Click on “ Technical Training” above to select “Pin to Top”
Over 140,000 industrial control professionals follow this WeChat platform: technical sharing, learning exchange, industrial control videos


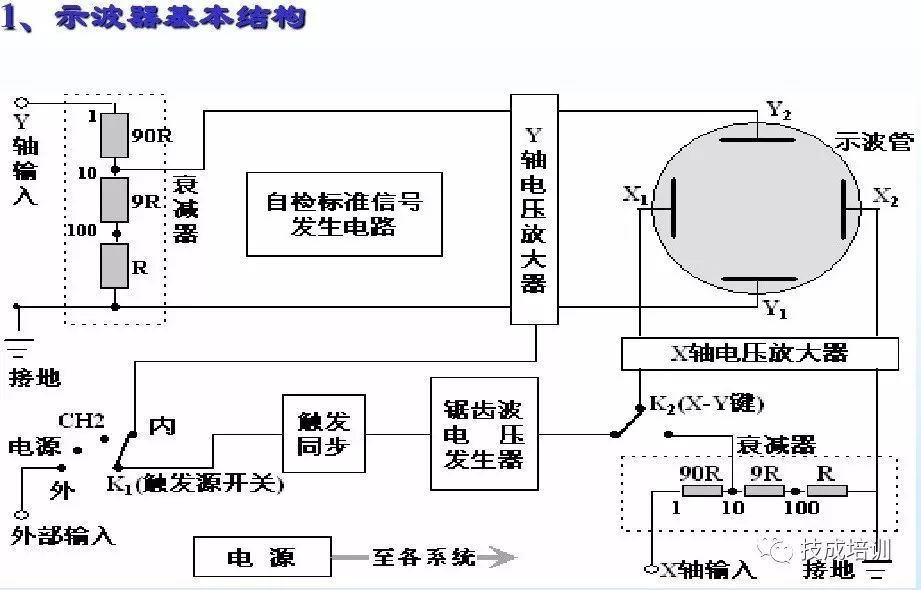
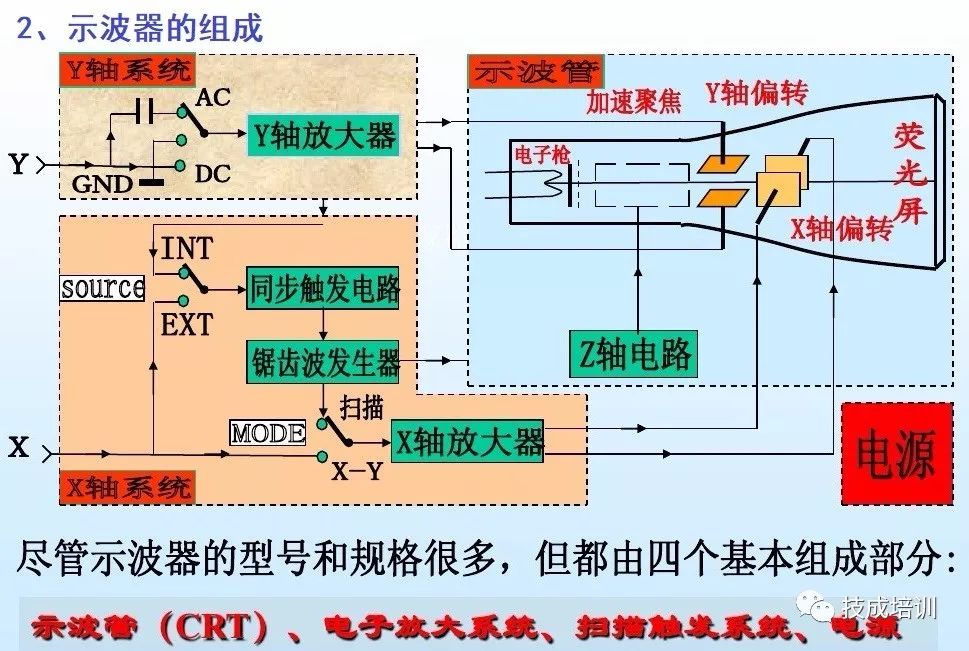



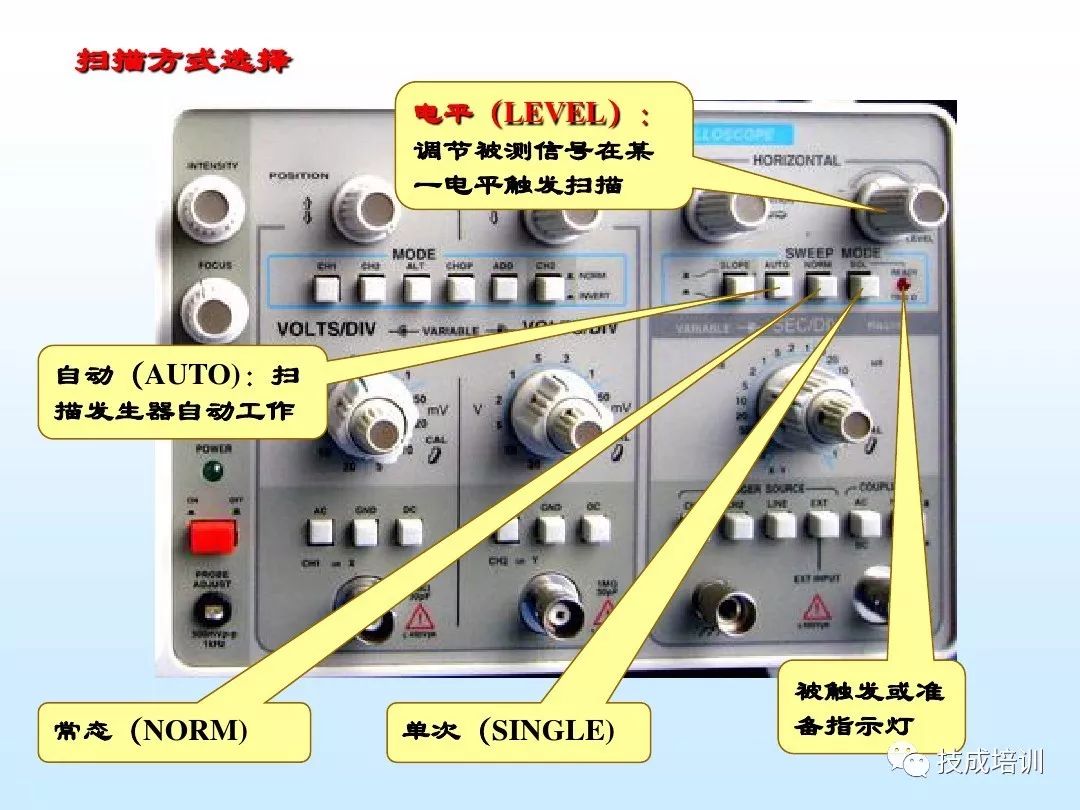
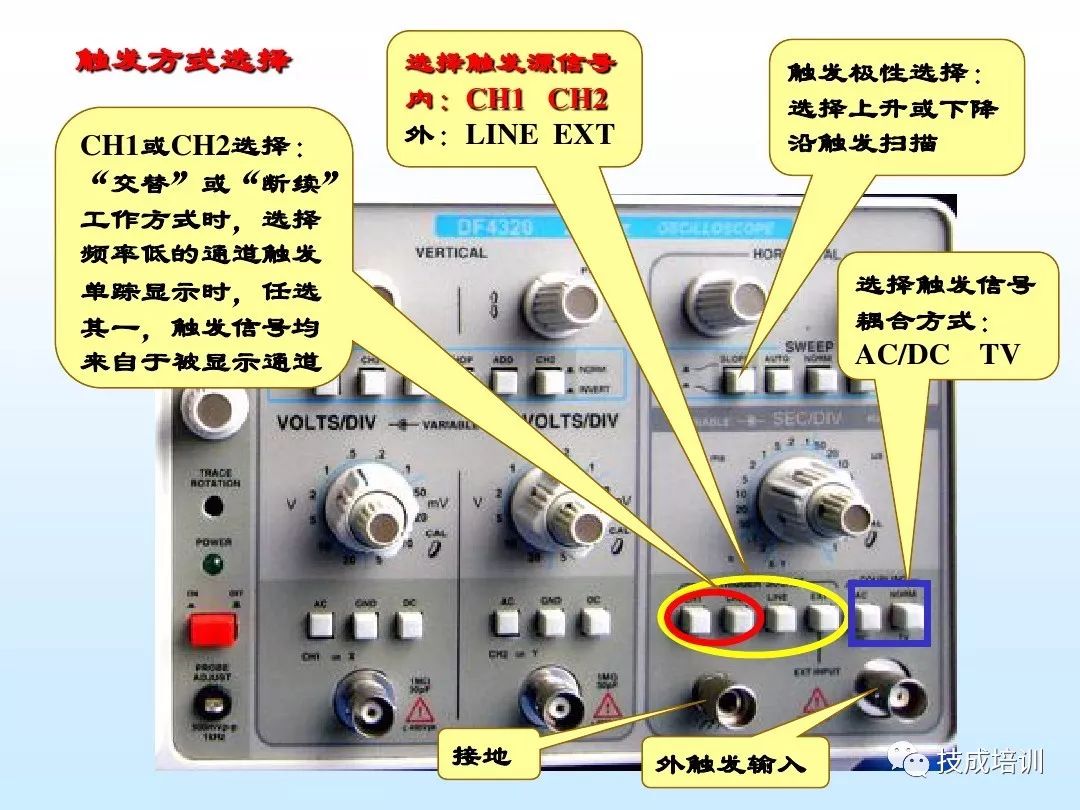
4. Usage
(1) Pre-Usage Check
Before using the oscilloscope for the first time or after long-term storage, it is necessary to perform a simple check to see if it works and to adjust the stability of the scanning circuit and the DC balance of the vertical amplification circuit. When performing quantitative tests of voltage and time, it is also essential to calibrate the gain of the vertical amplification circuit and the horizontal scanning speed.
