1
Siemens Industrial Control System Industry Data Analysis

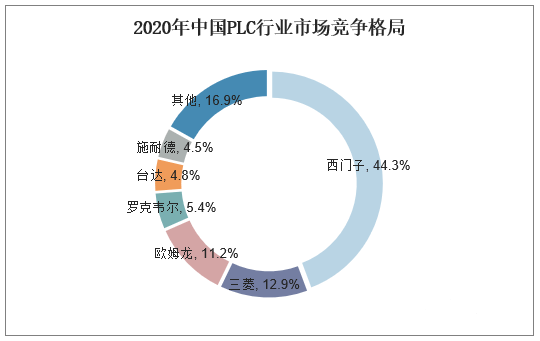
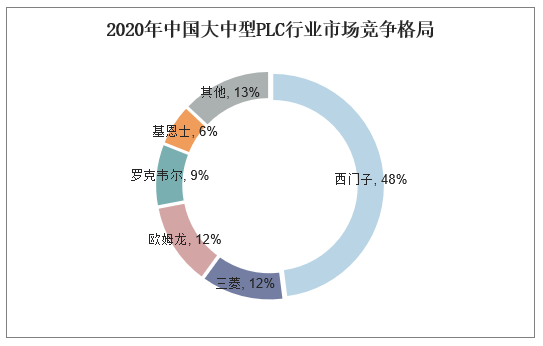
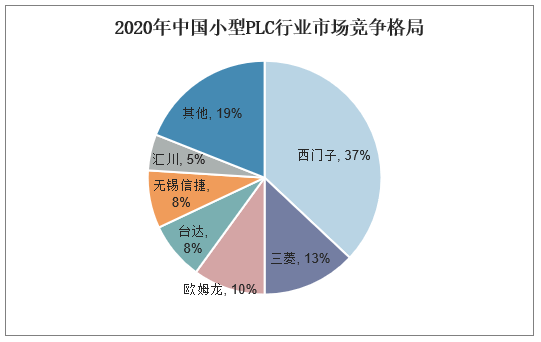
According to statistics, in 2020, the share of medium and large PLCs in China’s industrial control system segment was 51.20%, while small PLCs accounted for 48.80%; regionally, European and American brands accounted for 63%, Japanese brands for 26%, and local brands only 11%; in terms of brands, Siemens ranked first in the market with sales of 5.753 billion yuan, occupying 44.3% of the domestic market share. Siemens AG, founded in 1847, is a leading company in the field of electronic and electrical engineering globally. It focuses on industrial, infrastructure, transportation, and medical technology, with applications in various sectors such as petroleum and petrochemicals, tobacco, municipal, intelligent manufacturing, and metallurgy.
2
Introduction to Siemens Industrial Control System Communication Protocol

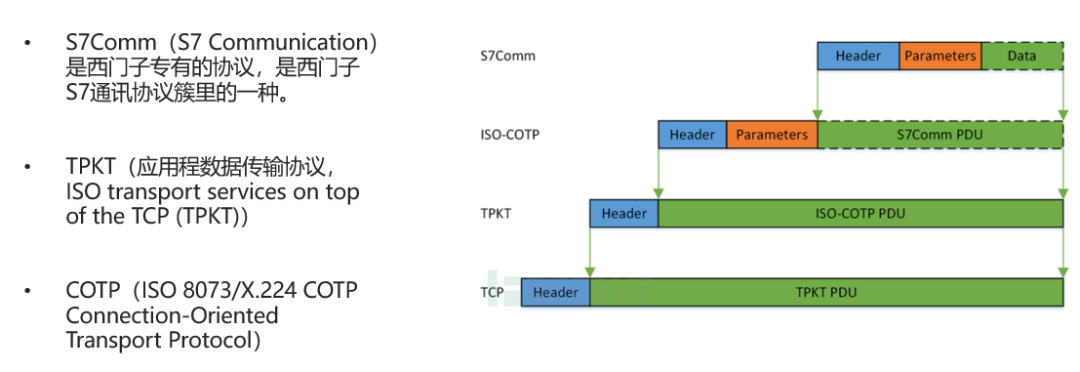
Siemens PLCs use a proprietary protocol for communication, which utilizes the TPKT and ISO8073 binary protocol. The communication ports for Siemens PLCs are all TCP port 102. There are three versions of Siemens PLC protocols: S7Comm protocol, the earlier S7CommPlus protocol, and the latest S7CommPlus protocol.
