
Low Power Design Techniques:
Data Gating (Data Gating) and
Operand Isolation (Operand Isolation)
Previously, we discussed Clock Gating (Clock Gating), which is a well-known low power design technique. It can be easily applied during the logic synthesis stage without requiring changes to the RTL, making it one of the more straightforward methods for achieving low power design.
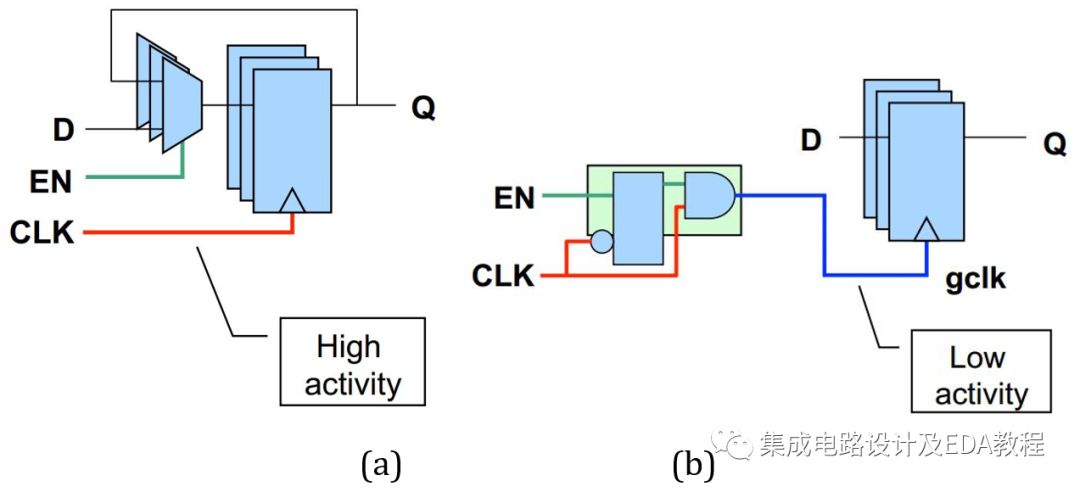
(a) Circuit structure synthesized without clock gating technology
(b) Circuit structure synthesized after applying latch-based clock gating units
Today, we will discuss Data Gating (Data Gating) in low power design.
We know that Clock Gating reduces dynamic power consumption by lowering the toggle rate of the clock signal. Similarly, Data Gating reduces dynamic power consumption by lowering the toggle rate of non-clock signals.
Basic Implementation Idea:
If some logic or arithmetic units do not use their computed results, we can “turn off” the incoming data before executing these calculations, setting it to a fixed value. This way, unnecessary calculations will not be executed, and the toggles will not propagate downstream, thereby reducing dynamic power consumption.
Application Example (Operand Isolation Technique):
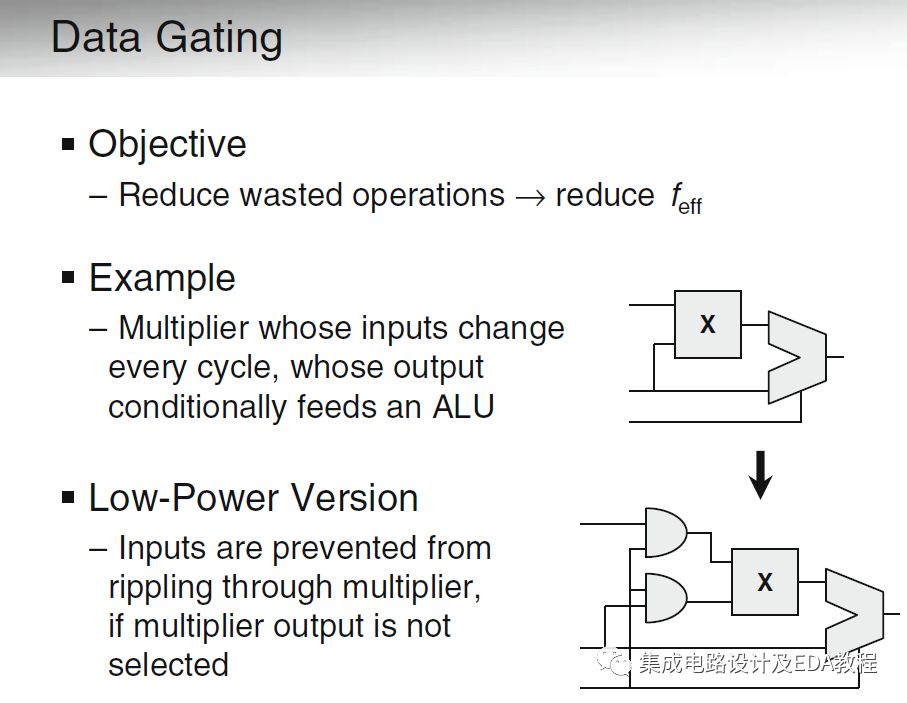
A common application in Data Gating is the Operand Isolation (OI) technique. As shown in the figure below, the inputs of a multiplier (X) toggle every clock cycle, but its output is connected to a MUX, meaning its computed results may not always be useful. If the computed result is not ultimately selected by the MUX, the computation is wasted, and if there are other logic units following the multiplier, these toggles will continue to propagate, causing dynamic power waste.
