Ransomware is a new type of virus trojan that has emerged alongside the rise of digital currencies. It typically spreads through various forms such as brute force cracking, exploiting vulnerabilities, spam emails, and bundled software. Once a machine is attacked by ransomware, most files will be modified by encryption algorithms and have a special suffix added, rendering the original files unreadable to the user, causing immeasurable losses. Ransomware usually employs a combination of asymmetric and symmetric encryption algorithms to encrypt files. Most ransomware cannot be decrypted through technical means; obtaining the corresponding decryption private key is necessary to restore the encrypted files without loss. Hackers exploit this behavior to extort high ransoms from victimized users, which must be paid in digital currencies that are generally untraceable, thus posing a significant threat.
-
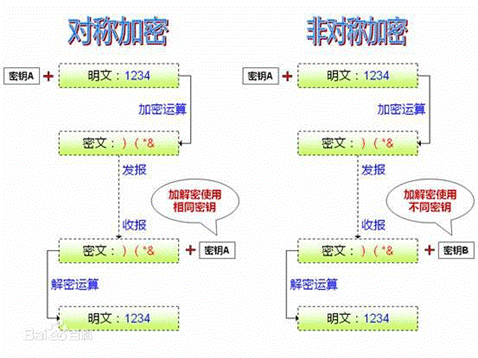
1. Symmetric Encryption:
Generally uses only one key and an initialization vector (IV). The same key and IV are used for both encryption and decryption.
-
2. Asymmetric Encryption:
Generally involves two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key can be shared and is used to encrypt data (as shown in the diagram with keyA), while the private key must be kept secret and is used to decrypt data (as shown in the diagram with keyB).
-
3. Hash Algorithms:
Common examples includeMD5, SHA1, and SHA256. These are irreversible; even a change of just1 bit in the plaintext will cause a significant change in the ciphertext.
A.1 Security Recommendations
Once it is confirmed that a server has been infected with ransomware, the infected host should be immediately isolated. Isolation mainly includes physical isolation and access control. Physical isolation typically involves disconnecting from the network or cutting off power; access control refers to strictly authenticating and controlling access to network resources.
For Infected Hosts
1)Physical Isolation
The common methods for physical isolation are disconnecting from the network and shutting down the machine.
Disconnecting from the network mainly involves: unplugging the network cable, disabling the network card, and if it is a laptop, turning off the wireless network.
2)Access Control
Common methods for access control include adding policies and changing login passwords.
Adding policies mainly involves: using security devices on the network side for further isolation, such as firewalls or endpoint security monitoring systems; avoiding exposing Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP, default port3389) to the public internet (if it is necessary to enable it for remote maintenance, access should only be allowed after logging in viaVPN), and closing unnecessary ports such as445, 139, and 135.
The main operation for changing login passwords is: immediately change the login password of the infected server; next, change the passwords of other servers on the same local area network; third, change the login password of the highest-level system administrator account. The new passwords should be complex and of high strength, generally requiring a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols, with a sufficient length (15 characters, with at least two types of combinations).
For Non-Infected Hosts
1)Globally close the3389 port on the network boundary firewall or only open the3389 port to specificIPs.
2)Enable theWindows firewall and try to close high-risk ports such as3389, 445, 139, and 135.
3)Set a unique password for each server, with complexity requirements including a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols, with a sufficient length (15 characters, with at least two types of combinations).
4)Install the latest antivirus software or hardened server versions to prevent hacking.
5)Timely apply patches to system application services to block virus transmission pathways;
6)If a virtualized environment exists, it is recommended to install a virtualization security management system to further enhance protection against malware and brute force attacks.