The S7-200, S7-300, and S7-400 series PLCs use the earlier Siemens proprietary protocol S7comm for communication. This protocol does not have the encryption capabilities of S7Comm-Plus and does not involve any replay attack prevention mechanisms, leading to security vulnerabilities. The specific protocol structure is shown in the figure below:
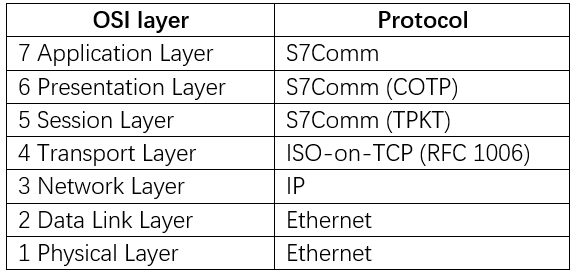
Communication between S7-1200 v3.0 uses the earlier S7Comm-Plus protocol;
S7-1200 v4.0 and S7-1500 series use the latest S7Comm-Plus protocol;
The latest S7Comm-Plus protocol introduces session IDs to prevent replay attacks. The specific protocol structure is similar to the figure above, with the seventh layer being S7comm-plus.
3
Introduction to Siemens Industrial Control System Software
Siemens’ industrial control software is divided into three different categories:
(1) Programming and Engineering Tools: These include all tools based on PLC or PC for programming, configuration, simulation, and maintenance required for control. Among them, S7200 and S7200-smartstep7 are unique, using programming software called step7MicroWIN and step7Microwinsmart, respectively. The S7300/400/1200/1500 series generally use TIA Portal—TIA Portal is Siemens’ redefined automation concept, platform, and standardized automation tool platform; the latest version is V16, which enhances support for S7 series PLCs and WinAC controllers, improving software startup speed and compatibility.
(2) PC-based Control Software: The PC-based control system WinAC allows the use of a personal computer as a programmable logic controller (PLC) to run user programs, operating on SIMATIC industrial computers or any commercial machine with Windows NT4.0 installed. WinAC provides two types of PLCs, one is a software PLC that runs as a Windows task on the user’s computer. The other is a slot PLC (which installs a PC card on the user’s computer), which has all the functions of a hardware PLC. WinAC is fully compatible with SIMATIC S7 series processors, and programming uses unified SIMATIC programming tools (such as STEP 7), allowing the compiled programs to run on both WinAC and S7 series processors.
(3) Human-Machine Interface Software: This software provides human-machine interface (HMI) or SCADA systems for user automation projects, supporting a wide range of platforms. There are two types of human-machine interface software: one is ProTool for machine-level applications, and the other is WinCC for monitoring-level applications.
ProTool is suitable for configuration of most HMI hardware, effectively completing configuration from operator panels to standard PCs integrated in STEP 7. ProTool/lite is used for text display configuration, such as: OP3, OP7, OP17, TD17, etc. ProTool/Pro is used for configuration of standard PCs and all Siemens HMI products; ProTool/Pro is not just configuration software; its runtime version is also used for monitoring systems on Windows platforms.
WinCC is a SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) software for monitoring and data collection that can run on any standard PC. WinCC is easy to operate, highly reliable, integrates with STEP 7 functionality, and can directly access the PLC’s hardware fault system. Its design is suitable for a wide range of applications, capable of connecting to existing automation environments, with a large number of communication interfaces and comprehensive process information and data processing capabilities.

4
Overview of Attacks Exploiting Siemens Industrial Control Systems
Currently, the main attack methods targeting Siemens industrial control systems include: IP spoofing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, TCP SYN Flood attacks, Land attacks, ICMP Smurf attacks, Ping of Death attacks, UDP Flood attacks, Teardrop attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and replay attacks. This chapter focuses on two types of attacks: man-in-the-middle attacks and replay attacks.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack
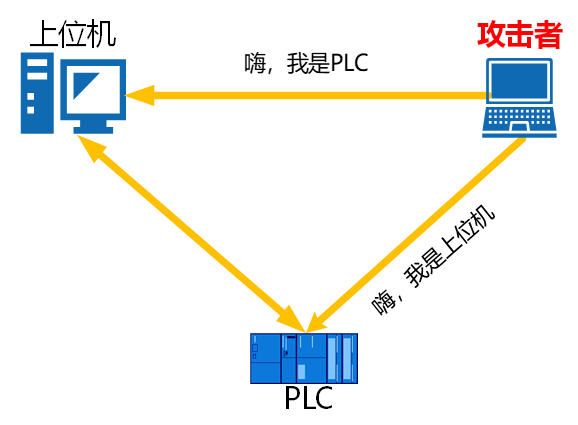
A man-in-the-middle attack (MITM) is an indirect intrusion attack where the attacker uses various techniques to place a computer under their control virtually between two communicating computers on a network. This computer is referred to as the “man-in-the-middle”.
