1. LiteOS OC COAP Abstract Component
Overview
To accommodate various modes of using CoAP to connect to Huawei OC, this layer interface is adopted, providing the necessary interfaces for applications above and allowing flexible adaptation of access methods below.
The OC COAP AL API interface is declared in <oc_coap_al.h>, and you need to include this header file to use the related interfaces.
Configuration and Connection
All information for connecting to the server is stored in the structure oc_config_param_t, which is defined in oc_coap_al.h, as follows:
typedef struct
{
en_oc_boot_strap_mode_t boot_mode; ///< bootmode, if boot client_initialize, then the bs must be set
oc_server_t boot_server; ///< which will be used by the bootstrap, if not, set NULL here
oc_server_t app_server; ///< if factory or smart boot, must be set here
fn_oc_coap_msg_deal rcv_func; ///< receive function caller here
void *usr_data; ///< used for the user
}oc_config_param_t;
Among them, boot_mode is the connection mode, corresponding to the two modes of the Huawei platform:
typedef enum
{
en_oc_boot_strap_mode_factory = 0,
en_oc_boot_strap_mode_client_initialize,
en_oc_boot_strap_mode_sequence,
}en_oc_boot_strap_mode_t;
The app_server parameter contains server information, defined as follows:
typedef struct
{
char *ep_id; ///< endpoint identifier, which could be recognized by the server
char *address; ///< server address, maybe domain name
char *port; ///< server port
char *psk_id; ///< server encode by psk, if not set NULL here
char *psk;
int psk_len;
}oc_server_t;
Parameter descriptions are as follows:
-
ep_id: Device identifier
-
address: Server address
-
port: Server port
-
psk_id: Used for DTLS, set to NULL if not used
The rcv_func is the function pointer for the callback function, which is called when the device receives a CoAP message:
typedef int (*fn_oc_coap_msg_deal)(void *msg, int len);
After completing the configuration structure, call the configuration function to perform configuration and connection, the API is as follows:
/**
* @brief the application uses this function to configure the CoAP agent
* @param[in] param, refer to tag_oc_coap_config
* @return OC CoAP handle else NULL failed
*/
void *oc_coap_config(oc_config_param_t *param);
The function parameter is clear, just pass the pointer to the structure containing the connection information, and the return value of the API is the OC CoAP handle pointer for subsequent use.