To avoid power waste, we can add an AND gate to both inputs of the multiplier, so that when its output is not selected, the data at its inputs is completely turned off. The longer the turn-off time, the more significant the power savings.
RTL and EDA Implementation:
Automatic Implementation by EDA:
Similar to Clock Gating, logic synthesis EDA tools (such as DC) can automatically insert these Data Gating Cells during logic synthesis. However, in some cases, the tools may not accurately identify all cases.
Years ago, DC had specific settings for implementing Operand Isolation, but in the latest Design Compiler/Power Compiler tools and their User Guide, no related commands were found, possibly because it has been integrated into the tool’s automatic optimization engine. At the end of this article, I will provide some older content regarding EDA implementation from the “Practical Guide to ASIC Design”.
RTL Implementation:
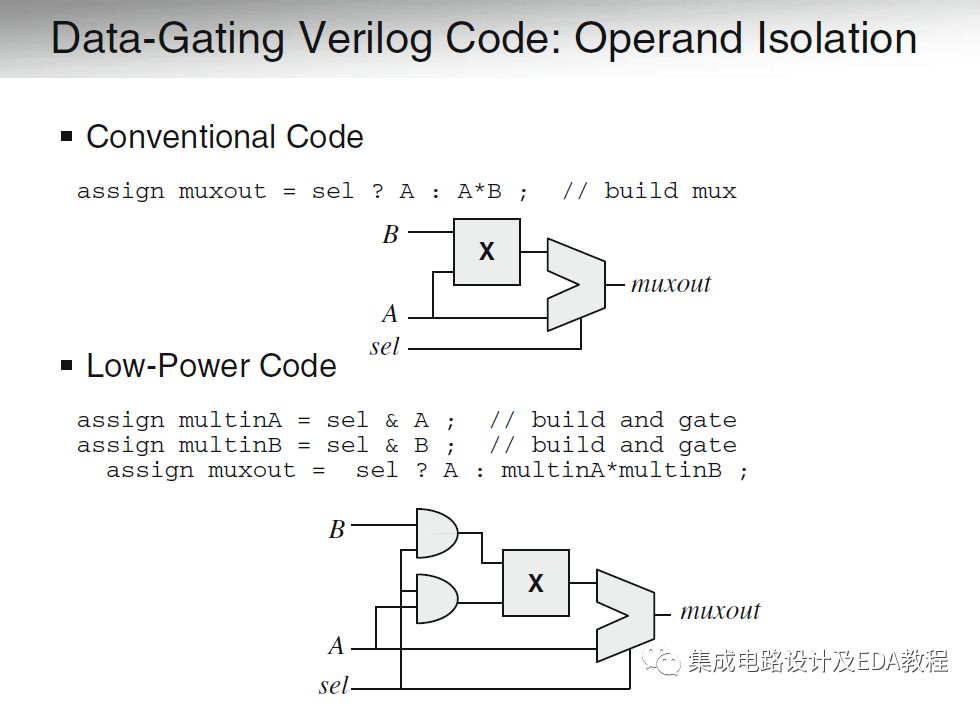
RTL designers can also manually specify in the RTL. Below is an example of how to write Verilog style with Operand Isolation in the RTL.
Advantages and Disadvantages / Trade Off:
Advantages:
1. It can reduce dynamic power consumption, and EDA tools can automatically implement it, or it can be specified in the RTL.
2. The longer the turn-off time compared to the turn-on time, and the more computation units turned off, the more significant the low power effect.
Disadvantages:
1. Similar to clock gating technology, in some cases, it may not reduce power consumption and may even cause an increase in power consumption, depending on the ratio of the turn-off time to the turn-on time of the controlled computation units;
2. Unlike clock gating, additional Gating Cells are introduced in the design, thus increasing area;
3. Due to the introduction of additional units in the Data Path, the delay in the Data Path increases, which is detrimental to Setup.