In a man-in-the-middle attack, there are two victims: the host computer and the PLC. The man-in-the-middle carries out the attack without the knowledge of either party, targeting the transmission content between the host computer and the PLC transmitted through the man-in-the-middle. If the intercepted information contains usernames and passwords, the harm is even greater, and the man-in-the-middle attack does not damage the communication between the two parties. The attack process is illustrated in the figure below.
Attack Preconditions:
The attacker is on the same subnet as the PLC device.
Attack Steps:
1. The first and most crucial step is to use ARP spoofing to hijack traffic. Normally, PLC devices do not communicate with each other, and the hijacked traffic is likely to be between the PLC and the host computer or between the touchscreen and the PLC.
2. Then, analyze the captured traffic in a series of steps, such as finding the PLC, since the communication port for Siemens PLCs is port 102; after finding it, determine the PLC type by analyzing the data packets containing CPU information; after determining the version, continue to simulate loading payloads, such as stopping the PLC operation, reading memory, etc.
Recently, CNVD disclosed the man-in-the-middle attack on the S7 series, as shown in the figure below:
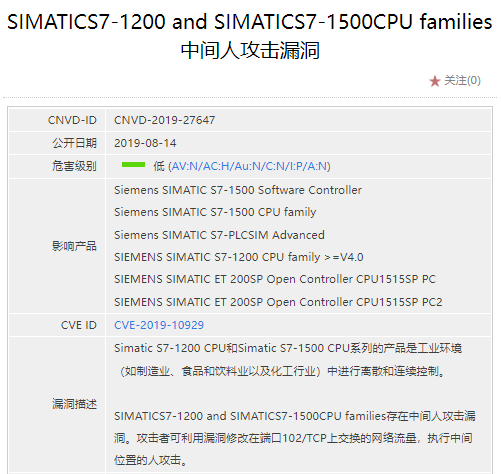
Figure 7: Vulnerability Illustration of Man-in-the-Middle Attack (Note: Siemens has modified this vulnerability and released a patch.)
Replay Attack
A replay attack is an attack where the attacker sends a packet that the destination host has already received to deceive the system, primarily used during the authentication process to undermine the correctness of authentication. In industrial control systems, a replay attack involves reloading the compiled program from the host software onto the PLC machine; the data packets captured must be from the beginning to the end of the connection.
Basic Attack Principle:
The basic principle of a replay attack is to resend previously eavesdropped data to the receiver unchanged. Often, data transmitted over the network is encrypted, making it difficult for the eavesdropper to understand the exact meaning of the data. However, if they know the purpose of the data, they can deceive the receiving end by resending the data without knowing its content.
Attack Steps:
When the host computer sends a message to the PLC, the owner of the replay attack can be either the host computer or the attacker.
1. If it is the host computer, it will resend the same message to the PLC.
2. If it is the attacker, they have intercepted the message sent from the host computer to the PLC and impersonate the host computer to send the intercepted message to the PLC.

The message sent from the host computer to the PLC is intercepted by the attacker, who then impersonates the host computer to send the intercepted message to the PLC, which mistakenly believes the attacker is the host computer and sends the response message back to the attacker.
5
Minimization Protection Scheme for Siemens Industrial Control Systems
In the increasingly severe network security situation for industrial control systems, Winut has proposed a network security solution based on a “whitelist” mechanism for the protection of Siemens industrial control systems. By monitoring industrial control network traffic, the status of industrial control hosts, etc., collecting and analyzing industrial control network data and software operating status, establishing a security state baseline and model under normal operating conditions of the industrial control system, and comprehensively building an industrial control security technology system, it ensures the stable operation of Siemens industrial control systems.
