Author: Ada
IoT Think Tank Compilation and Release
Please indicate the source and origin when reprinting
Introduction
Indoor positioning technology is needed in scenarios such as smart homes, smart factories, smart logistics, and smart elderly care to improve positioning accuracy. With the sudden increase in demand, indoor positioning technology is also rapidly developing, presenting a flourishing trend.

The home field has always been one of the most potential markets for the consumer end. Tech giants like Alibaba, Baidu, Huawei, and Xiaomi entered early, while traditional appliance manufacturers like Midea and Haier have also adapted to market trends and have laid out smart home businesses. A few years ago, when people talked about smart homes, they were full of amazement and expectation, eagerly paying for various human-computer interaction terminals. However, with the large-scale popularization of technologies such as the Internet of Things and artificial intelligence, if there is no significant improvement in the quality of users’ lives, it may be difficult to “pry open” users’ wallets again.
Today, the smart home industry has successively gone through the “automation” and “single product intelligence” stages and has officially entered the “scenario-based intelligence” stage. The key to building a fully connected intelligent scenario is connection and positioning— open connection technologies help individual products within home scenarios achieve interconnectivity; precise indoor positioning technologies help users achieve intelligent control.
The AI butler JARVIS of “Iron Man” Tony Stark fulfills people’s fantasies about intelligent home scenarios, and its ability to accurately and quickly execute Iron Man’s commands also relies on indoor positioning technology— it can not only accurately locate intelligent terminals within range but also achieve precise control. Imagine, when Iron Man issues the command to “make coffee,” if JARVIS doesn’t even know where the coffee machine is, how can it coordinate? In reality, “smart home accidents” such as vacuum robots getting “lost,” smartphones losing contact with smart home terminals, and smart speakers malfunctioning are also frequent.
In addition to the home field, indoor positioning technology is also needed in scenarios such as smart factories, smart logistics, and smart elderly care to improve positioning accuracy, and with the sudden increase in demand, indoor positioning technology is also rapidly developing.
A Variety of Indoor Positioning Technologies
According to a survey by Market&Markets, the global indoor positioning market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 42.0% in the coming years, expanding from $7.11 billion in 2017 to $40.99 billion in 2022, with its underlying technologies also presenting a flourishing trend.
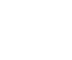
Currently, indoor positioning technologies mainly include UWB, Bluetooth 5.1 AOA, WiFi positioning, infrared positioning, inertial navigation positioning, ultrasonic positioning, Zigbee positioning, etc.
UWB (Ultra-Wideband Technology)
UWB technology is a high transmission rate (up to over 1000Mbps), low transmission power, strong penetration capability wireless technology based on extremely narrow pulses. It does not require the use of carriers in traditional communication systems; instead, it transmits data by sending and receiving extremely narrow pulses with nanosecond or sub-nanosecond duration, resulting in a bandwidth in the range of 3.1-10.6GHz.
UWB indoor positioning technology commonly uses the TDOA (Time Difference of Arrival) ranging positioning algorithm, which locates the ultra-wideband system through the time difference of signal arrival, using hyperbolic intersections that include the generation, transmission, reception, and processing of extremely narrow pulse signals.
In the past two years, smartphone manufacturers represented by Apple and Xiaomi have actively integrated UWB chips into smartphones, speakers, and various smart home devices, achieving direction, distance, and relative position perception between smartphones and smart homes.
Bluetooth 5.1 AOA
In January 2018, the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) released the Bluetooth specification implementing version 5.1. The released Bluetooth 5.1 can not only detect the distance of specific objects but also determine their direction, enabling a Bluetooth positioning system with centimeter-level positioning accuracy. Compared to UWB positioning technology with accuracy of 0.1 – 0.3 meters, Bluetooth AOA can achieve an accuracy of 0.3-0.5 meters and can achieve more than ten times the accuracy compared to traditional RSSI.
The biggest advantage of Bluetooth indoor positioning technology is its small device size, easy integration into PDAs, PCs, and smartphones, making it easy to promote and popularize. Theoretically, for users with mobile terminal devices integrated with Bluetooth functionality, as long as the Bluetooth function is enabled, the Bluetooth indoor positioning system can determine their location. When using this technology for short-range indoor positioning, it is easy to detect devices, and signal transmission is not affected by line of sight. Its shortcomings include the relatively high cost of Bluetooth devices and equipment, and the slightly lower stability of the Bluetooth system in complex spatial environments, which is greatly affected by noise signal interference.