Recommendations:
Considering the above disadvantages, it is recommended to implement Operand Isolation technology in the RTL for those computation units that are not frequently turned off or for paths with poor Setup Timing.
—————————————————————————————-
Automatic Implementation by EDA:
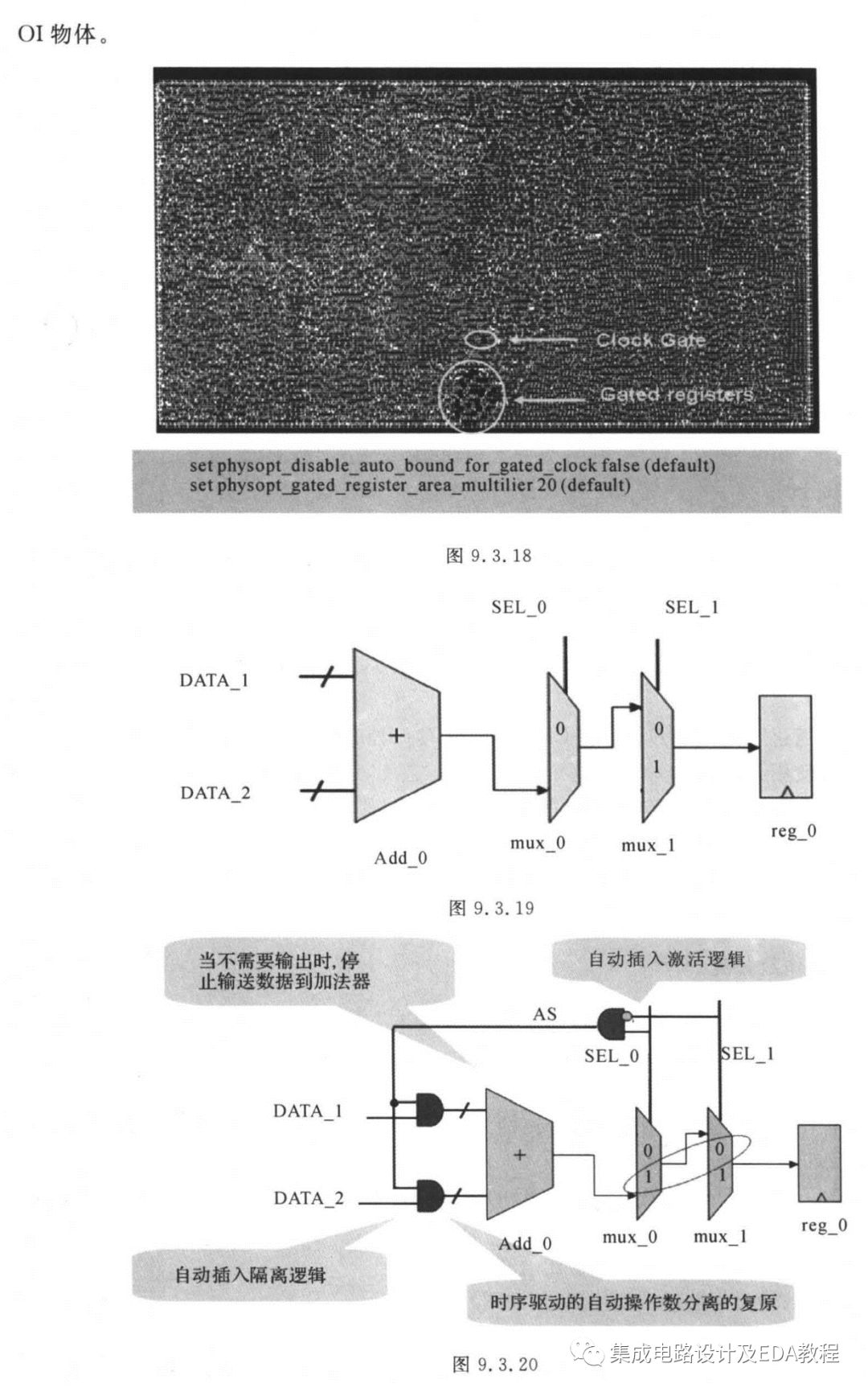
Below are some older contents regarding manual implementation of EDA from the “Practical Guide to ASIC Design”:


 Announcement
Announcement
NetEase Cloud Classroom Course
Link: https://study.163.com/course/introduction/1005909004.htm
“Calibredrv Tutorial – Improving Process Automation”

“Building EDA Virtual Machines/Servers for IC Design”

