He Qin, Xie Yinggang, Zhao Minglang
(Beijing Information Science and Technology University, School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing 100101)
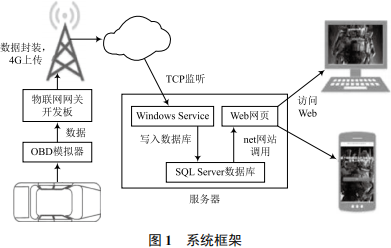
Abstract: In response to vehicle pollution emissions and real-time vehicle monitoring issues, a vehicle information self-inspection monitoring system based on Internet of Things (IoT) technology is designed. The system uses an OBD simulator to replace real vehicles and connect to the IoT gateway development board, simulating the car status and collecting the data for reporting, which facilitates real-time monitoring of engine operation, exhaust treatment status, fuel conditions, etc. The collected OBD data is transmitted to Huawei Elastic ECS cloud server via 4G transmission, and the data is stored in the SQL Server database. The vehicle self-inspection information reporting platform based on the IoT gateway retrieves data from the database and displays it on the platform page, allowing vehicle owners to understand the current status of their vehicles more intuitively, providing important evidence for diagnosing vehicle faults and monitoring exhaust emissions.
Keywords: Vehicle information self-inspection monitoring; IoT technology; IoT gateway; 4G transmission; OBD simulator; SQL Server
Classification number: TP391 Literature identification code: A
Article number: 2095-1302 (2022) 08-0013-02
As of June 2020, the number of cars in the country has reached 360 million, of which 270 million are passenger cars. This has led to many problems, such as frequent traffic accidents and serious environmental pollution caused by exhaust emissions. To strengthen real-time status monitoring and information collection of vehicles, this paper designs and implements a vehicle self-inspection information reporting system based on the IoT gateway, using OBD to obtain real-time data of vehicles, and uploading it to the platform via the IoT gateway, facilitating monitoring of vehicle pollution emissions and sharing real-time vehicle detection results. [1-3]
1 System Design
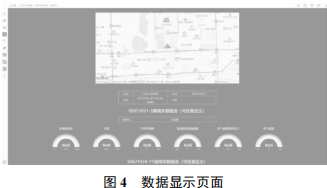
The effect of the data display page dynamically showing real-time data is shown in Figure 4.
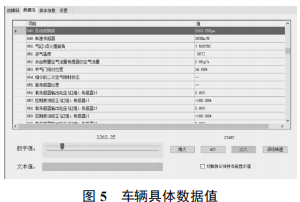
During driving, the car status (ACC, off, ignition) and specific data values (engine RPM, vehicle speed, engine coolant temperature, fuel system status, etc.) can be displayed in a list format, as shown in Figure 5.
References
[1] Wang Yuequn, Tang Lijuan, Song Jie, et al. Routing Technology of Vehicle Network Based on 5G Transmission. [J]. IoT Technology, 2020, 10(10): 33-34.
[2] Guo Zhijie, Zhang Bin, Yang Tao, et al. Project Design of Intelligent Connected Vehicles and Smart Traffic Application Demonstration Area. [J]. Traffic Science and Technology, 2020, 46(6): 123-127.
[3] Xie Yao. Research on Intelligent Vehicle IoT System under the Background of Informatization. [J]. Electronic World, 2020, 42(23): 5-6.
[4] Zheng Zhen. Analysis of Motion Control of Unmanned New Energy Vehicles under Vehicle Network Technology. [J]. Modern Automobile, 2020, 17(23): 100-101.
[5] She Hongyan. Introduction to Key Technologies of 5G Vehicle Networking. [J]. Communication and Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 50-51.
[6] Zheng Xin. Research and Design of Vehicle Networking Information Platform Based on NGTP Framework Protocol. [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2020.
[7] Xu Yong. Research on Vehicle Networking Communication Protocol and System Development. [J]. Journal of Guilin University of Electronic Technology, 2010, 30(5): 457-461.
[8] Huo Wenhui, Li Jingzhao. Smart Logistics Monitoring System Based on IoT. [J]. IoT Technology, 2020, 10(9): 19-23.
[9] Zhong Yiming. Design of Vehicle Information Collection System. [D]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou University of Electronic Technology, 2014.
[10] Li Hang. Research on Vehicle Information Interaction and Control System Based on Android Platform. [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2013.
[11] Chen Yanyan, Su Zixun, Fan Bo, et al. New Vehicle Networking System Architecture and Key Technologies of Human-Machine-Network Integration. [J]. Mobile Communication, 2020, 44(11): 58-64.
[12] Yu Le. Research on Emission Management of In-Use Vehicles Based on OBD. [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2010.
[13] Ouyang Bing. Research on Vehicle Monitoring System Based on OBD. [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[14] Hao Yajie, Hu Xinyu, Li Fuzhong. Research on Vehicle Networking System Based on Beidou Satellite Navigation. [J]. IoT Technology, 2019, 9(7): 57-60.
[15] Li Zhengguo, Lin Yu, Zhou Guoyou, et al. Remote Monitoring and Early Warning System for Vehicles Based on IoT. [A]. China Communications Society, China Electronics Society. Proceedings of the 2018 National Conference on IoT Technology and Applications. China Communications Society, 2018: 1.