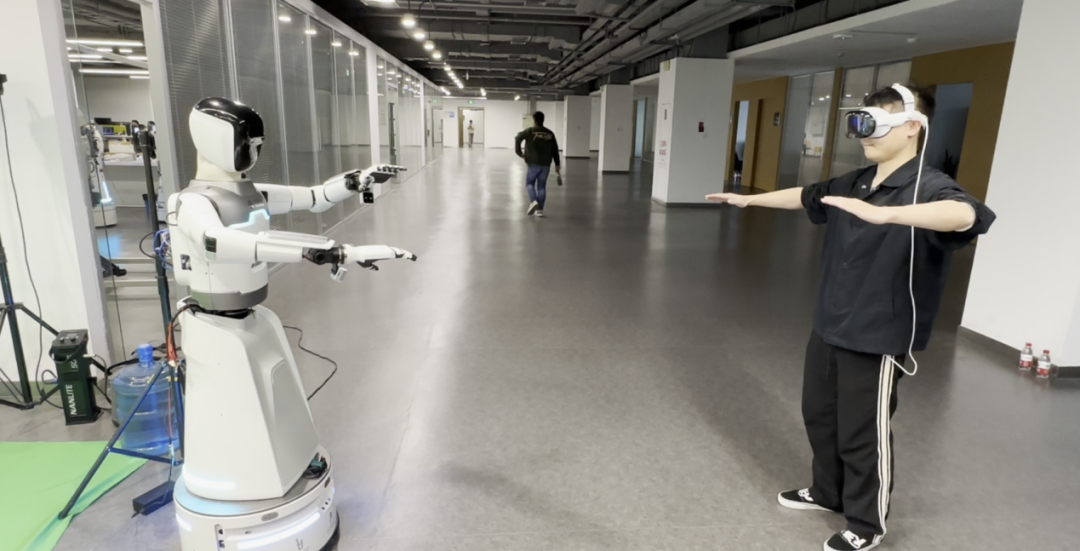
Autonomous Movement: The “Dream of Free Walking for Robots”
For robots, autonomous movement is like human “legs”, transitioning from “being led” to “going wherever they want”. In the L0 – L1 stage, robots must rely on remote control by humans; once they leave the operator’s line of sight, they become “lost”.As they develop to L2 – L3 stages, robots gain a bit of “independence”, able to autonomously follow their owners and avoid obstacles.At the Digital Summit, the quadruped robotic dog, Xiao Li, could autonomously navigate indoors, leading guests to various exhibition areas, but in complex environments like stairs or outdoor uneven surfaces, they still require human supervision.In the future, robots reaching L4 – L5 stages will realize the dream of free walking. They will be able to navigate freely in neighborhoods and streets, adjusting their routes based on weather and other conditions, completely without human intervention.Currently, the quadruped robot Xiao Li from the China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center has achieved indoor autonomous navigation (L3 level Demo), while robots from Yushu and Yunshen can “walk” indoors, but they are still in the testing phase for outdoor complex scenarios.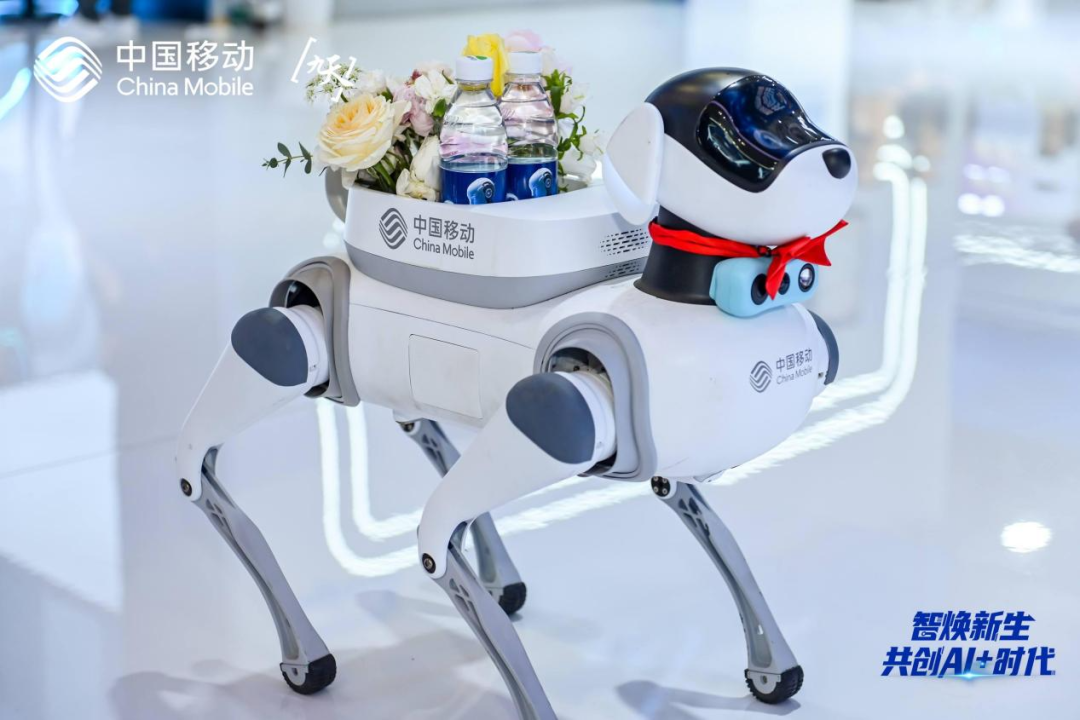
Autonomous Learning: The “Brain Upgrade Path for Robots”
Autonomous learning is the “brain training” that allows robots to continuously improve themselves, evolving from “rote memorization” to “self-learning”. Robots at the L0 – L2 stages can only perform tasks according to human-written programs, lacking flexibility. For example, a vacuum robot cleans along a fixed route and cannot adjust its path when encountering new obstacles.When robots reach L3 stages, they can optimize their actions through “practice”. For instance, a quadruped robot can adjust its balance after falling, and a wheeled robot can optimize its walking route based on user habits.In the future, at L4 – L5 stages, robots will possess the ability to “learn from