In the Linux world, there are many ways to obtain hardware information, such as <span>lscpu</span>, <span>free</span>, <span>lsblk</span>, and so on, but these commands usually focus on specific aspects. The uniqueness of <span>inxi</span> lies in its ability to integrate these scattered pieces of information. Today, we will explore this amazing tool.
Installing inxi
inxi can be found in the software repositories of almost all mainstream Linux distributions, and it can be installed using the package installation tool of your respective system. For Debian-based systems, use the <span>apt</span> command to install it. After installation, run the <span>inxi --version</span> command; if the version number is displayed, the installation was successful.
Basic Usage
Executing the <span>inxi</span> command will provide an overview of the system’s hardware information, which is quite convenient.
If you want more information, you can try the <span>inxi -b</span> command, which will list detailed information about all hardware.
<span><span>If you want to see more detailed information, please continue reading the professional and advanced usage sections, which is also the main purpose of this article.</span></span>
Professional Usage
1. CPU Information
The CPU is the core of the system, and its various metrics directly determine the system’s performance.
inxi -CThe output information is as follows:
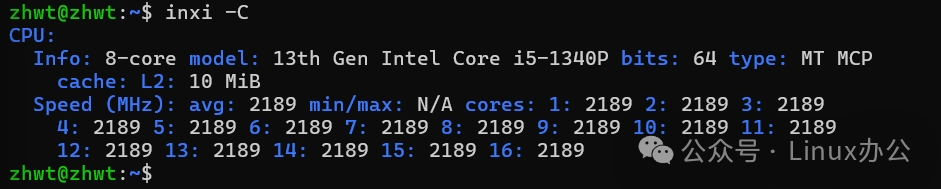
2. Memory Information
The adequacy of memory directly affects the stability of system operation, especially when running databases or virtual machines.
inxi -mThe output information is as follows:
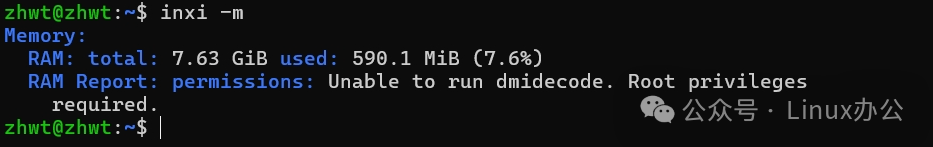
If the RAM report cannot be displayed, please run it with root privileges. The output is as follows:
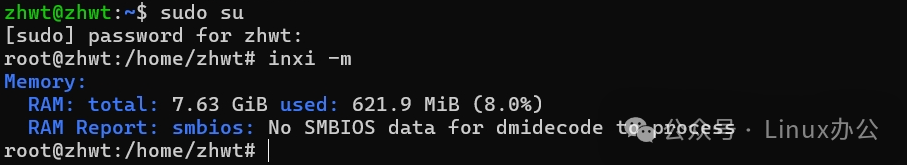
3. Storage Information
Use the <span>-D</span> parameter to view hard disk information; use the <span>-p</span> parameter to view partition information. Regularly monitor storage status to prevent storage from running low.
inxi -DThe output information is as follows: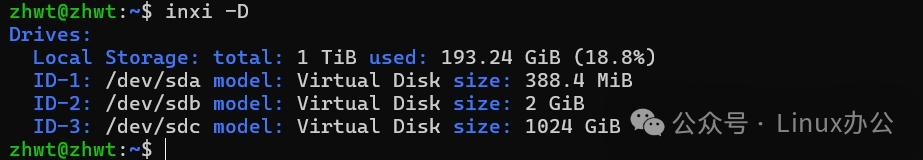
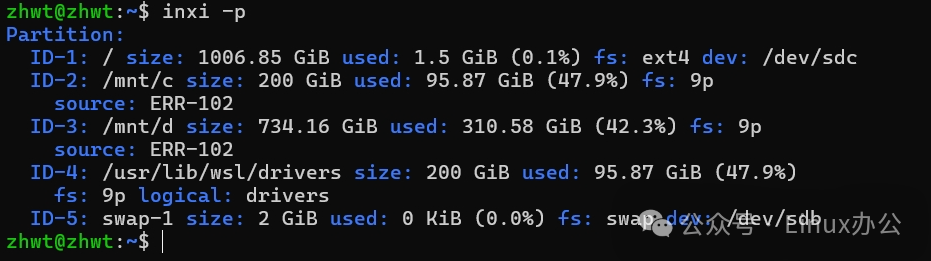
inxi -p
The output information is as follows:
4. Network Information
Use the <span>-N</span> parameter to view network devices; use the <span>-n</span> parameter to view network interfaces.
