With the gradual development of technology, various industries are increasingly integrating intelligence.For example, in traditional restaurants, the serving model used to involve human servers bringing dishes to customers’ tables. Now, some restaurants are beginning to equip each table with an iPad for self-service ordering, with delivery robots bringing the food to the table, which customers can either pick up themselves or have a dedicated staff member handle.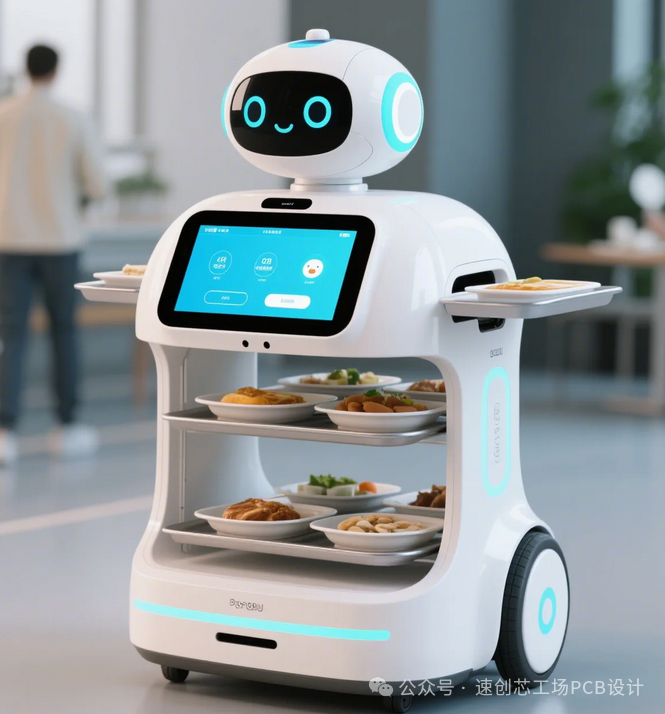 Similarly, in today’s tech companies, with the exponential growth of data and the need for confidentiality, independent data centers have become an essential component for every tech company. Traditional monitoring of data centers only stored data in a control room, requiring dedicated personnel for real-time operations. Now, some companies are beginning to aggregate data from all electronic products in the data center (smoke detectors, temperature and humidity sensors, air conditioning, UPS, etc.), allowing direct access via online mini-programs or apps. In case of emergencies, they can directly contact customers or the police.
Similarly, in today’s tech companies, with the exponential growth of data and the need for confidentiality, independent data centers have become an essential component for every tech company. Traditional monitoring of data centers only stored data in a control room, requiring dedicated personnel for real-time operations. Now, some companies are beginning to aggregate data from all electronic products in the data center (smoke detectors, temperature and humidity sensors, air conditioning, UPS, etc.), allowing direct access via online mini-programs or apps. In case of emergencies, they can directly contact customers or the police.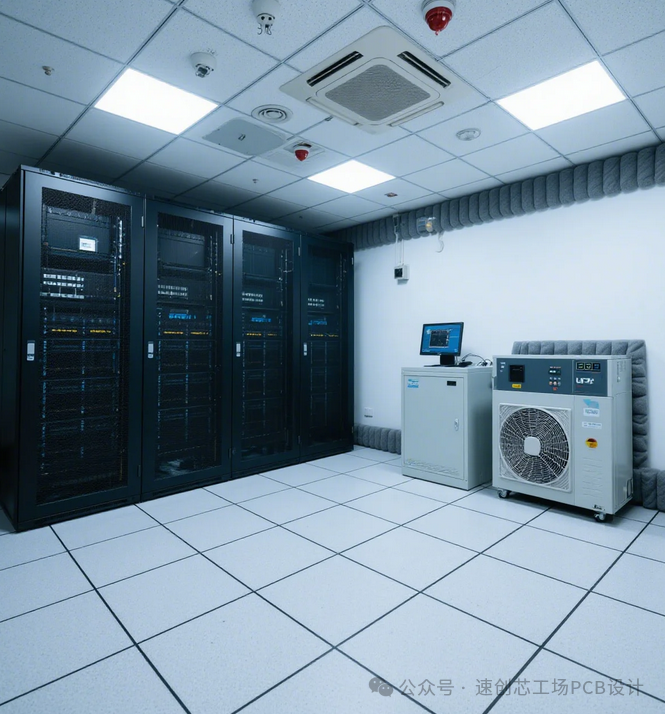 Today, I will share a PCB design project for intelligent warehouse robots. Robots like these used to be operated by dedicated warehouse personnel for loading and unloading, but now they are gradually transitioning to warehouse robots. As technology continues to advance, these robots are replacing human labor.
