In assembly language (especially in the x86 architecture), <span>dword ptr </span>is a term used to specify the size of data and the addressing mode for memory operations.
1 dword
It stands for “double word,” which refers to 32 bits (4 bytes) of data.
In the x86 architecture:
1 word = 16 bits (2 bytes)
1 dword = 32 bits (4 bytes)
Other common sizes include:
byte = 8 bits
qword = 64 bits (8 bytes)
2 ptr
It stands for “pointer,” indicating that the operation is on data at a memory address rather than a direct immediate value or register value. It tells the assembler that data needs to be read from or written to a specified memory address.
3 Combining dword ptr
dword ptr is a type modifier used to explicitly specify that the data being read from or written to a memory address is of 32 bits (4 bytes) in size.
It is typically used with memory addresses in the following format:
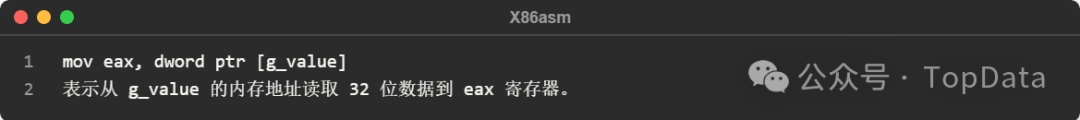
4 Why is dword ptr needed?
In assembly language, memory operations may involve data of different sizes (8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits, etc.). The compiler or assembler needs to know the specific size of the data being operated on to generate the correct machine code. dword ptr explicitly specifies the data size, avoiding ambiguity.
For example, if the size is not specified, the assembler may not be able to determine whether to read 8 bits (byte), 16 bits (word), or 32 bits (dword).
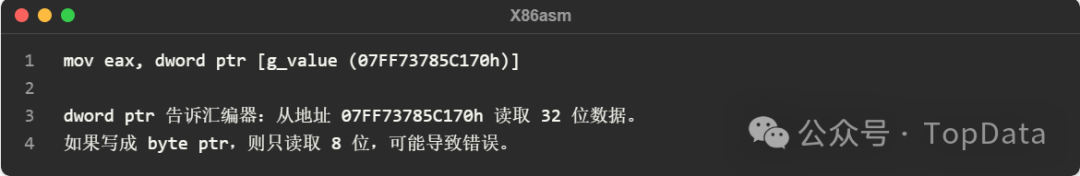
Here is a corresponding piece of code in C language:
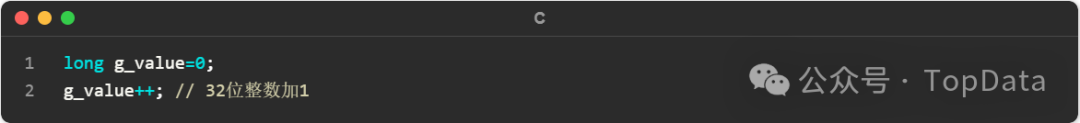
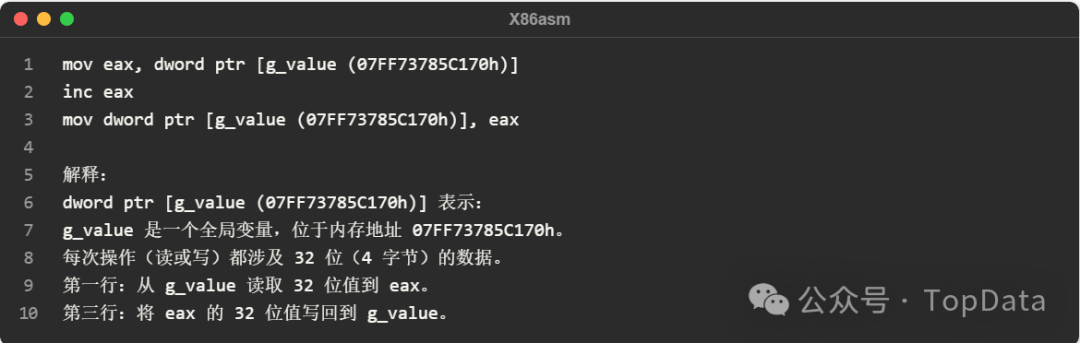
The corresponding assembly language for <span>g_value++</span> is as follows:
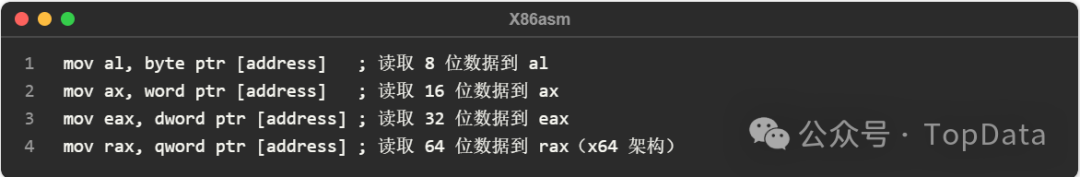
5 Other Similar Modifiers
In x86 assembly, common data size modifiers include:
<span>byte ptr: 8 bits (1 byte)</span>
<span>word ptr: 16 bits (2 bytes)</span>
<span>dword ptr: 32 bits (4 bytes)</span>
<span>qword ptr: 64 bits (8 bytes)</span>
6 Conclusion
<span>dword ptr</span> indicates that the memory data being operated on is 32 bits (4 bytes), and specifies that this is an access to a memory address. <span>dword ptr [g_value (07FF73785C170h)]</span> ensures that 32-bit data is read from or written to the address of g_value. It is a key modifier in assembly language used to eliminate ambiguity regarding data size.