WiFi Positioning
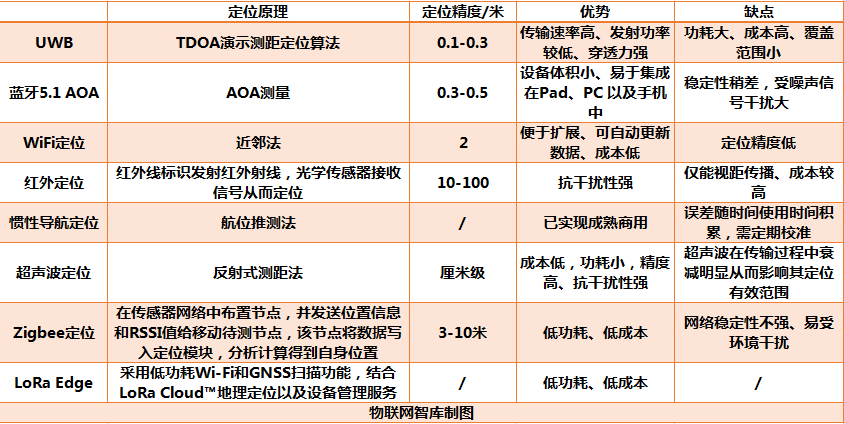
WiFi positioning generally uses the “nearest neighbor method” to determine which hotspot or base station is closest, thus determining the location. If there are multiple signal sources nearby, triangulation can be used to improve positioning accuracy. The greatest advantage of WiFi positioning is that it does not require the installation of dedicated equipment for positioning; users can become data sources by turning on Wi-Fi and mobile cellular networks when using smartphones. This technology has advantages such as ease of expansion, automatic data updates, and low cost, thus achieving large-scale implementation first.
WiFi positioning can achieve complex large-range positioning, but the accuracy can only reach about 2 meters, making precise positioning impossible. Therefore, it is suitable for positioning and navigation of people or vehicles and can be applied in scenarios such as smart healthcare, smart factories, and smart parking, but it is rarely used in home scenarios.
Infrared Positioning
Infrared indoor positioning technology uses modulated infrared rays emitted by infrared markers, which are received by optical sensors installed indoors for positioning. Although the positioning accuracy is high, infrared rays cannot penetrate obstacles, meaning infrared rays can only propagate in line of sight. When markers are placed in pockets or obstructed by walls or other barriers, they cannot function normally, necessitating the installation of receiving antennas in each room and corridor, which is costly. This technology is currently mainly used for passive positioning of infrared radiation sources such as aircraft, tanks, and missiles in military applications, and can also be used for positioning of indoor autonomous robots.
Additionally, there is a method of infrared positioning called infrared weaving, which covers the space to be measured with a network of multiple pairs of emitters and receivers, directly locating moving targets. Its advantage is that it does not require the positioning object to carry any terminals or tags, providing strong concealment, and is often used in security fields. The disadvantage is that to achieve high-precision positioning, a large number of infrared receivers and emitters must be deployed, which is very expensive, so this technology is only adopted by high-level security applications.
Inertial Navigation Technology
Inertial navigation indoor positioning mainly utilizes motion data collected from terminal inertial sensors, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, to measure the speed, direction, and acceleration of objects, using dead reckoning to calculate the object’s position through various computations.
As walking time increases, the error in inertial navigation positioning continues to accumulate. It requires more accurate external data sources for calibration. Therefore, inertial navigation is generally combined with WiFi fingerprinting, requesting indoor location through WiFi at intervals to correct the errors generated by MEMS. Currently, this positioning technology is widely used in vacuum robots.
Ultrasonic Positioning
Ultrasonic positioning mostly uses reflective ranging methods. The system consists of a main ranging device and several electronic tags, with the main ranging device placed on the mobile robot and each electronic tag fixed in the indoor space.
Zigbee Positioning
ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4) is a short-range, low-rate wireless network technology characterized by low power consumption and low cost, positioned between RFID and Bluetooth, primarily aimed at wireless personal area networks.
ZigBee indoor positioning technology is constructed by arranging reference nodes and mobile nodes in a sensor network. Reference nodes are static nodes that send location information and RSSI values to the mobile node, which writes the data into the positioning module and analyzes it to determine its own position. This system often uses distributed node settings, which can reduce network data workload and communication latency issues, with an accuracy within 2m, but network stability needs improvement and is easily affected by environmental interference.
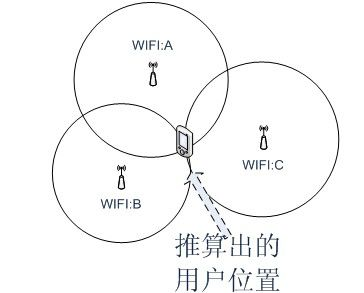
LoRa Edge
Recently, Semtech launched the LoRa Edge™ product portfolio, which includes a geographic positioning solution that utilizes low-power Wi-Fi and GNSS scanning functions, combined with the easy-to-use and cost-effective LoRa Cloud™ geographic positioning and device management services, which can significantly reduce the cost and complexity of using IoT for locating and monitoring assets. Its target application markets include industrial, building, home, agriculture, transportation, and logistics.
The Booming Indoor Positioning Application Market
People’s main living and working places are concentrated indoors, so the future indoor positioning market holds immense opportunities and possibilities.
In terms of smart home industry, although the market shows a “contested” pattern, major giants have begun to seek industrial-level ecological integration. While establishing a unified connection standard, positioning technology will gradually unify, with the current industry trend focusing mainly on UWB and BLE AOA, two emerging forces.

