Internet of Things IoT (Internet of things)
The Internet of Things is an application extension of the Internet. Rather than saying that the IoT is a network, it is more accurate to say that it is a business and application. Therefore, application innovation is the core of IoT development, and innovation centered around user experience is the soul of IoT development.
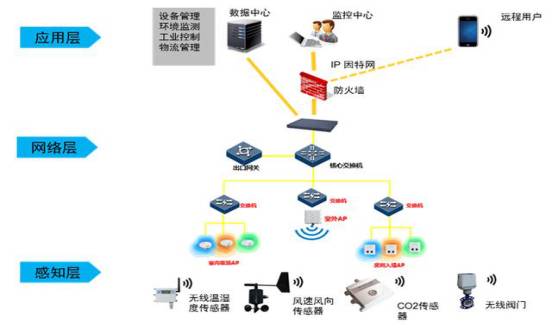
As shown in the following diagram, the IoT can be roughly divided into the following layers: the perception layer, the network layer, and the application layer.
Analysis of the Relationship Among IoT, Cloud Computing, Big Data, and AI
The perception layer is equivalent to human senses and nerve endings, used to perceive and collect various data from the application environment. This includes various sensors such as temperature, humidity, speed, location, vibration, pressure, flow, gas, etc. The requirements for the perception layer include high sensitivity and accuracy, low power consumption, and wireless transmission capabilities.
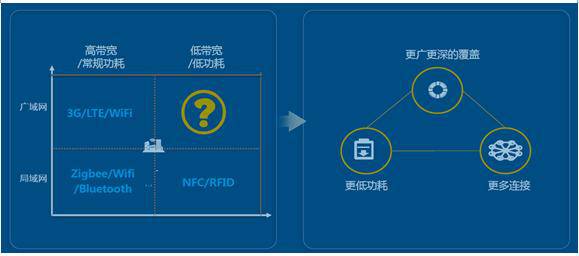
The network layer is equivalent to the human nervous system, used to transmit data. This includes various wireless communication technologies and standards, such as Zigbee/BLE/Wifi/NFC/RFID/LTE, etc. Low power consumption, wide coverage, and more connections are the development directions of wireless networks. Currently, new communication technologies and standards like NB-IoT, LoRa, and eLTE-IoT are striving in this direction. Future 5G will replace many existing wireless communication technologies and unify the field.
The application layer is equivalent to the human brain’s instructions and responses, controlling output in reverse through commands. This includes device management, environmental monitoring, industrial control, etc.
Cloud Computing (Cloud)
Cloud computing is equivalent to the human brain, serving as the nerve center of the IoT. Cloud computing is an increase in services based on the Internet, involving the delivery model of dynamic, scalable, and often virtualized resources via the Internet.
Currently, many IoT servers are deployed in the cloud, providing various services at the application layer through cloud computing. Cloud computing can be considered to include the following levels of service: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
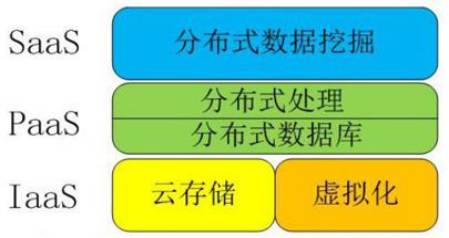
Cloud Computing IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Infrastructure as a Service. Consumers can obtain services from a complete computer infrastructure via the Internet. For example, hardware server leasing.
Cloud Computing PaaS: Platform as a Service
PaaS (Platform as a Service): Platform as a Service. PaaS actually refers to providing the software development platform as a service, submitted to users in a SaaS model. Therefore, PaaS is also an application of the SaaS model. However, the emergence of PaaS can accelerate the development of SaaS applications, especially speeding up the development of SaaS applications. For example: personalized software development.
Cloud Computing SaaS: Software as a Service
SaaS (Software as a Service): Software as a Service. It is a model of providing software via the Internet, where users do not need to purchase software but rent web-based software from providers to manage business operations.
Amazon was one of the first companies to realize the value of services, pushing its internal infrastructure, platforms, and technology to the market after maturity, providing various services to society, thus becoming a leader in the global cloud computing market.
Big Data (Big Data)
Big data is equivalent to the vast knowledge that a human brain accumulates from elementary school to university. This knowledge can only create greater value through digestion, absorption, and reconstruction.
The definition given by the McKinsey Global Institute is: a data set so large that it exceeds the capabilities of traditional database software tools in terms of acquisition, storage, management, and analysis, characterized by massive data scale, rapid data flow, diverse data types, and low value density. The strategic significance of big data technology lies not in mastering vast amounts of data information, but in the specialized processing of meaningful data. In other words, if big data is likened to an industry, the key to profitability in this industry lies in enhancing the “processing capability” of data, realizing the “value addition” of data through “processing”.

Technically, the relationship between big data and cloud computing is inseparable, like two sides of a coin. Big data cannot be processed by a single computer; it must use a distributed architecture. Its characteristic lies in distributed data mining of massive data. However, it must rely on cloud computing’s distributed processing, distributed databases, and cloud storage, as well as virtualization technology.
Artificial Intelligence AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Artificial intelligence can be likened to a person absorbing a vast amount of human knowledge (data), continuously deep learning and evolving into a highly skilled individual. Artificial intelligence is inseparable from big data and is based on cloud computing platforms to complete deep learning evolution.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a new technology science that studies and develops theories, methods, technologies, and application systems for simulating, extending, and enhancing human intelligence. Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science that attempts to understand the essence of intelligence and produce a new type of intelligent machine that can respond in a way similar to human intelligence. Research in this field includes robotics, language recognition, image recognition, natural language processing, and expert systems.

Simple Summary:
Through the Internet of Things, massive data is generated and stored on cloud platforms, which is then analyzed through big data, and even higher forms of artificial intelligence provide better services for human production activities and daily needs. This will undoubtedly be the direction of the evolution of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Reprinted from Today’s Headlines

Editor: Guo Yudan, Shang Xiaobin
