Click the above  “Follow Electronics” for easy learning of electronic knowledge.
“Follow Electronics” for easy learning of electronic knowledge.
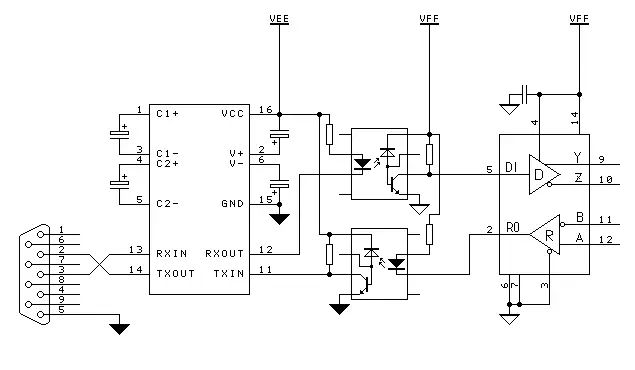
<RS232 and RS422 Interface Circuits>
1. RS-485 The RS-485 bus is widely used when communication distances range from dozens of meters to thousands of meters. The RS-485 serial bus uses balanced transmission and differential reception, which suppresses common-mode interference. Additionally, the bus transceiver has high sensitivity and can detect voltages as low as 200mV, allowing the transmission signal to be recovered over distances exceeding a kilometer. RS-485 operates in half-duplex mode, meaning only one point can be in sending mode at any time, so the sending circuit must be controlled by an enable signal. RS-485 is very convenient for multipoint interconnection, allowing for numerous signal lines to be eliminated. By using RS-485, a distributed system can be formed that allows for a maximum of 32 drivers and 32 receivers to be connected in parallel. 3. RS-422 The RS-422 bus has a similar circuit principle to RS-485, both using differential transmission and reception without needing a digital ground line. The differential operation is the fundamental reason for the longer transmission distance under the same rate conditions, which is the fundamental difference between the two and RS-232, as RS-232 is single-ended input/output and requires at least a digital ground line for duplex operation. There are three lines (asynchronous transmission) for sending and receiving, and additional control lines can be added to achieve synchronization and other functions. RS-422 can operate in full duplex using two pairs of twisted pairs, allowing sending and receiving to not interfere with each other, while RS-485 can only operate in half-duplex, meaning sending and receiving cannot occur simultaneously, but it only requires one pair of twisted pairs. RS-422 and RS-485 can transmit 1200 meters at 19kbps. With new transceiver circuits, multiple devices can be connected on the line.
2. RS-232 RS-232-C is a serial physical interface standard established by the Electronic Industry Association (EIA) in the United States. RS is the abbreviation for “Recommended Standard,” 232 is the identification number, and C indicates the number of modifications. The RS-232-C bus standard has 25 signal lines, including a main channel and an auxiliary channel. In most cases, the main channel is primarily used, and for general duplex communication, only a few signal lines are needed, such as one sending line, one receiving line, and one ground line. The RS-232-C standard specifies data transmission rates of 50, 75, 100, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, and 19200 baud. The RS-232-C standard allows for a capacitive load of 2500pF on the driver, and communication distance will be limited by this capacitance. For example, using a communication cable with 150pF/m, the maximum communication distance is 15m; if the cable’s capacitance per meter is reduced, the communication distance can be increased. Another reason for the short transmission distance is that RS-232 transmits single-ended signals, which suffer from common ground noise and cannot suppress common-mode interference, thus it is generally used for communications within 20m.
> > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > > >
==> Visit www.eeskill.com to learn more!