Today, I will share a PCB design project for intelligent warehouse robots. Robots like these used to be operated by dedicated warehouse personnel for loading and unloading, but now they are gradually transitioning to warehouse robots. As technology continues to advance, these robots are replacing human labor. The project details are as follows:
The project details are as follows: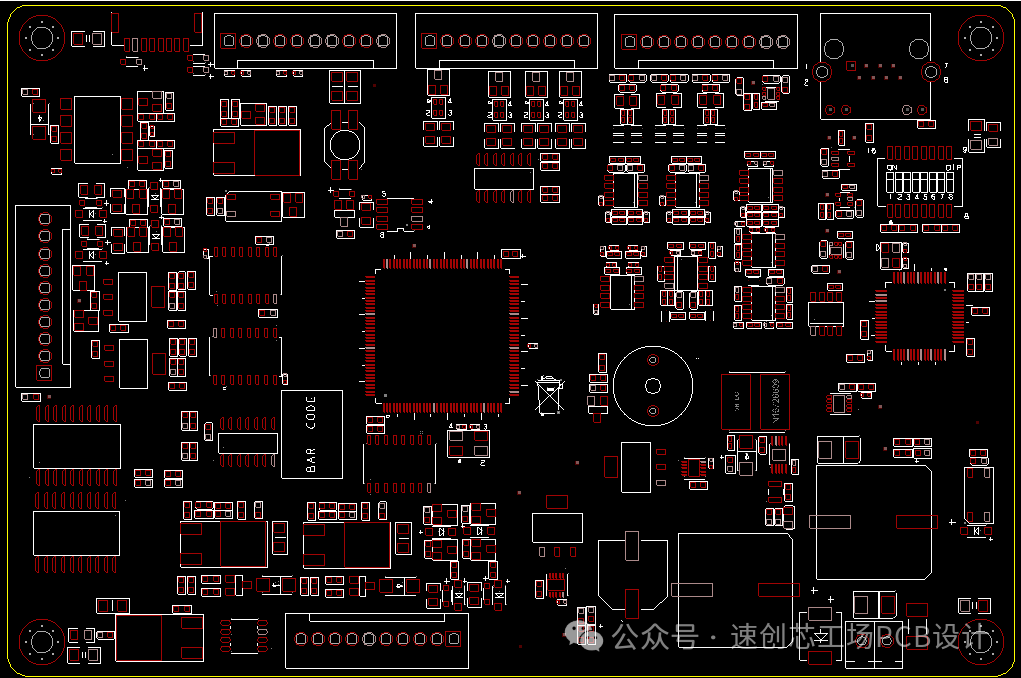 The main chip is from the STM32 series microcontrollers, with the upper interfaces including a programming interface, an RS232 communication interface (for communication with other independent devices), two encoder interfaces (providing PWM input for detection), and a Gigabit Ethernet port (for connecting to servers or debugging). The lower interfaces are for motor drive control and power supply.The main focus of this sharing is on the grounding considerations in PCB design. There are many analog signals within the board, so it is important to distinguish the grounds. It is advisable to add ESD protection to every incoming line at the interface and to use separate grounds for return paths, connecting them through resistors and capacitors to avoid mutual EMC interference.