On one hand, UWB has gained widespread recognition in the industry due to its simple system structure, high-speed data transmission, and centimeter-level positioning accuracy, aided by Xiaomi’s “One Finger Connect” product layout. However, issues such as high power consumption, high costs, and small coverage area still exist. Additionally, the deployment of domestic UWB base stations has already affected the signals of 5G base stations, causing various interferences such as co-frequency and adjacent frequency. Furthermore, in actual deployment, to improve coverage, there are cases where UWB base stations exceed the design power limits, which can also impact 5G signals.
On the other hand, BLE AOA technology can also achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy, with slight advantages in terms of cost and power consumption. Meanwhile, Bluetooth operates in the 2.40GHz to 2.41GHz frequency band, utilizing the outermost channel for communication, which can avoid conflicts with WiFi signals operating in the same band, ensuring smooth signal flow. However, the inherent instability of Bluetooth technology and its susceptibility to noise signal interference greatly limit the large-scale application of BLE AOA.
Both technologies have their pros and cons, but ultimately, the significance of precise positioning in smart homes is undeniable. It is believed that through the refinement of practical applications, the technology will continue to innovate and upgrade.
In the smart elderly care industry, there are pain points such as limited caregivers and the inability to provide real-time monitoring. Families also have a need to check elderly health data at any time. Considering cost and implementation difficulty, WiFi positioning is widely used in this field. After the elderly wear electronic wristbands, the system can collect data and determine positioning through devices that cover the signals of the electronic wristbands, although the positioning accuracy is limited, it can fully meet scenarios such as preventing the elderly from getting lost and fall alarms.
In the smart healthcare industry, positioning technology is mainly used for medical equipment management and infant anti-theft scenarios. Firstly, the medical equipment management system does not have high requirements for positioning accuracy, mainly using WiFi positioning, Bluetooth positioning, RFID tag positioning, and other low-cost technologies to track medical equipment, achieving centralized management and usage; infant anti-theft scenarios also use electronic wristbands/anklets to enable real-time monitoring.
We can see that cost and accuracy are the keys to whether technology can achieve large-scale industrial implementation. As intelligent application scenarios become increasingly rich, users’ demand for indoor positioning is also increasing, and precise positioning has entered a golden period of development. It is believed that with the joint efforts of the entire industry chain, low-cost and high-precision positioning technology will contribute to precise control in scenario-based intelligence.
References:
1. “Bluetooth 5.1 AOA vs. UWB, Which Indoor Positioning Technology is the Future?” Challey, Electronic Technology Design
2. “Today, Xiaomi Has Caused a “Revolution” in Interaction Modes!” IoT Think Tank
3. “Comprehensive Analysis of IoT Positioning Technologies! Positioning is Moving from Outdoors to Indoors~”, IoT Think Tank
4. “Comparison of UWB Indoor Positioning Technology with Other Positioning Technologies”, IoT Media
We sincerely invite you to attend,
to jointly grasp the main direction of the AIoT era!
Scanthe QR code in the imageto register for participation

Selected Past Issues
Harbin Institute of Technology is too difficult! It was banned in the National College Student
Mathematical Modeling Competition……

The ultimate killing move! The United States has started
“Unlimited Traceability” against Huawei, blacklisting 38 companies……

Huawei’s high-end Kirin chips may become obsolete,
Yu Chengdong: A solution is already in place!

Just now, the United States announced the “Clean Network” action:
Ban Chinese operators, disable BAT cloud……

History will remember today, we were robbed by the American empire
successfully! ByteDance agrees……

Huawei plans to enter lithography machine manufacturing,
mass-produce 5nm lithography machines within two years?……

Just now, the United States announced the “Clean Network” action:
Ban Chinese operators, disable BAT cloud……