Data Reporting
After a successful connection, since the platform has deployed a codec plugin, you can directly report binary data to the Huawei cloud platform, the API provided by oc_coap is as follows:
/**
* @brief the application uses this function to send the message to the CDP
* @param[in] handle: the CoAP handle returned by oc_coap_config
* @param[in] report: the message to report
*
* @return 0 success while <0 failed
*/
int oc_coap_report(void *handle, char *msg, int len);
Command Reception
When the OC platform publishes the topic data, the oc_coap component will trigger the reception callback function to save the data, allowing the user to parse the received data.
Automatic Initialization of oc_coap Component
The automatic initialization function can be seen in IoT_LINK_1.0.0\iot_link\link_main.c in the SDK directory:

2. Configuration Preparation
Makefile Configuration
Since this experiment uses many components:
-
AT Framework
-
ESP8266 Device Driver
-
Serial Port Driver Framework
-
SAL Component
-
CoAP Component
-
oc_coap Component
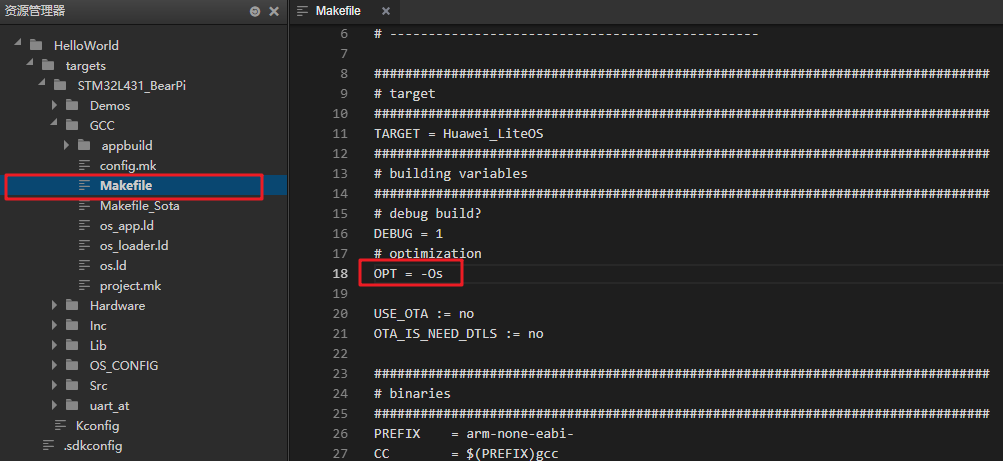
Compiling all these experimental codes results in 350KB, while the main control chip STM32L431RCT6 used by the BearPi development board has only 256KB of Flash, which will cause the compiler to be unable to link an executable file. Therefore, you need to modify the optimization options in the Makefile, changing it to -Os parameter, which optimizes the code size to the maximum extent, and remove the -g parameter, which means the code can only be downloaded and run, but cannot be debugged, as shown in the figure:
ESP8266 Device Configuration
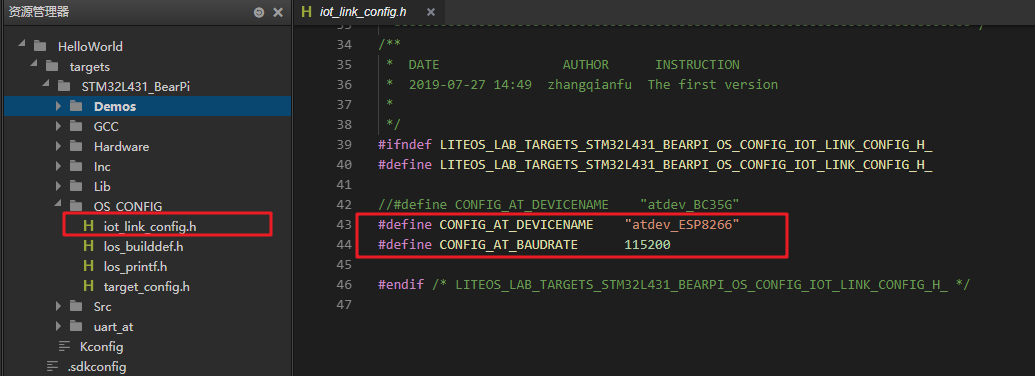
In the project directory, configure the baud rate and device name of the ESP8266 device in the OS_CONFIG/iot_link_config.h file:
WIFI Connection Information Configuration
SDK:
C:\Users\Administrator\.icode\sdk\IoT_LINK_1.0.0(where Administrator is the username of the experimental computer).
In the SDK directory, configure the connection information in iot_link\network\tcpip\esp8266_socket\esp8266_socket_imp.c file:

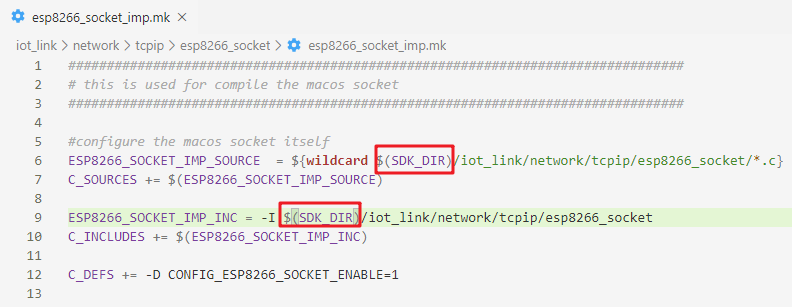
Then modify the esp8266_socket_imp.mk file in the same path, as shown in the figure, changing TOP_DIR to SDK_DIR:
3. Cloud Experiment
Writing Experiment File
Create a folder cloud_test_demo under the Demo folder, and create the file oc_coap_demo.c within it.