The methods to check whether the oscilloscope works correctly, as well as the calibration methods for the vertical amplification circuit gain and horizontal scanning speed, vary slightly due to differences in the amplitude, frequency, and other parameters of the calibration signals for different models of oscilloscopes.
(2) Usage Steps
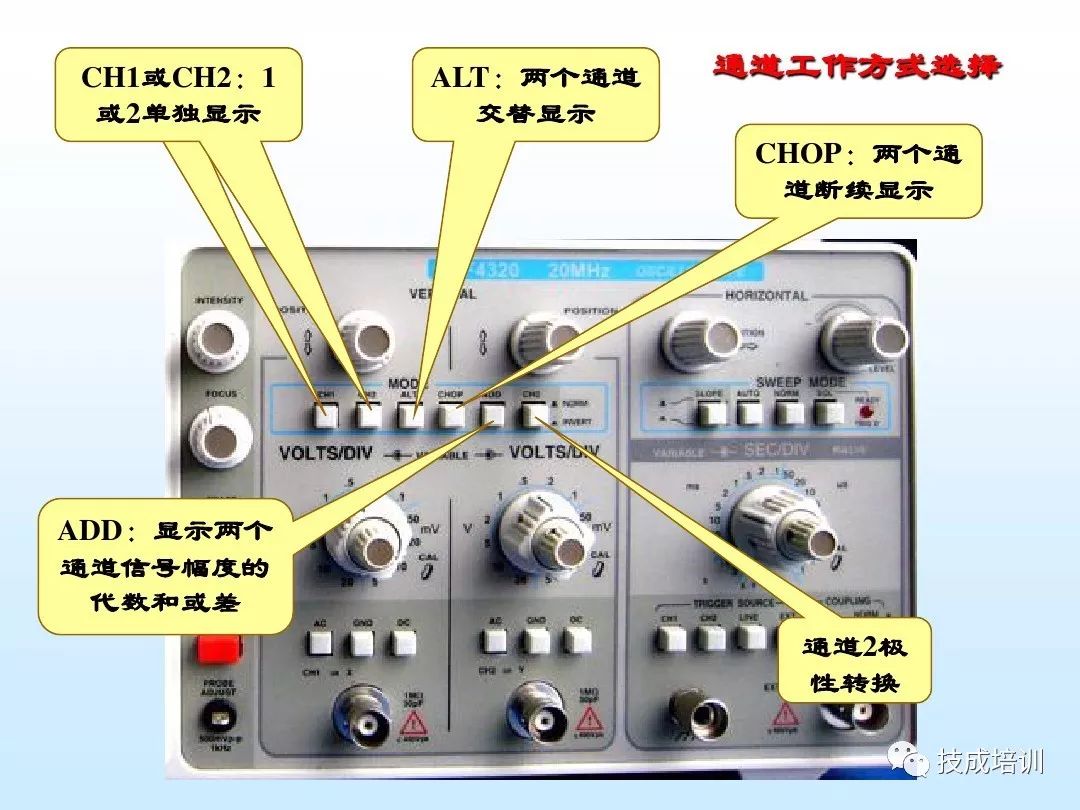
The oscilloscope can observe the waveform of various electrical signals changing over time, and based on this, it can be used to measure electrical parameters such as voltage, time, frequency, phase difference, and modulation depth. Below are the steps for using the oscilloscope to observe electrical signal waveforms.
