Upon seeing the news that the United States announced exemptions from tariffs on certain semiconductor equipment, many immediately thought of “bad news being fully priced in.” However, they overlooked the hidden information behind it: products originating from China can be exempt from a 125% tariff if they meet the condition of “U.S. content ≥ 20%” (the exemption covers 20 categories of goods including smartphones, computers, chips, communication equipment such as routers, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment). Meanwhile, the China Semiconductor Industry Association issued an “Emergency Notice on the Rules for Determining the ‘Country of Origin’ of Semiconductor Products.”
These two policies may seem independent, but they actually complement each other and create a powerful synergistic effect, profoundly impacting the domestic semiconductor equipment industry. So, how exactly does the U.S. tariff policy reshape the semiconductor industry chain? What stage has domestic substitution reached? Next, we will delve into the analysis.
01
How do policies reshape the semiconductor industry chain?
The U.S. semiconductor exemption policy can be aptly described as “looser on the surface, tighter behind the scenes.” On the surface, it appears to relax tariff restrictions, but in reality, it raises the entry threshold for the supply chain through technical component requirements. Currently, many core technologies of high-end semiconductor equipment are still firmly held by U.S. companies. If Chinese companies want to enjoy this tariff benefit, they must procure a certain proportion of U.S. components or technology, which will undoubtedly lead to increased actual costs. In this situation, domestic companies have to reassess supply chain security, and the significant rise in costs is forcing them to accelerate the shift towards domestic materials and equipment, making the demand for a self-controllable supply chain increasingly urgent..
Moreover, China’s adjustment of the rules for determining the country of origin is also significant. Some semiconductor products need to declare tariffs based on the wafer fabrication location during import customs clearance. If the chips are fabricated in the U.S., they will incur additional tariffs upon import. This policy directly affects the upstream of the industry chain, using tariff leverage to promote the transfer of the industry chain to domestic sources. At the same time, it also incentivizes local companies to accelerate their technological breakthroughs, injecting strong momentum into the localization of semiconductor equipment.
02
What is the outlook for domestic substitution in semiconductors?
We will discuss the current state of domestic semiconductor equipment and the demand in the semiconductor industry from two aspects.
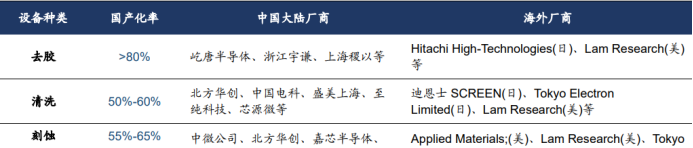
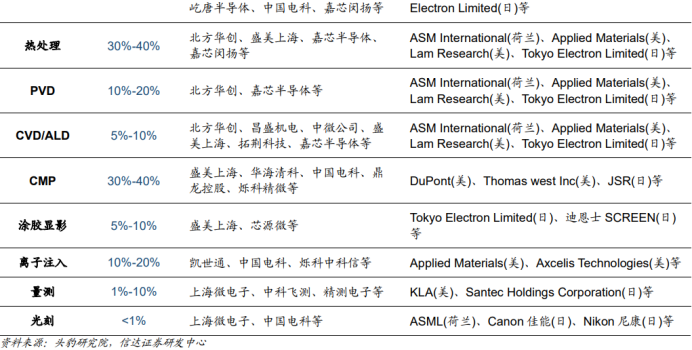
1) Semiconductor equipment is the core link in semiconductor manufacturing. In recent years, the domestic localization rate of semiconductor equipment has steadily increased, but the development is uneven across different subfields.
According to statistics from the Head Leopard Research Institute, Chinese semiconductor equipment manufacturers have a high localization rate in de-bonding, cleaning, and etching equipment, have made breakthroughs in CMP, thermal processing, and thin film deposition equipment, while the localization level in measurement, coating and developing, photolithography, and ion implantation equipment remains low. This indicates that there is significant potential for domestic substitution in these areas, waiting for domestic companies to explore.
2) On the demand side, three major demand engines are driving the growth of the semiconductor industry.