Write the following code:
#include <osal.h>
#include <oc_coap_al.h>
#include <link_endian.h>
#include <string.h>
#define cn_endpoint_id "654654654"
#define cn_app_server "49.4.85.232"
#define cn_app_port "5683"
#define cn_app_light 0
#define cn_app_ledcmd 1
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct
{
int8_t msgid;
uint16_t intensity;
}app_light_intensity_t;
typedef struct
{
int8_t msgid;
char led[3];
}app_led_cmd_t;
#pragma pack()
#define cn_app_rcv_buf_len 128
static int8_t s_rcv_buffer[cn_app_rcv_buf_len];
static int s_rcv_datalen;
static osal_semp_t s_rcv_sync;
static void *s_coap_handle = NULL;
static int app_msg_deal(void *msg, int len){
int ret = -1;
if(len <= cn_app_rcv_buf_len)
{
memcpy(s_rcv_buffer,msg,len);
s_rcv_datalen = len;
osal_semp_post(s_rcv_sync);
ret = 0;
}
return ret;
}
static int app_cmd_task_entry(){
int ret = -1;
app_led_cmd_t *led_cmd;
int8_t msgid;
while(1)
{
if(osal_semp_pend(s_rcv_sync,cn_osal_timeout_forever))
{
msgid = s_rcv_buffer[0];
switch (msgid)
{
case cn_app_ledcmd:
led_cmd = (app_led_cmd_t *)s_rcv_buffer;
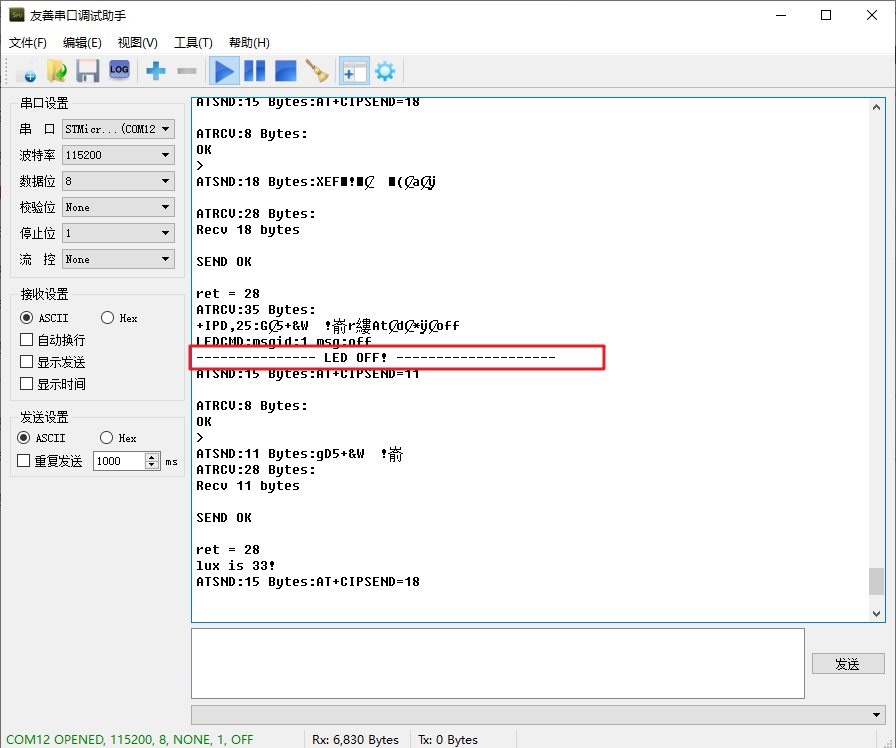
printf("LEDCMD:msgid:%d msg:%s \n\r",led_cmd->msgid, led_cmd->led);
if (led_cmd->led[0] == 'o' && led_cmd->led[1] == 'n')
{
printf("--------------- LED ON! --------------------\r\n");
}
else if (led_cmd->led[0] == 'o' && led_cmd->led[1] == 'f' && led_cmd->led[2] == 'f')
{
printf("--------------- LED OFF! --------------------\r\n");
}
else
{
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
static int app_report_task_entry(){
int ret = -1;
int lux = 0;
oc_config_param_t oc_param;
app_light_intensity_t light;