1. Regional Boundary Access Control
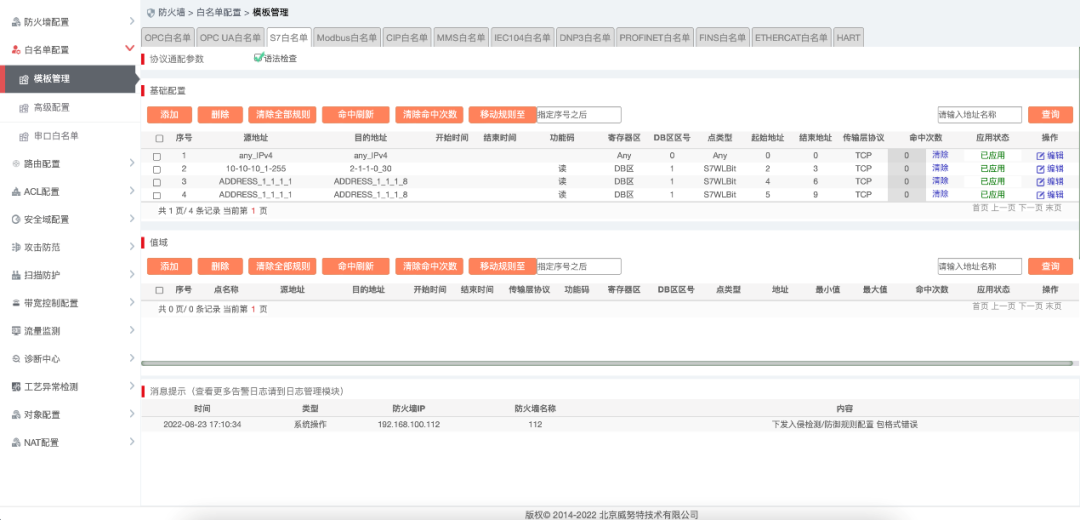
Deploy industrial firewalls between the host computer and PLC devices on the production network to identify and deeply analyze industrial control protocols such as S7, and to intercept illegal commands and malicious instructions in real-time; after the production business is solidified on the industrial site, use the intelligent learning function of the industrial firewall to solidify the security protection policies, synchronize with production business, and combine the hardware-level security policy write protection feature of the industrial firewall to achieve physical-level control of security policy read-only permissions. Strengthen the boundary isolation and protection of Siemens industrial control systems to ensure the continuous and stable operation of the control systems.


2. Security Protection and Reinforcement of Industrial Control Hosts
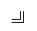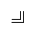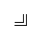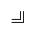
Deploy industrial host guardians on the industrial control hosts in the production network, using “whitelist” technology, vulnerability defense, security baselines, and peripheral control measures to achieve security protection and reinforcement of industrial control hosts, preventing replay attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and other attack methods from harming production business safety.

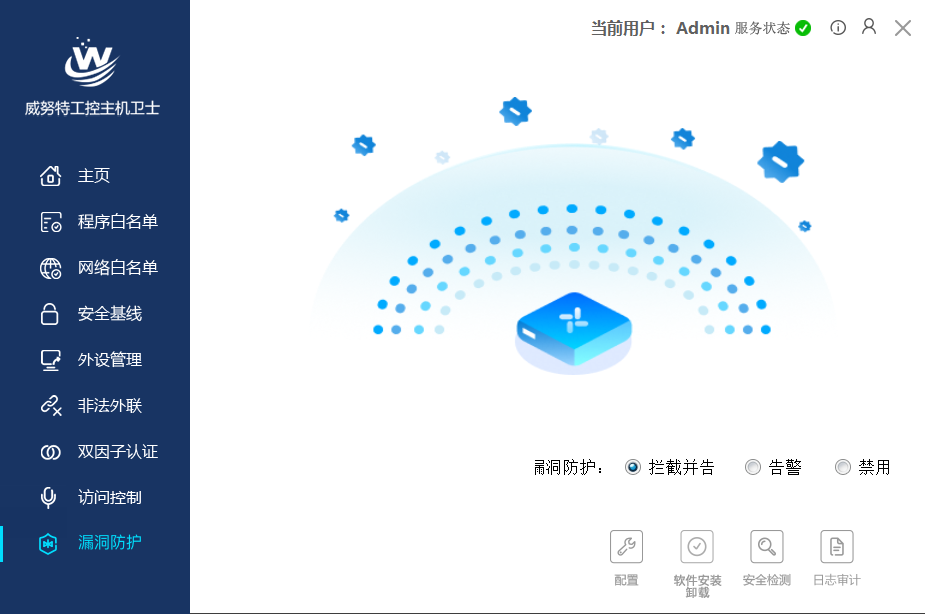
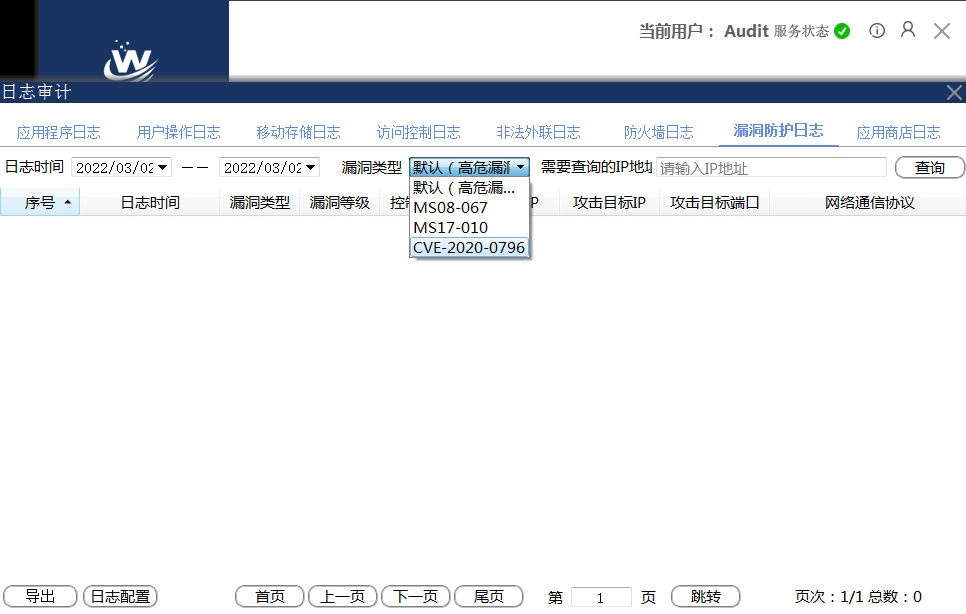

3. Monitoring and Early Warning of Production Network Traffic
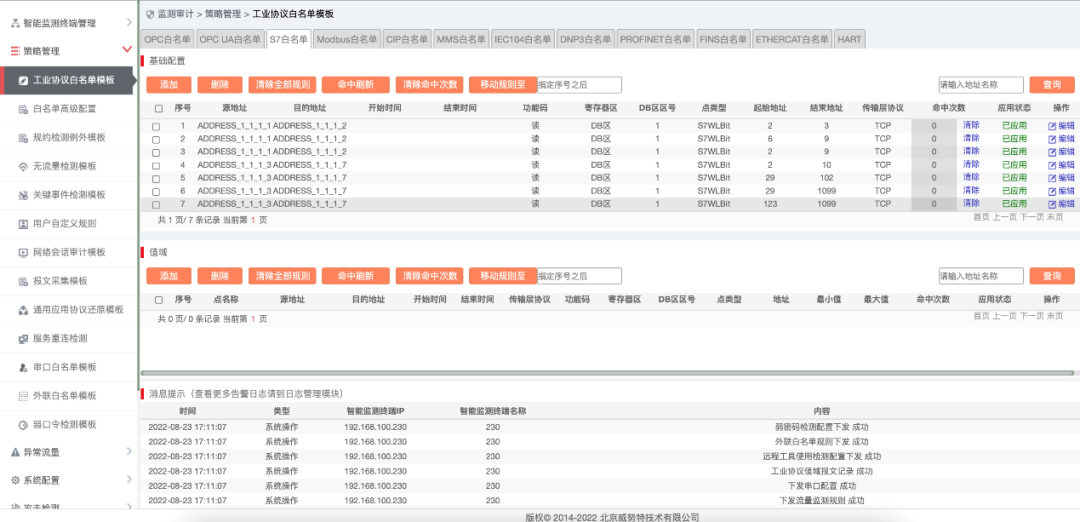
By deploying industrial security monitoring and auditing systems at key network nodes within the production network, real-time detection of network attacks targeting the S7 protocol, user misoperations, user violations, illegal device access, and the spread of malicious software such as worms and viruses can be achieved, along with real-time alerts. Additionally, all network communication behaviors are meticulously recorded, including domain-level communication records of the S7 protocol, enabling operational personnel to quickly identify security issues and respond accordingly. The system is designed to have “zero impact” on the control network, achieving true one-way flow of traffic by altering the logic link layer design, thereby eliminating the possibility of packet injection from a hardware perspective.