inxi -NThe output information is as follows:

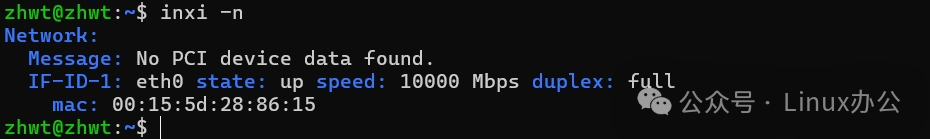
inxi -nThe output information is as follows:
5. Audio Information
Use the <span>-A</span> parameter to view audio device information.
inxi -AThe output information is as follows:

6. Graphics Card Information
Use the <span>-G</span> parameter to view graphics card information.
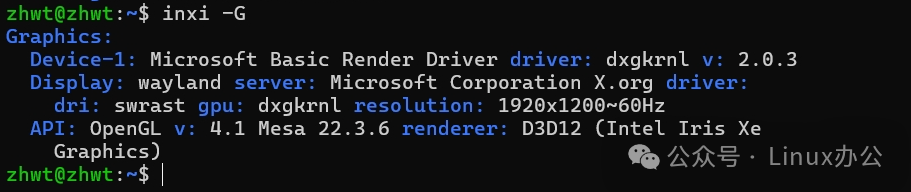
inxi -GThe output information is as follows:
7. Battery Information
Use the <span>-B</span> parameter to view battery information.
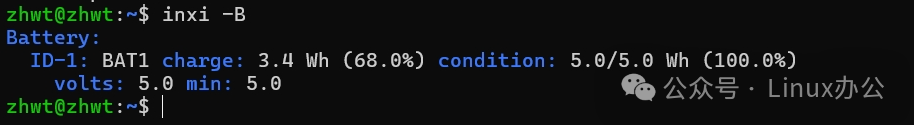
inxi -BThe output information is as follows:
Advanced Usage
inxi can not only check individual modules but also generate comprehensive reports and even allow you to customize the output.
1. Complete System Report
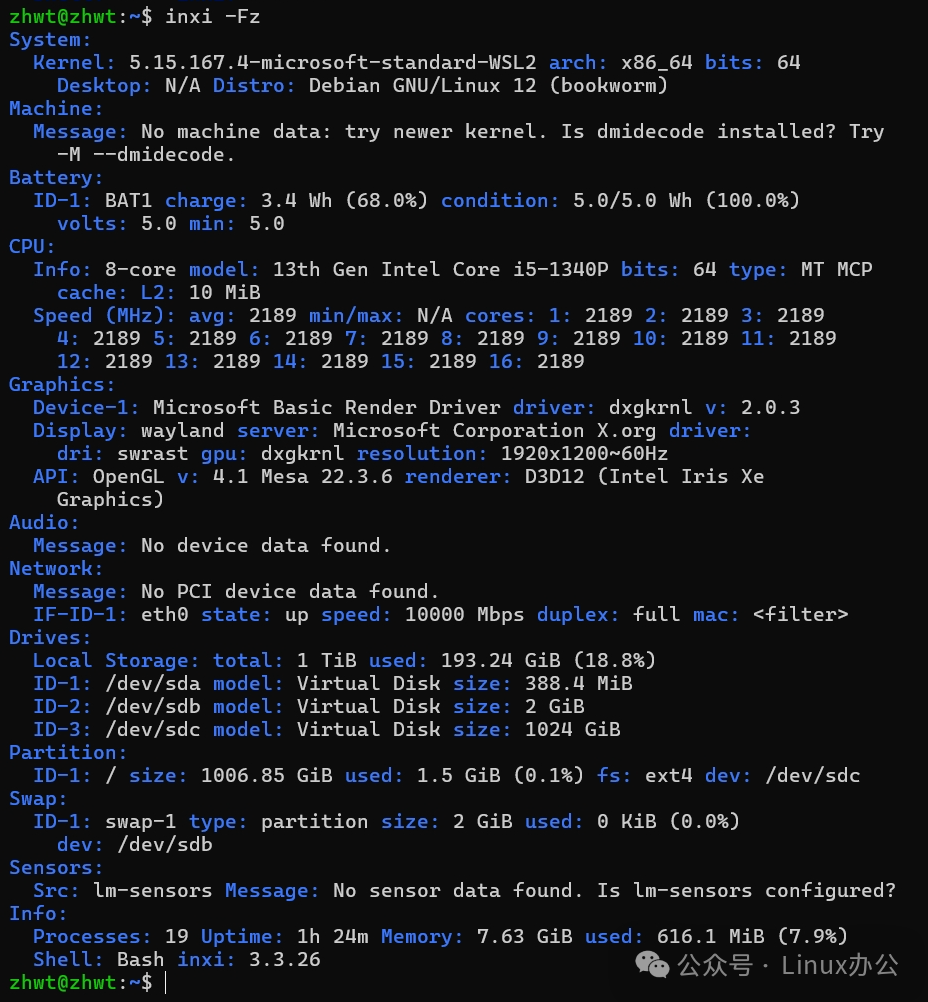
Want to see all information at once? Use the -F parameter. If you are concerned about privacy, you can add -z to hide sensitive data.