experience” like humans, autonomously acquiring new skills by observing their environment, potentially discovering methods that humans have not even thought of!Currently, most robots are at L2 – L3 stages, and the China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center robots can grasp different items through imitation learning, while industrial robots can adjust their actions based on production line changes, but their autonomous decision-making capabilities in complex scenarios are still under development.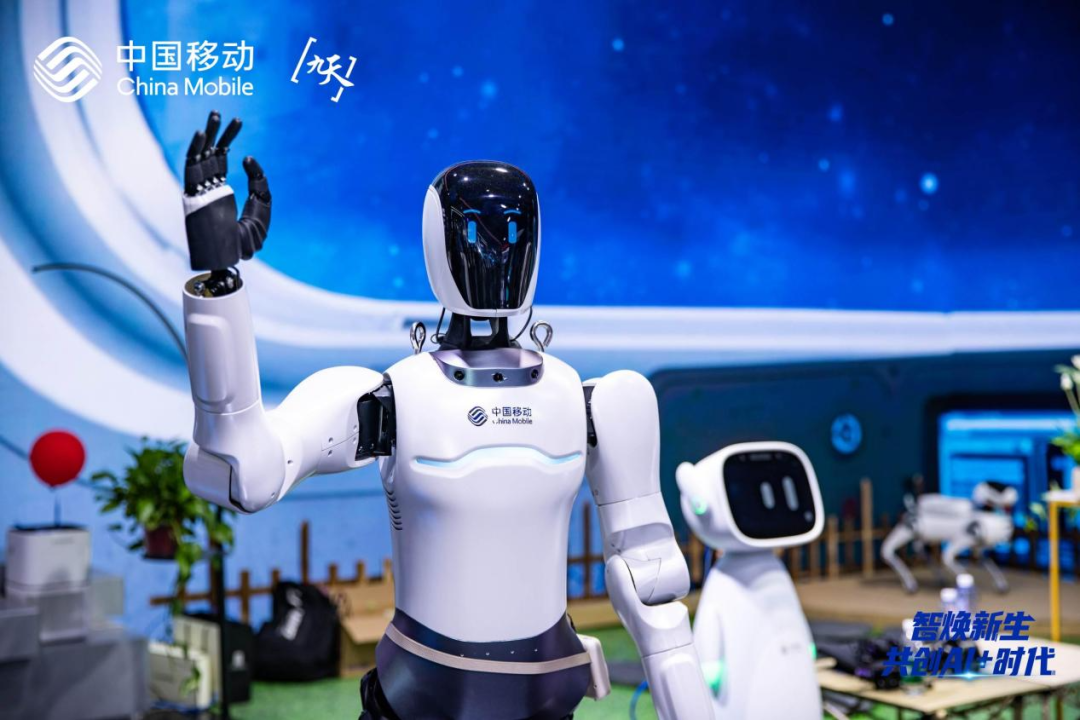
The Harmonious Collaboration of the Four Autonomous “Partners”
Imagine having an incredibly capable robot partner at home. When you say “pour a glass of milk”, it understands your request through autonomous interaction (L3); then, using autonomous movement (L3), it happily walks to the kitchen; once in the kitchen, it accurately picks up a cup and pours milk using autonomous operation (L2.8); during this process, it also remembers your preference for warm milk through autonomous learning, so the next time it pours milk, it can do it quickly and well, and their close cooperation transforms the robot from a “clumsy machine” into a thoughtful “life assistant”.At this year’s Digital China Summit, the China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center provided an answer with its “four autonomies” technology—intelligent robots are no longer cold machines, but “life partners” that can think, learn, and understand emotions. With the continuous development of these “four autonomies” technologies, although L3 capabilities are gradually being realized internationally, L4 – L5 will still require over ten years; domestic companies (such as China Mobile Embodied Intelligence Industry Innovation Center, Yushu) have caught up with international levels in certain scenarios, but core algorithms and hardware still need breakthroughs. In the future, robots will become “super assistants” in our lives and work, playing roles in more fields and bringing us immense convenience and surprises!