-
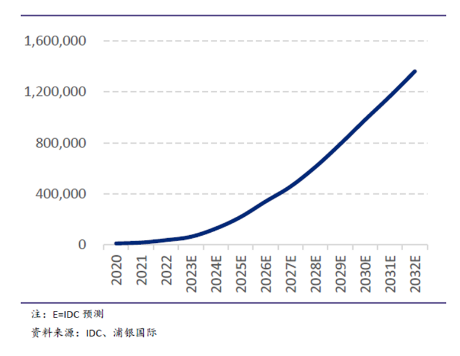
With the explosive development of AI technology, AI computing power serves as the infrastructure for large model training, and under the rapid iteration of large models, demand continues to expand. According to IDC data, from 2020 to 2023, the global generative AI market space has increased approximately sixfold, and it is expected to achieve a compound annual growth rate of 40% from 2024 to 2030, potentially reaching nearly one trillion dollars by 2030. As the most important support for the AI large model industry, AI computing power chips are fully enjoying the dividends brought by high industry growth.
Figure: Global Generative AI Market Space and Forecast (in millions of dollars)
- Demand for consumer electronics is gradually recovering. According to Statista data, the global consumer electronics industry market size has shown steady growth, reaching $1,051.6 billion in 2023, and is expected to grow to $1,176.7 billion by 2028. Such a large market size provides ample development space for the semiconductor industry.
- Sales of energy vehicles continue to grow. The China Association of Automobile Manufacturers released data showing that from January to March, automobile production and sales reached 7.561 million and 7.47 million units, respectively, representing year-on-year growth of 14.5% and 11.2%. Among them, new energy vehicles accounted for 3.182 million and 3.075 million units, with year-on-year growth of 50.4% and 47.1%, respectively. New energy vehicle sales reached 41.2% of total new car sales, indicating strong market demand.
Overall, the U.S. is attempting to maintain its technological dominance in the semiconductor field through tariff leverage, while China is actively promoting the localization of semiconductor equipment through policy guidance, accelerating the realization of a self-controllable industry chain. In this context, the domestic semiconductor equipment industry is entering a critical development period.
The Semiconductor Equipment ETF Fund (159327) closely tracks the CSI Semiconductor Materials and Equipment Theme Index, reflecting the overall performance of listed companies in semiconductor materials and equipment, helping investors to easily allocate to 40 leading semiconductor companies, focusing on the two critical areas of semiconductor equipment and materials, characterized by high growth and high elasticity. Since the base date of December 28, 2018, the CSI Semiconductor Materials and Equipment Theme Index has increased by 247.3%, with an annualized return of 22.66%. Driven by both policy support and market demand, the semiconductor industry is expected to usher in a new growth cycle. Investors optimistic about the semiconductor direction should pay close attention to the Semiconductor Equipment ETF Fund (159327). (Source: Wind, as of 2025.04.15)
Source:
Cinda Securities, “[Cinda Electronics] U.S. Tariff Policy Implementation, Semiconductor Industry Chain Restructuring Benefits Domestic Substitution,” 2025.04.08.
Puyin International, “Global AI Computing Power Chip Industry Review: Generative AI Opens a Super Growth Cycle for the Technology Industry,” 2024.12.03.
Risk Warning: Past performance of the fund does not indicate future performance, and the performance of other funds managed by the fund manager and the past performance of its investment personnel do not guarantee future performance of the fund. The securities market may fluctuate due to macroeconomic factors, which may lead to potential risks of fluctuations in fund returns. Investors should carefully read the fund’s contract, prospectus, product information summary, and other legal documents to understand the fund’s basic situation when purchasing the fund. There may be differences in the descriptions of the fund’s risk-return characteristics and product risk levels in the legal documents due to different reference factors. Investors should make prudent decisions based on their investment objectives, time horizon, risk preferences, and risk tolerance. When purchasing through distribution agencies, the risk rating rules of the distribution agency shall prevail. The fund manager promises to manage and utilize fund assets with honesty, diligence, and due diligence, but does not guarantee that the fund will be profitable or guarantee minimum returns. Fund investment must be cautious. The views in this article only represent the views at the time and may change in the future, and are for reference only, not constituting any investment advice or guarantee, nor serving as any legal document.