inxi -FzThe output information is as follows:
2. Monitor Resource Usage
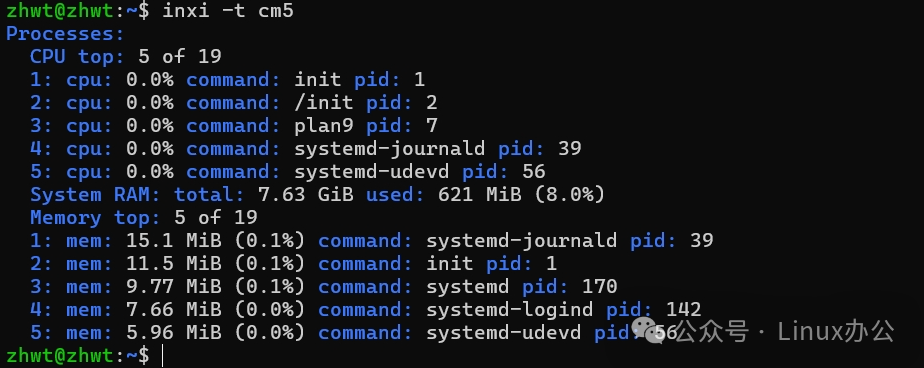
When system performance declines, <span>-t </span> can help you identify resource bottlenecks and pinpoint the “culprit”.
inxi -t c5 # Top five CPU usage
inxi -t m5 # Top five memory usage
inxi -t cm5 # View both CPU and memoryThe output information is as follows:
3. Custom Colors
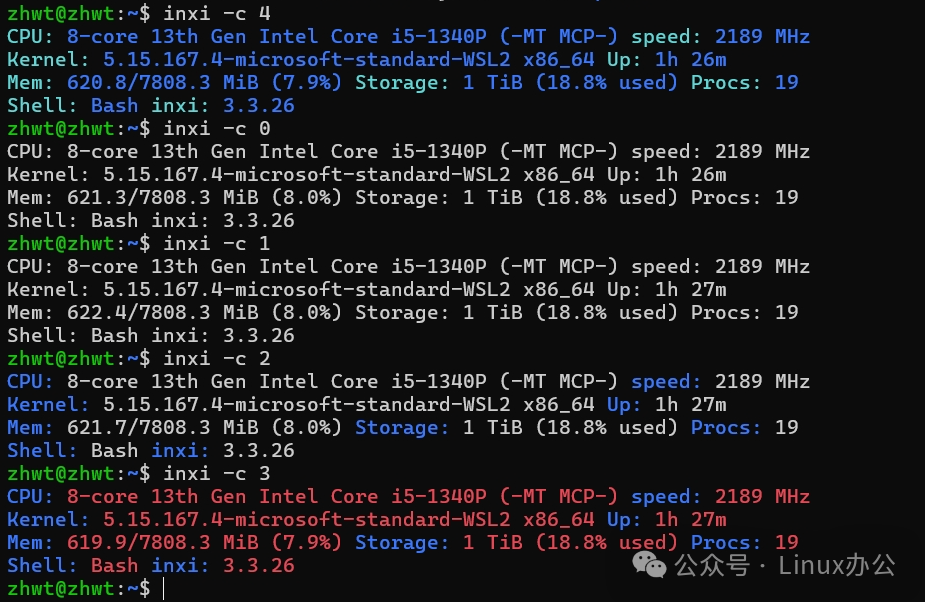
<span>inxi</span> uses colors by default to differentiate information; you can use <span>-c </span> to modify the output color at any time. If you don’t like it, you can turn it off. The <span>-c</span> parameter can be combined with other parameters, but it only takes effect for this call and will not change the default output color of the <span>inxi</span> command.
inxi -c 4 # Cyan: Blue
inxi -c 0 # Turn off color display
inxi -c 1 # Same as 0
inxi -c 2 # Blue: White (system default)
inxi -c 3 # Blue: RedThe output style is as follows:
This concludes the explanation. Thank you for reading. I hope it is helpful to you.
I am Nanshanzi Welcome to explore the wonderful world of Linux together