The main chip is from the STM32 series microcontrollers, with the upper interfaces including a programming interface, an RS232 communication interface (for communication with other independent devices), two encoder interfaces (providing PWM input for detection), and a Gigabit Ethernet port (for connecting to servers or debugging). The lower interfaces are for motor drive control and power supply.The main focus of this sharing is on the grounding considerations in PCB design. There are many analog signals within the board, so it is important to distinguish the grounds. It is advisable to add ESD protection to every incoming line at the interface and to use separate grounds for return paths, connecting them through resistors and capacitors to avoid mutual EMC interference.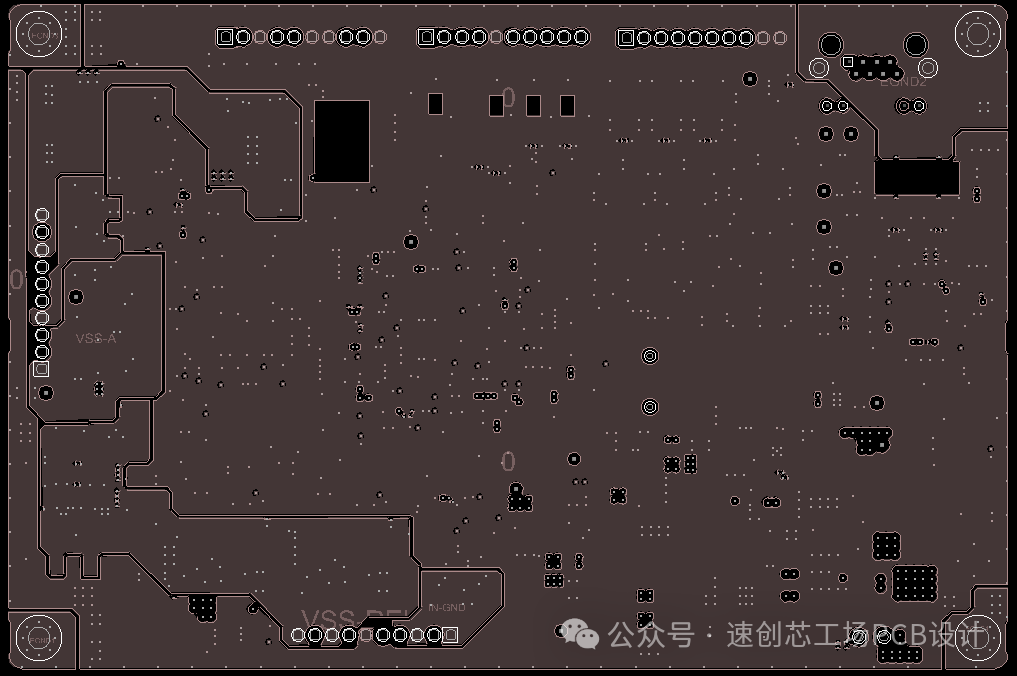 After segmenting the grounds, we must also control the routing paths to prevent crossing into other grounds. If space allows, it is best to add corresponding ground vias on both sides of the isolation zone. This design effectively places this module in a ‘cage’, resulting in excellent EMC performance.
After segmenting the grounds, we must also control the routing paths to prevent crossing into other grounds. If space allows, it is best to add corresponding ground vias on both sides of the isolation zone. This design effectively places this module in a ‘cage’, resulting in excellent EMC performance.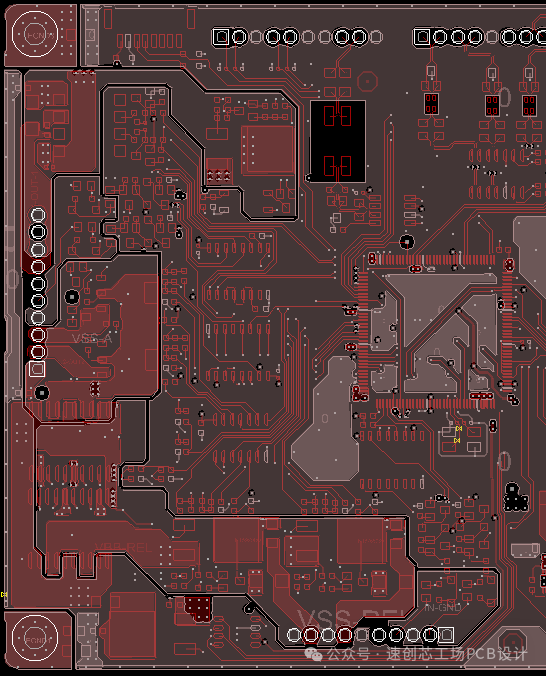 If you are still concerned about EMC, you can add a shielding cover, change the connector, or modify the routing to the inner layers; there is always a solution that suits your needs.
If you are still concerned about EMC, you can add a shielding cover, change the connector, or modify the routing to the inner layers; there is always a solution that suits your needs.