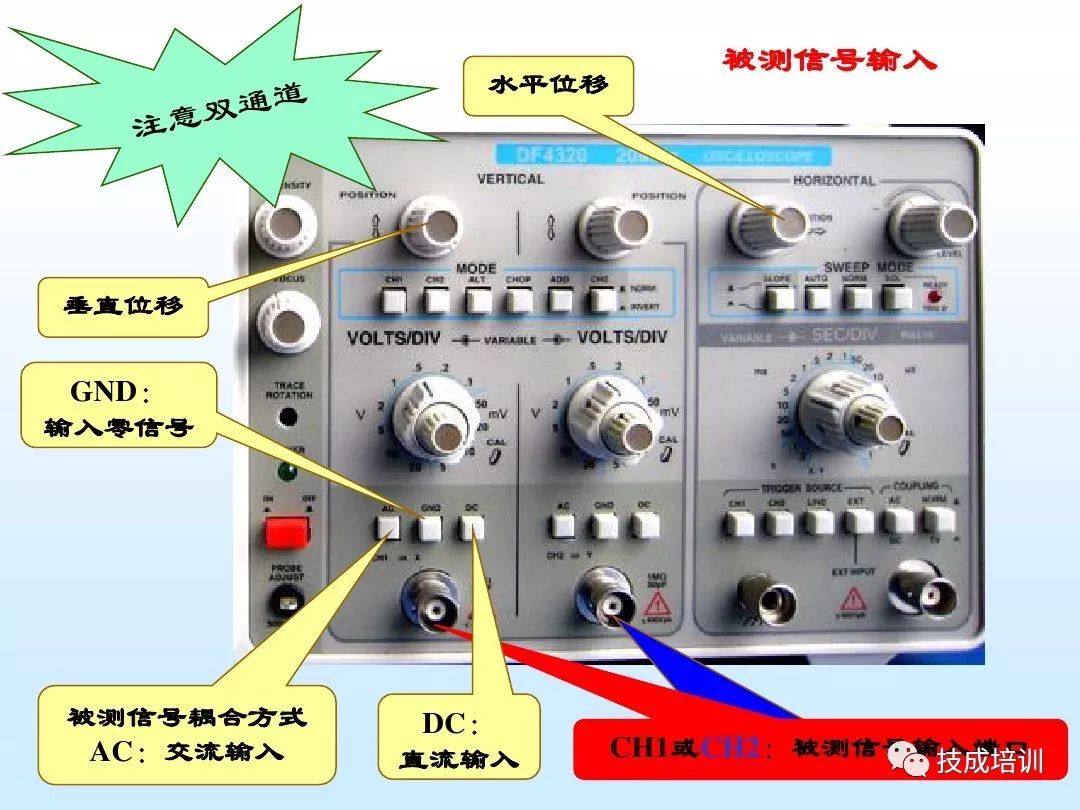
1. Select Y-Axis Coupling Mode
Depending on the frequency of the signal being measured, set the Y-axis input coupling switch to AC or DC.
2. Select Y-Axis Sensitivity
Based on the approximate peak-to-peak value of the signal being measured (if using an attenuator probe, divide by the attenuation factor; when in DC coupling mode, also consider any superimposed DC voltage), set the Y-axis sensitivity switch (or Y-axis attenuation switch) to the appropriate level. In practical use, if voltage readings are not needed, adjust the Y-axis sensitivity fine-tuning (or Y-axis gain) knob to display the desired height of the waveform on the screen.
3. Select Trigger (or Synchronization) Signal Source and Polarity
Usually, set the trigger (or synchronization) signal polarity switch to “+” or “-”.
4. Select Scanning Speed
Based on the approximate value of the signal cycle (or frequency) being measured, set the X-axis scanning speed t/div (or scanning range) switch to the appropriate level. In practical use, if time readings are not needed, adjust the scanning speed t/div fine-tuning (or scanning fine-tuning) knob to display the waveform corresponding to the desired number of cycles on the screen. If the edge of the signal is to be observed, the scanning speed t/div switch should be set to the fastest scanning speed level.
5. Input the Signal to be Measured
The signal to be measured is input to the oscilloscope through the Y-axis input terminal after being attenuated by the probe (or directly input by coaxial cable without attenuation, but this will reduce the input impedance and increase the input capacitance).
Share with friends and take a look
Click on Technical Training to learn about electrical engineering, PLC, frequency servo, CNC robots, and more.