4. Unified Security Management and Control
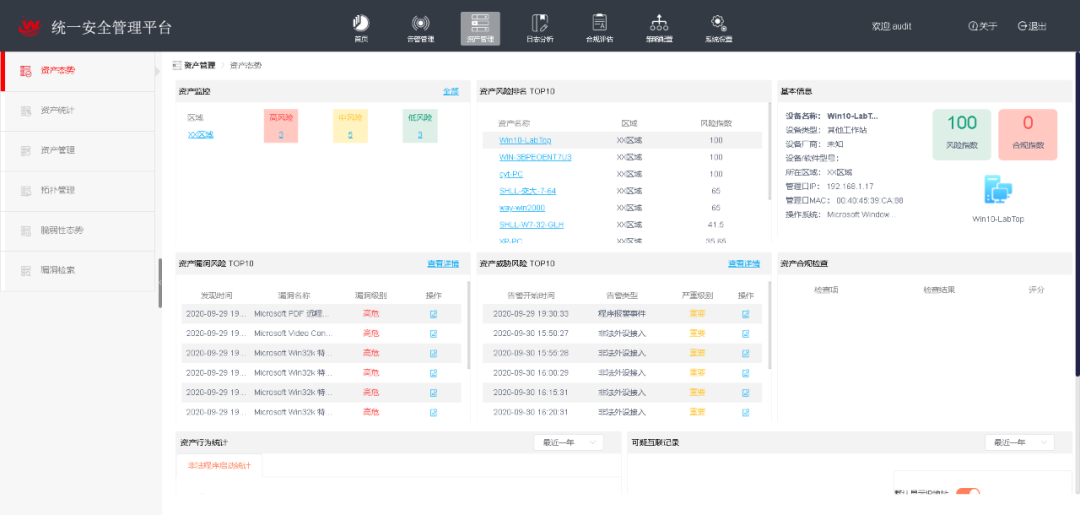
Establish a security management center and deploy a unified security management platform to centrally manage industrial security devices such as industrial firewalls, industrial host guardians, and industrial security monitoring and auditing systems deployed in the production network; simultaneously, the unified security management platform has centralized management capabilities based on assets, effectively assisting operational personnel in improving network security operational efficiency and reducing security operational costs.
6
Conclusion
As a leading enterprise in the domestic industrial control network security industry, Winut is one of the six companies globally to obtain the ISASecure CRT Tool certification from the International Society of Automation and one of the first national-level specialized and innovative “little giant” enterprises. It has provided innovative network security solutions centered on the “white environment” for Siemens’ industrial control systems in various industries such as petroleum and petrochemicals, tobacco, municipal, intelligent manufacturing, and metallurgy.


Beijing Winut Technology Co., Ltd. (referred to as Winut) is a leader in the domestic industrial control security industry and a company under the China State-owned Capital Risk Investment Fund. With its excellent technical innovation capabilities, it has become one of the six companies globally to obtain ISASecure certification from the International Society of Automation and one of the first national-level specialized and innovative “little giant” enterprises.
Winut relies on its pioneering core technology concept of the industrial network “white environment” and a full range of independently developed industrial control security products to provide comprehensive lifecycle defense solutions and specialized security services for important national industries such as power, rail transportation, petroleum and petrochemicals, municipal, tobacco, intelligent manufacturing, and military industry. To date, it has achieved safe and compliant operations for over 4,000 industry clients in China and along the “Belt and Road” countries.
As the national team for industrial control security in China, Winut actively promotes the construction of industrial clusters to develop ecological circles, leads and participates in the formulation of national and industry standards in the field of industrial control security, and is committed to protecting the network security of China’s critical information infrastructure, striving to become a backbone force in building a strong network country!