memset(&oc_param,0,sizeof(oc_param));
oc_param.app_server.address = cn_app_server;
oc_param.app_server.port = cn_app_port;
oc_param.app_server.ep_id = cn_endpoint_id;
oc_param.boot_mode = en_oc_boot_strap_mode_factory;
oc_param.rcv_func = app_msg_deal;
s_coap_handle = oc_coap_config(&oc_param);
if(NULL != s_coap_handle)
{
while(1)
{
lux++;
lux= lux%10000;
printf("lux is %d!\r\n",lux);
light.msgid = cn_app_light;
light.intensity = htons(lux);
oc_coap_report(s_coap_handle,(char *)&light,sizeof(light));
osal_task_sleep(5*1000);
}
}
return ret;
}
int standard_app_demo_main(){
osal_semp_create(&s_rcv_sync,1,0);
osal_task_create("app_report",app_report_task_entry,NULL,0x1000,NULL,2);
osal_task_create("app_command",app_cmd_task_entry,NULL,0x1000,NULL,3);
return 0;
}
Adding Path
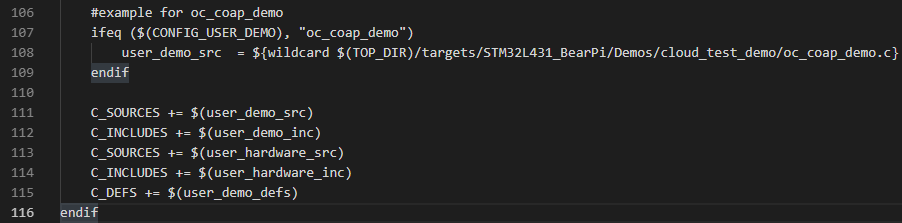
Add the following in user_demo.mk:
#example for oc_coap_demo
ifeq ($(CONFIG_USER_DEMO), "oc_coap_demo")
user_demo_src = ${wildcard $(TOP_DIR)/targets/STM32L431_BearPi/Demos/cloud_test_demo/oc_coap_demo.c}
endif
Add the position as shown:
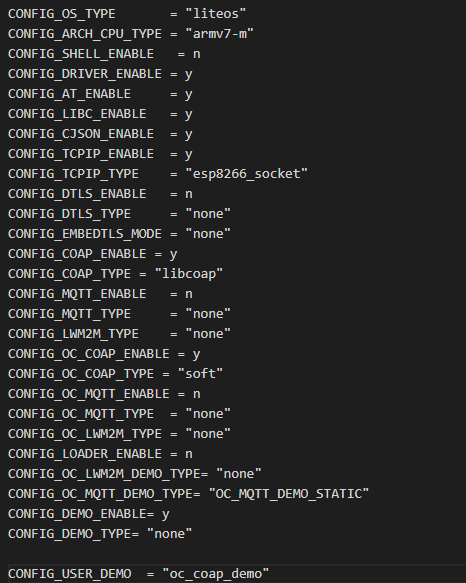
Configuring .sdkconfig
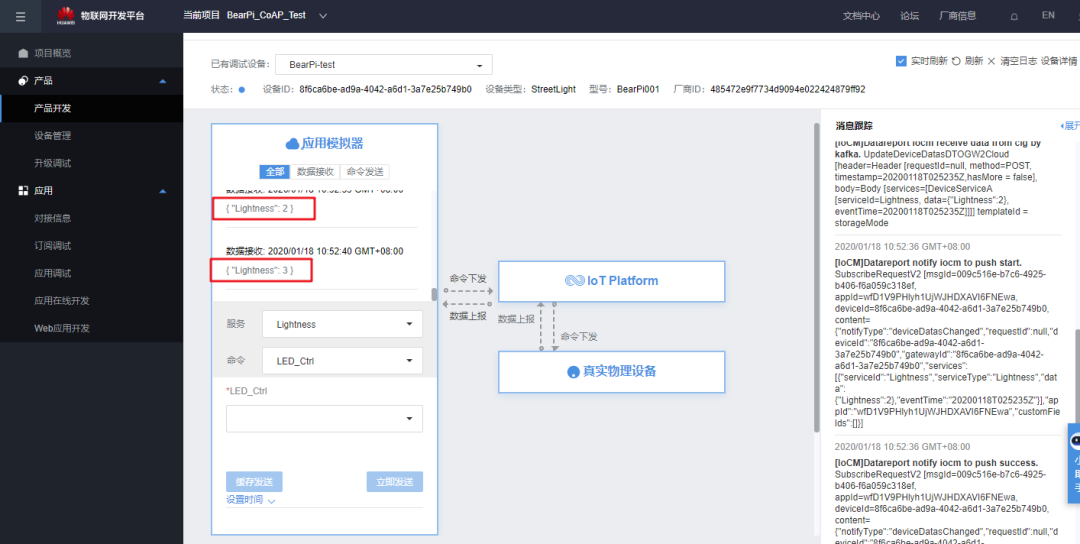
Data Reporting Experiment Results
Compile and download, the experimental phenomena on the cloud are as follows:
The experimental phenomena locally are as follows:
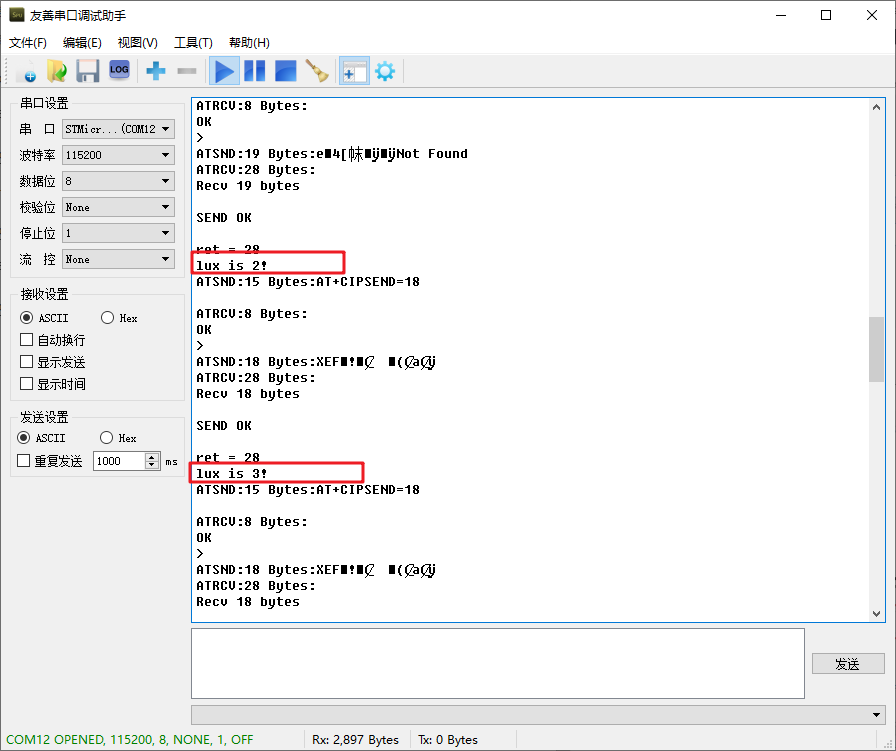
Command Issuance Experiment Results
Issue the “on” command on the cloud:
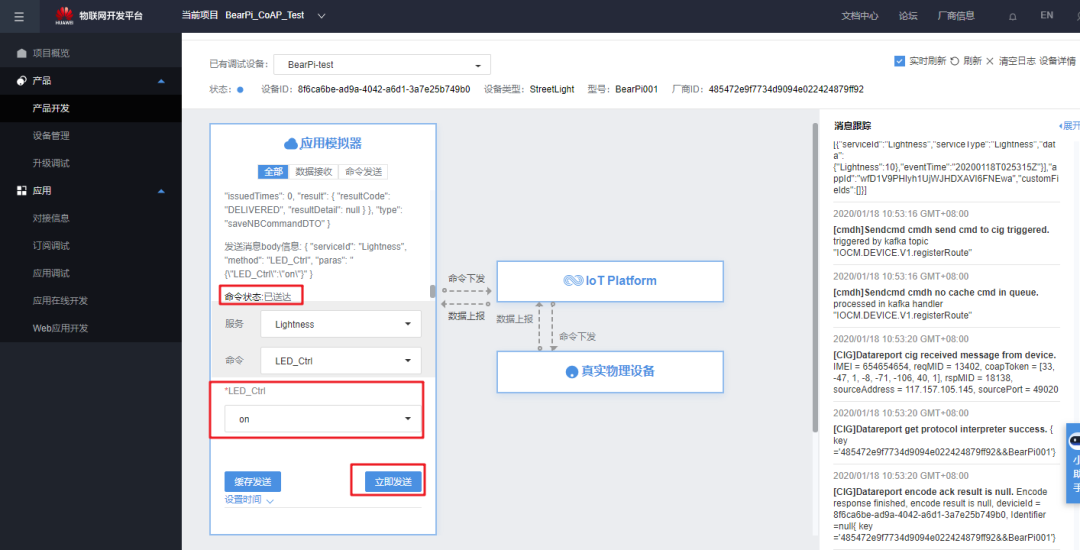
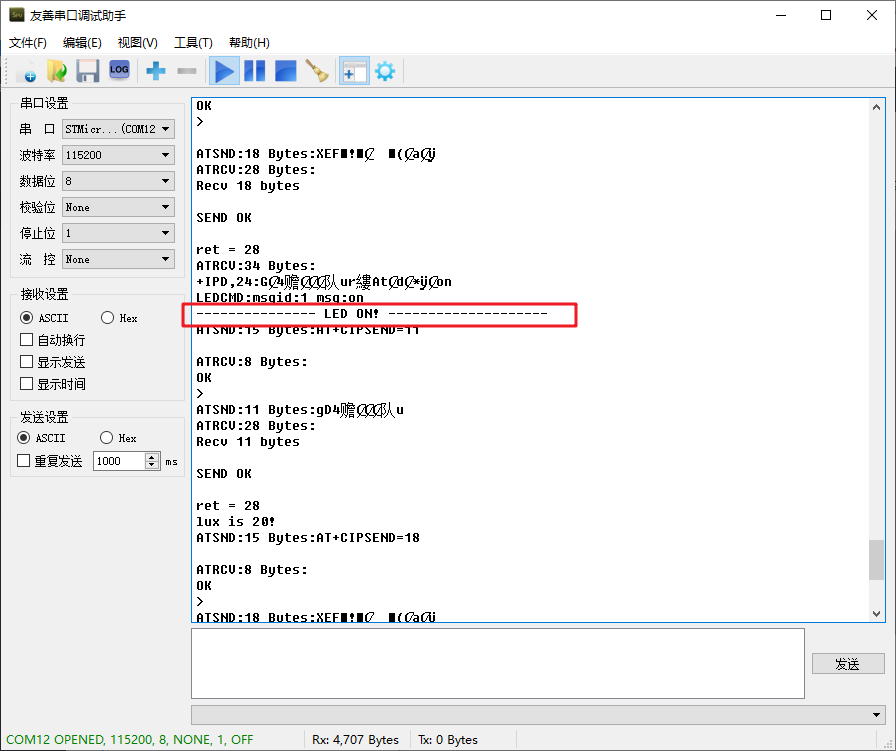
You can see in the serial assistant:
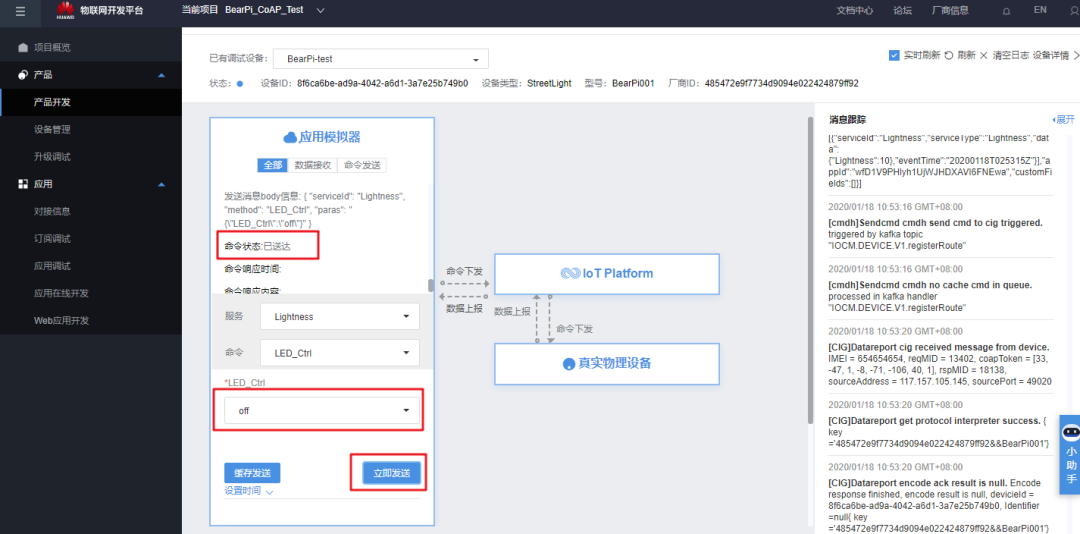
Issue the “off” command:
You can see in the serial assistant: